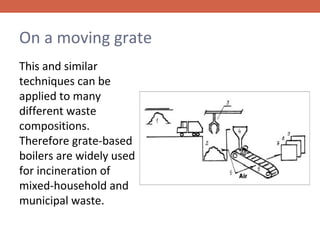
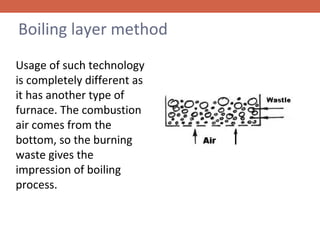
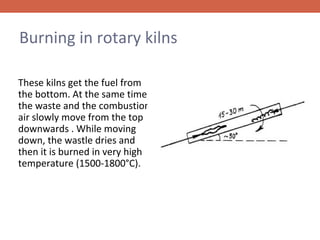
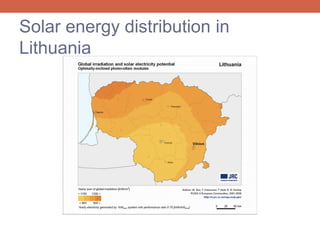
Biomass is a renewable source of energy derived from organic matter, such as wood and agricultural waste, through photosynthesis. It is the most widely used and oldest renewable energy source. In Lithuania, biomass accounts for the largest share of renewable energy consumption, primarily in the form of firewood and agricultural waste used as fuel. Solar energy is another major renewable source that has the potential to meet global energy needs many times over but current technologies have not enabled its effective use beyond a small fraction of worldwide electricity production. Wind power is a renewable alternative that is increasingly used through wind turbines to generate electricity without pollution.