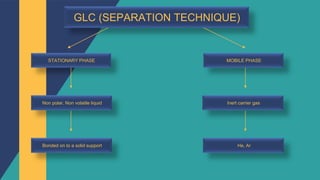
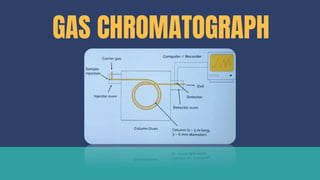
Lipids can be extracted from tissues using organic solvents. The extracted lipids are then separated using techniques like thin layer chromatography, gas liquid chromatography, or high-performance liquid chromatography. Individual lipids can be identified by their behavior during chromatography or through mass spectrometry. Lipidomic analysis determines the full lipid profile of a cell, tissue, or organism and how it changes in response to stressors or differentiation.