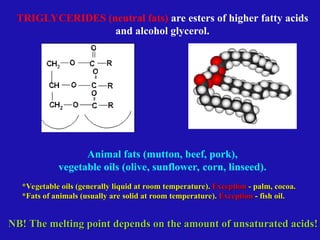
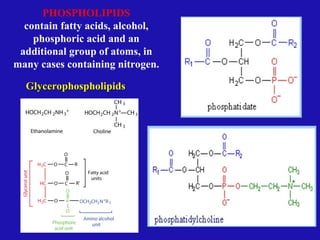
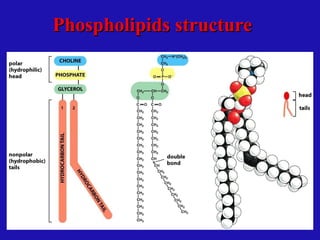
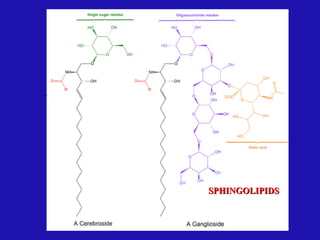
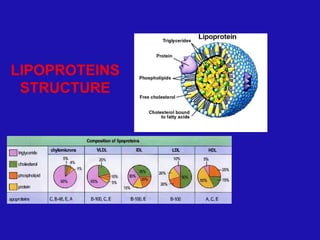
Lipids are organic compounds characterized by their poor solubility in water and their roles as energetic, structural, protective, and regulatory molecules in biological systems. They include various types such as triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids, which serve essential functions in cellular structure and metabolism. Understanding lipid classification and structure is crucial in biochemistry and medicine.