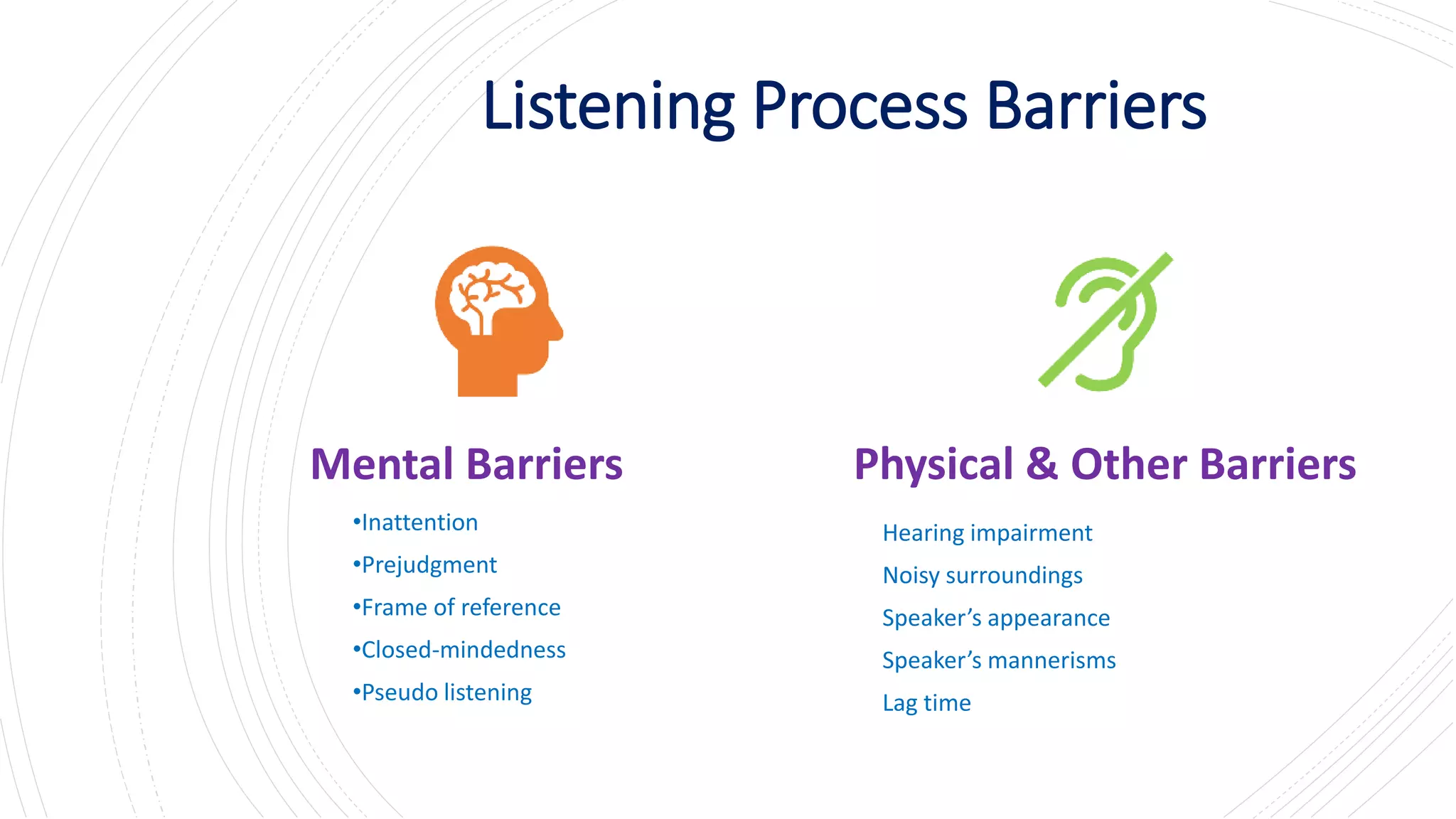
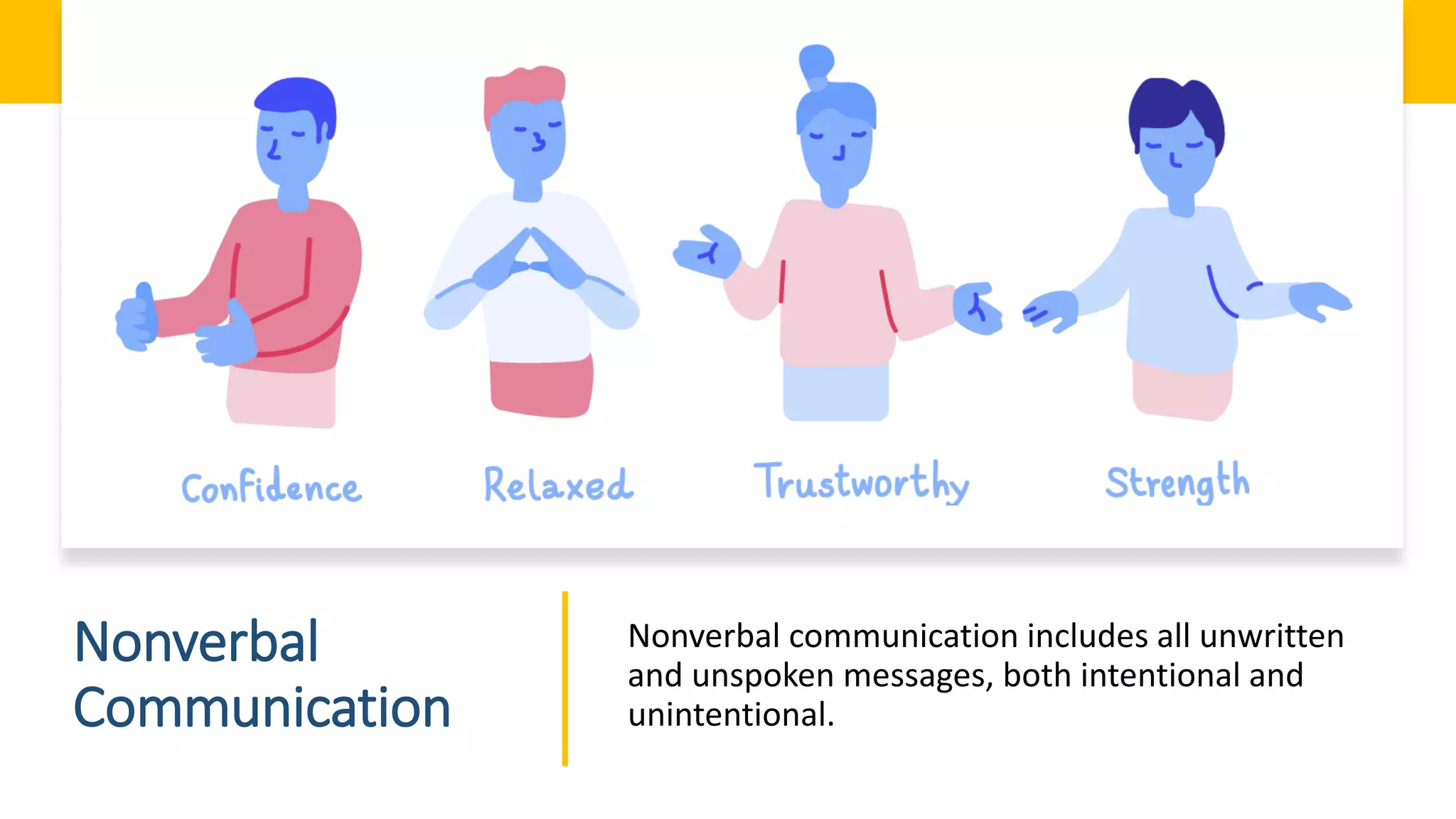
This document discusses listening and nonverbal communication. It covers the listening process and barriers to effective listening. Listening is important in the workplace when interacting with superiors, employees, and customers. Tips are provided for improving listening skills. Common misconceptions about listening are also addressed. Nonverbal communication conveys most meaning and includes body language, facial expressions, gestures, and other visual cues. Elements of nonverbal communication like body language convey more meaning than actual words. The document concludes with tips for improving nonverbal communication skills.