Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

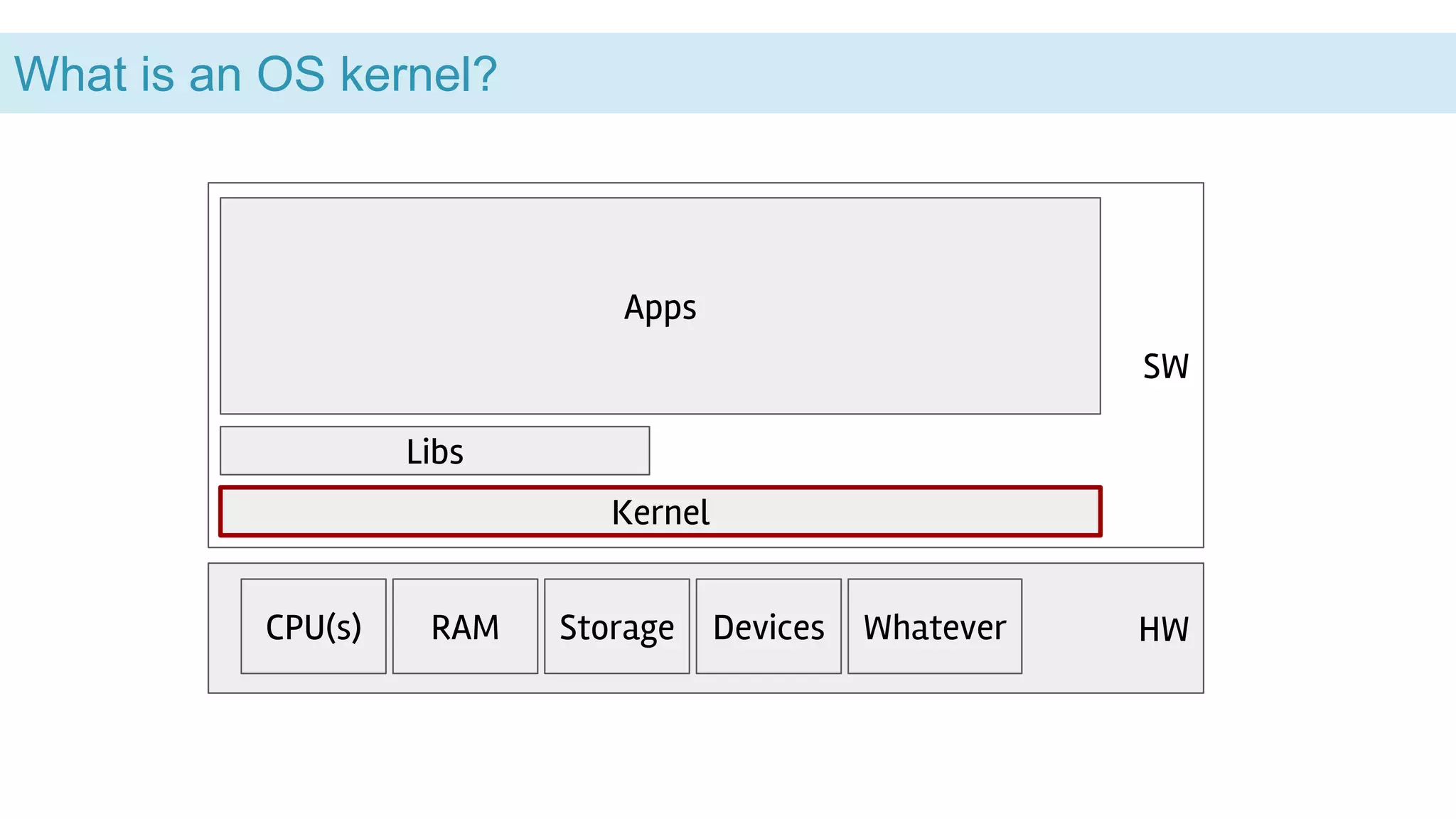
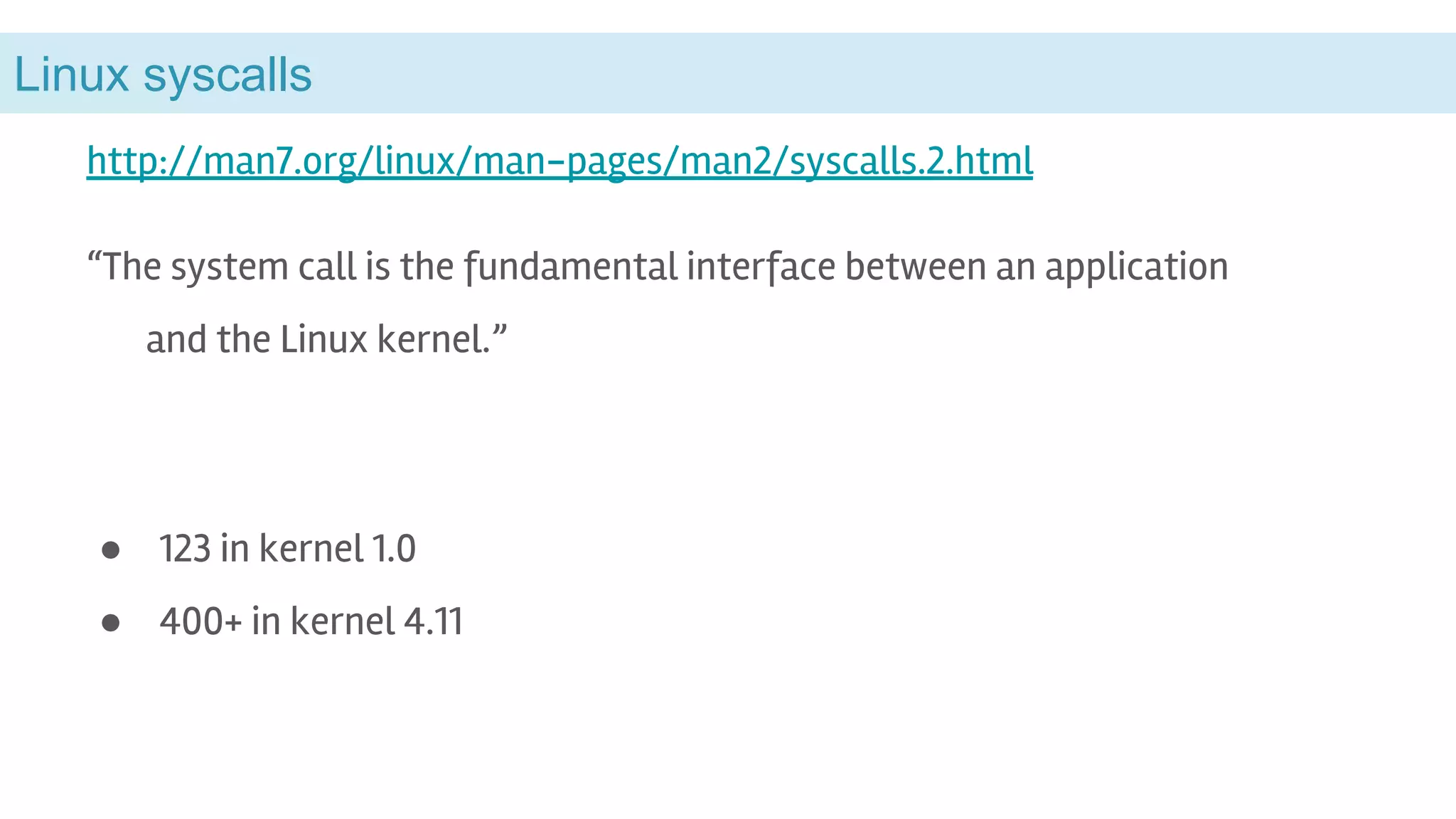

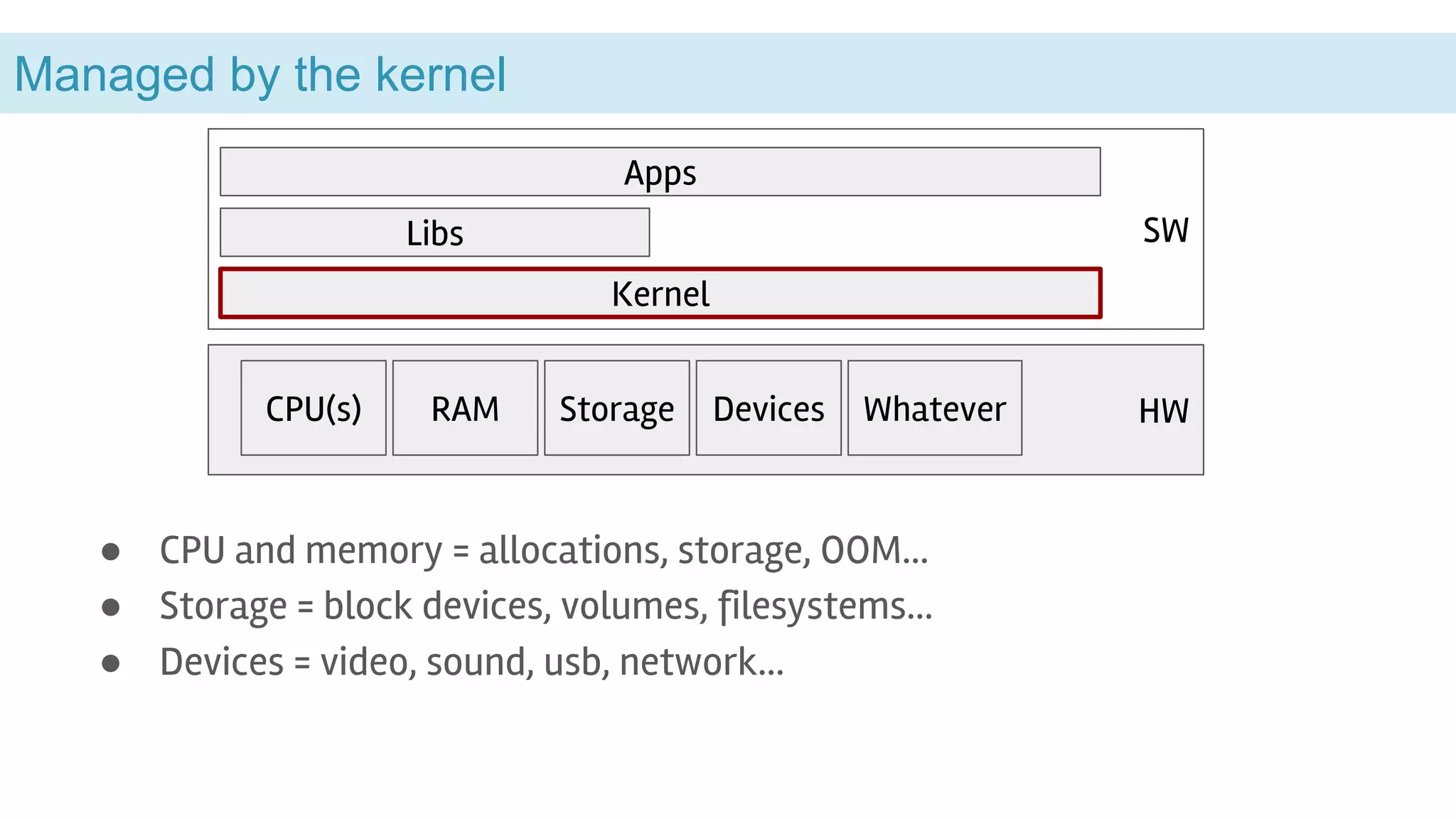



This document discusses the Linux kernel vs user space and provides examples of BPF and FUSE. It begins by explaining that the kernel manages hardware resources like the CPU, memory, storage and devices, while libraries and applications run in user space. It then discusses system calls as the interface between applications and the kernel, and how BPF and FUSE allow user space programs to interact with the kernel. It also briefly mentions some related projects like Gvisor and Cilium that use BPF.







