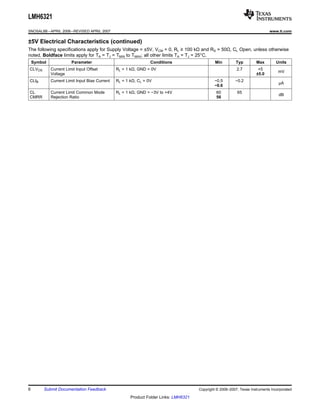
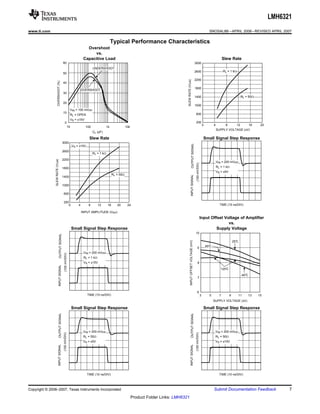
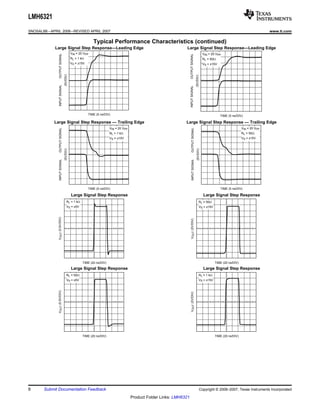
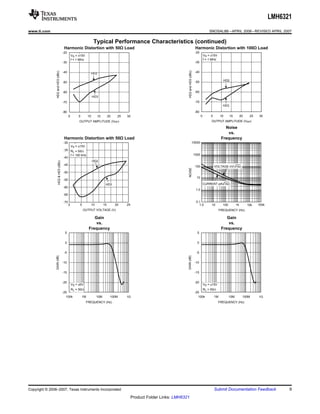
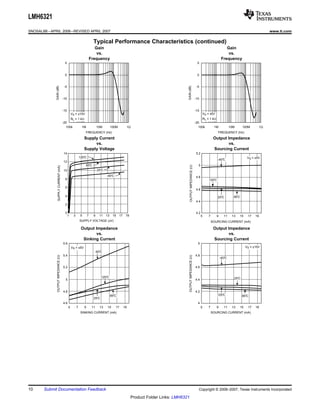
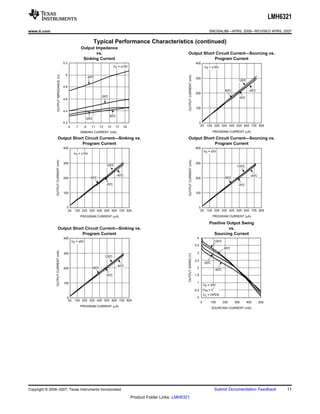
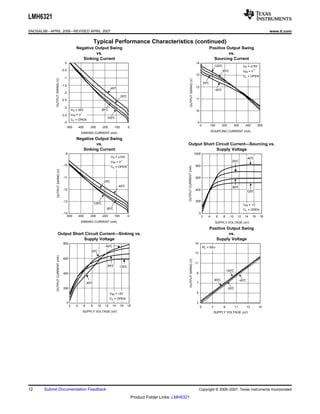
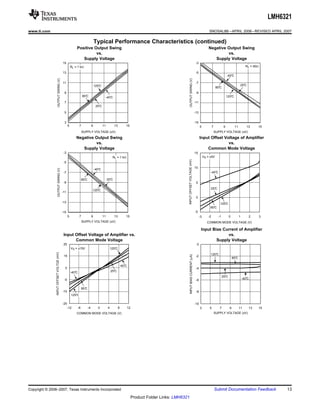
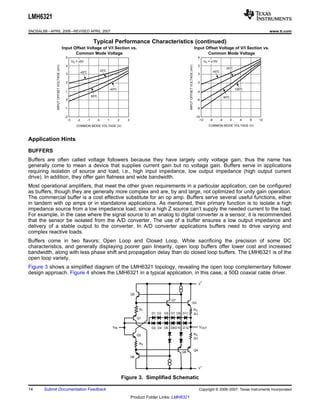
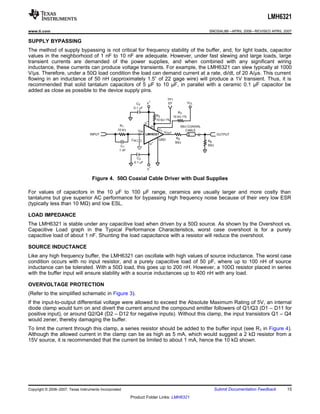
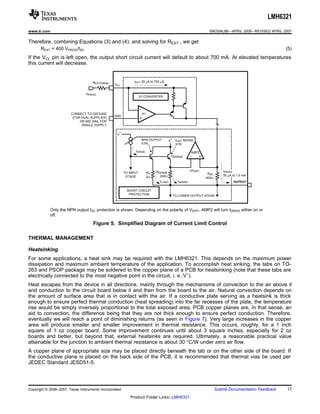
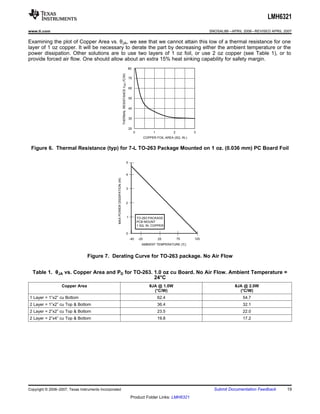
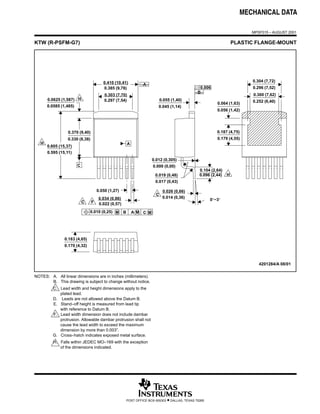
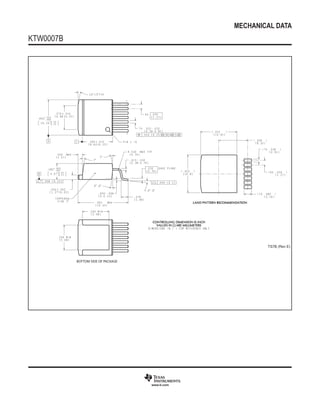
The LMH6321 is a high speed buffer that can drive ±300 mA continuously with an adjustable current limit between 10 mA and 300 mA. It has a high slew rate of 1800 V/μs and bandwidth of 110 MHz. The device features thermal shutdown protection and an error flag output. It is available in 8-pin PSOP and 7-pin TO-263 packages.