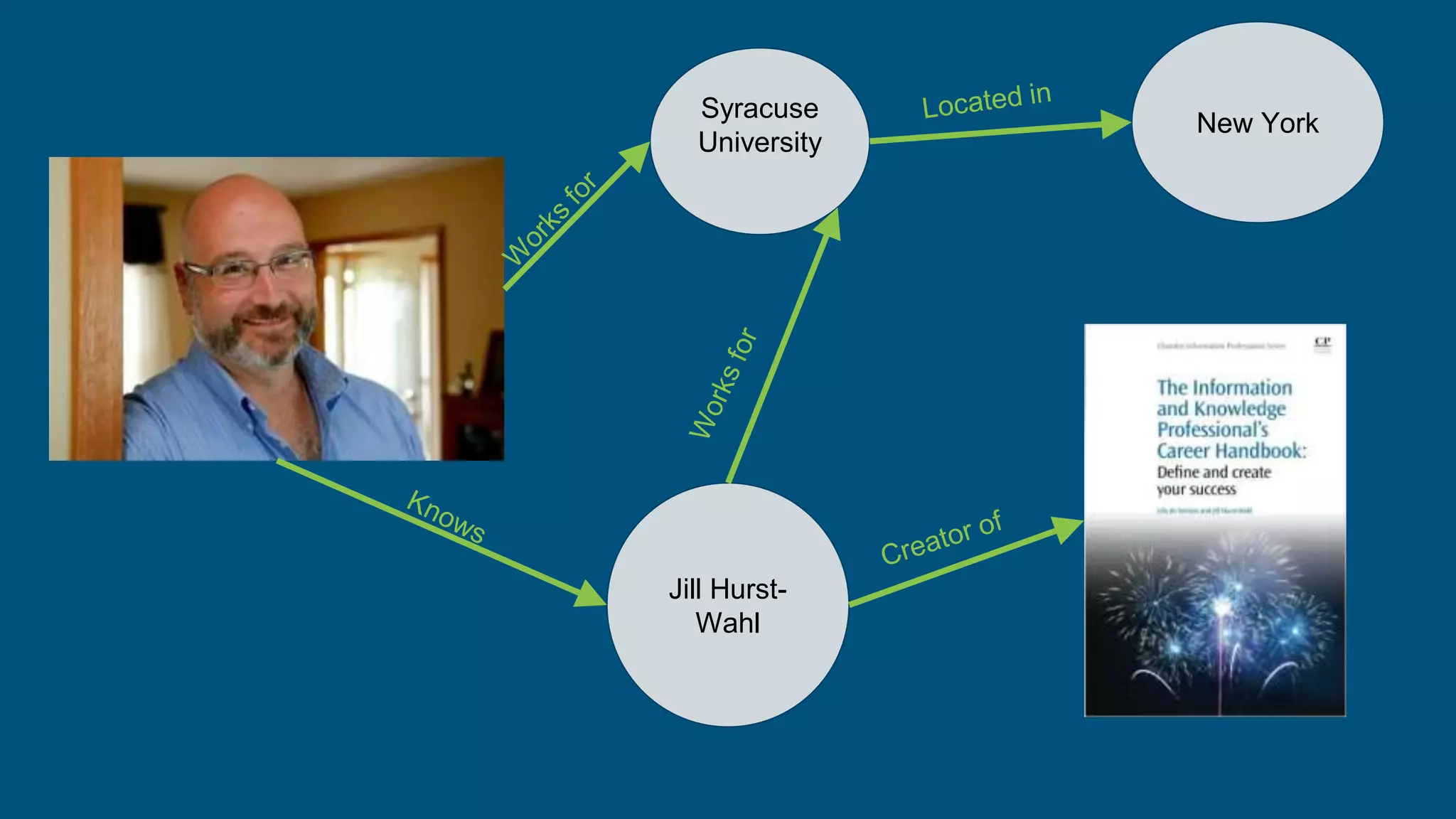
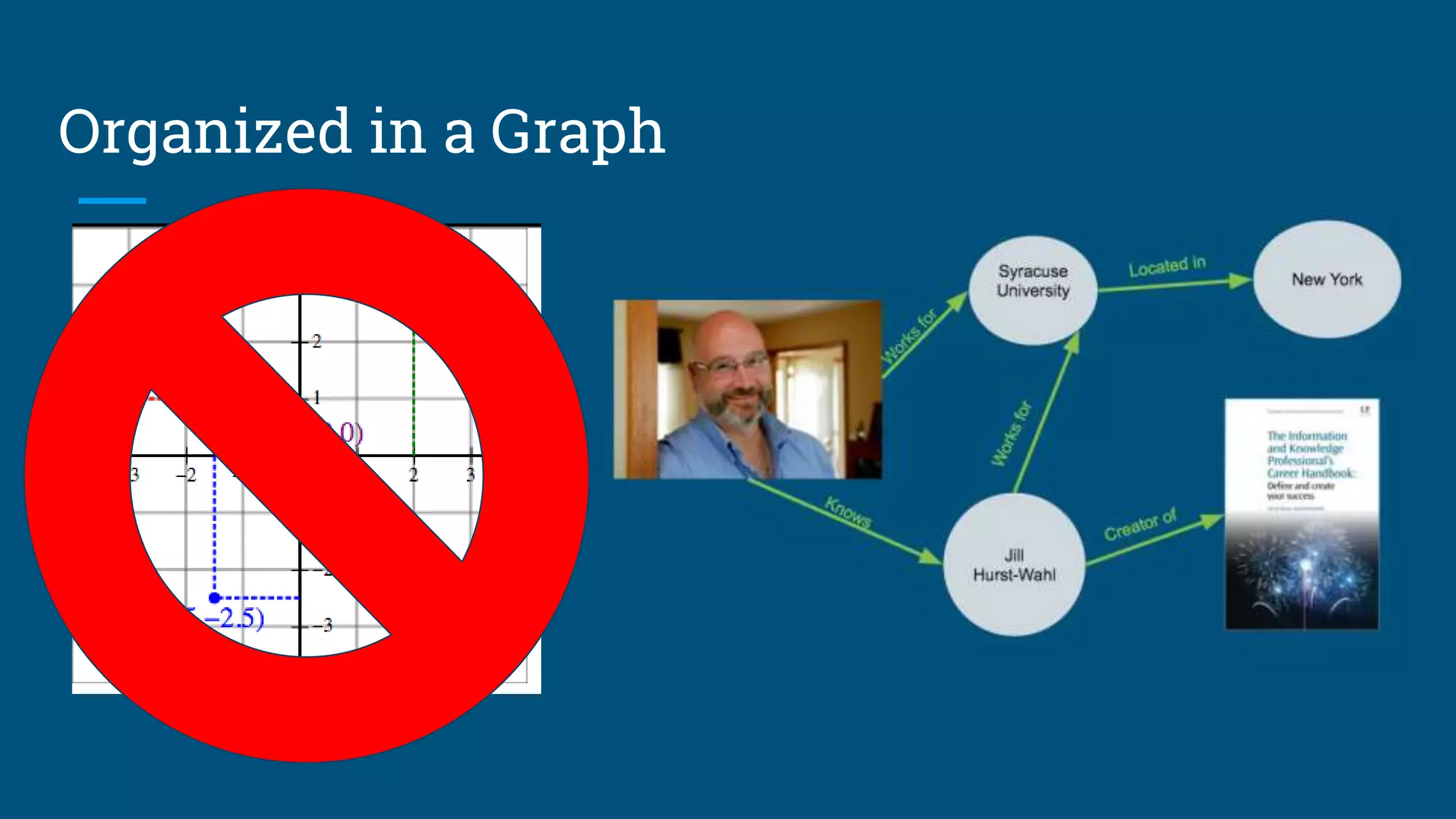
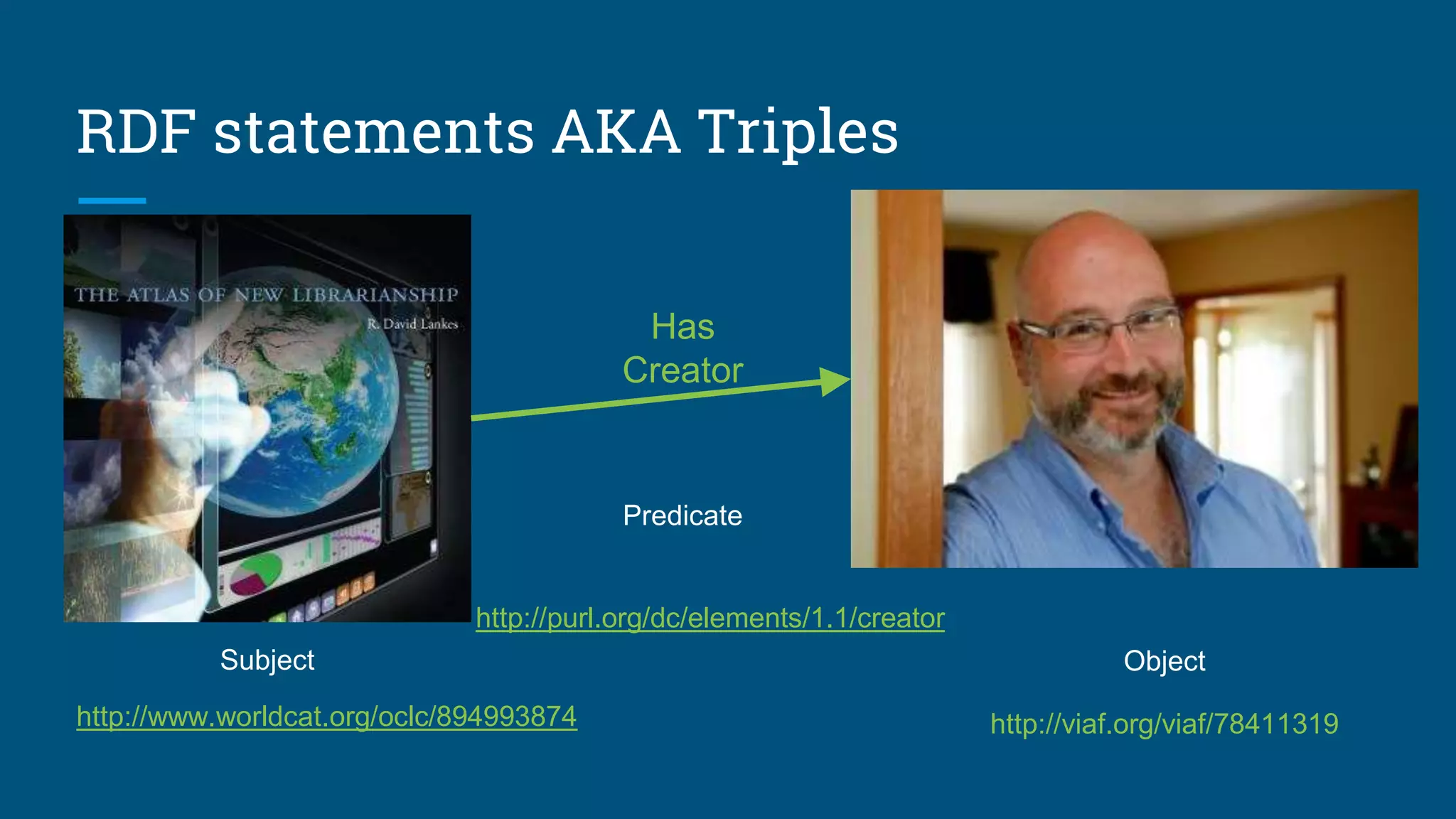
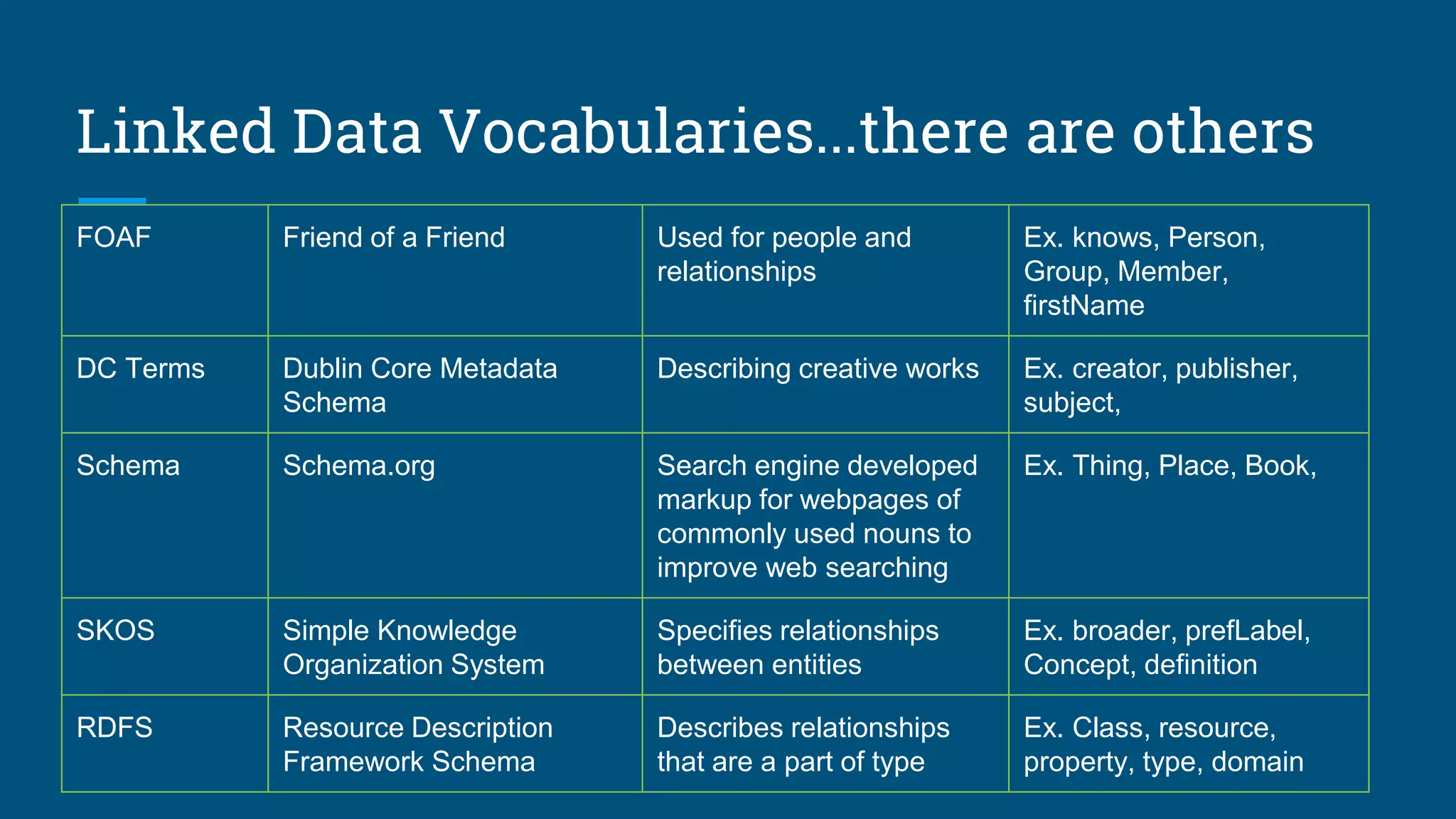
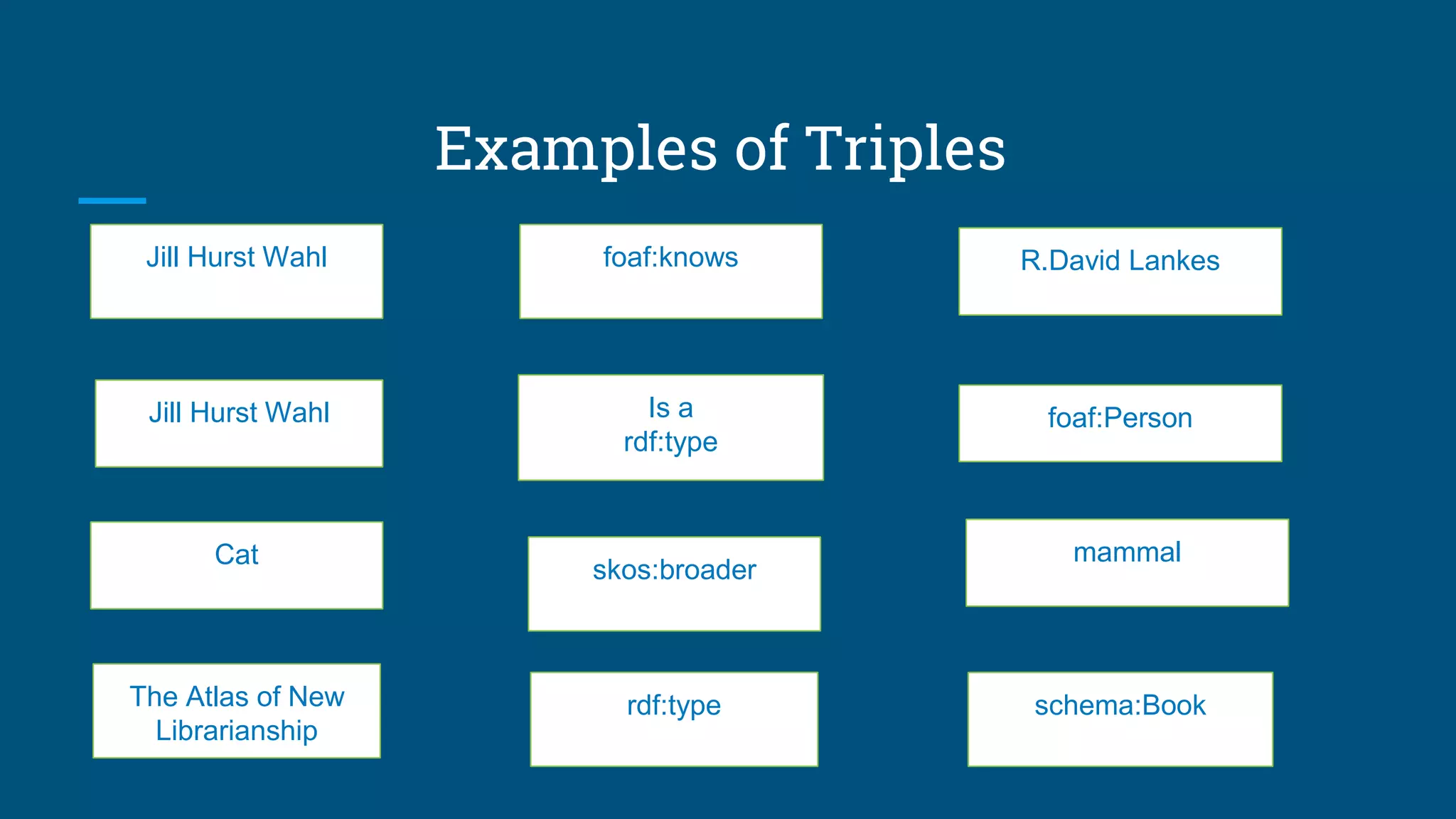
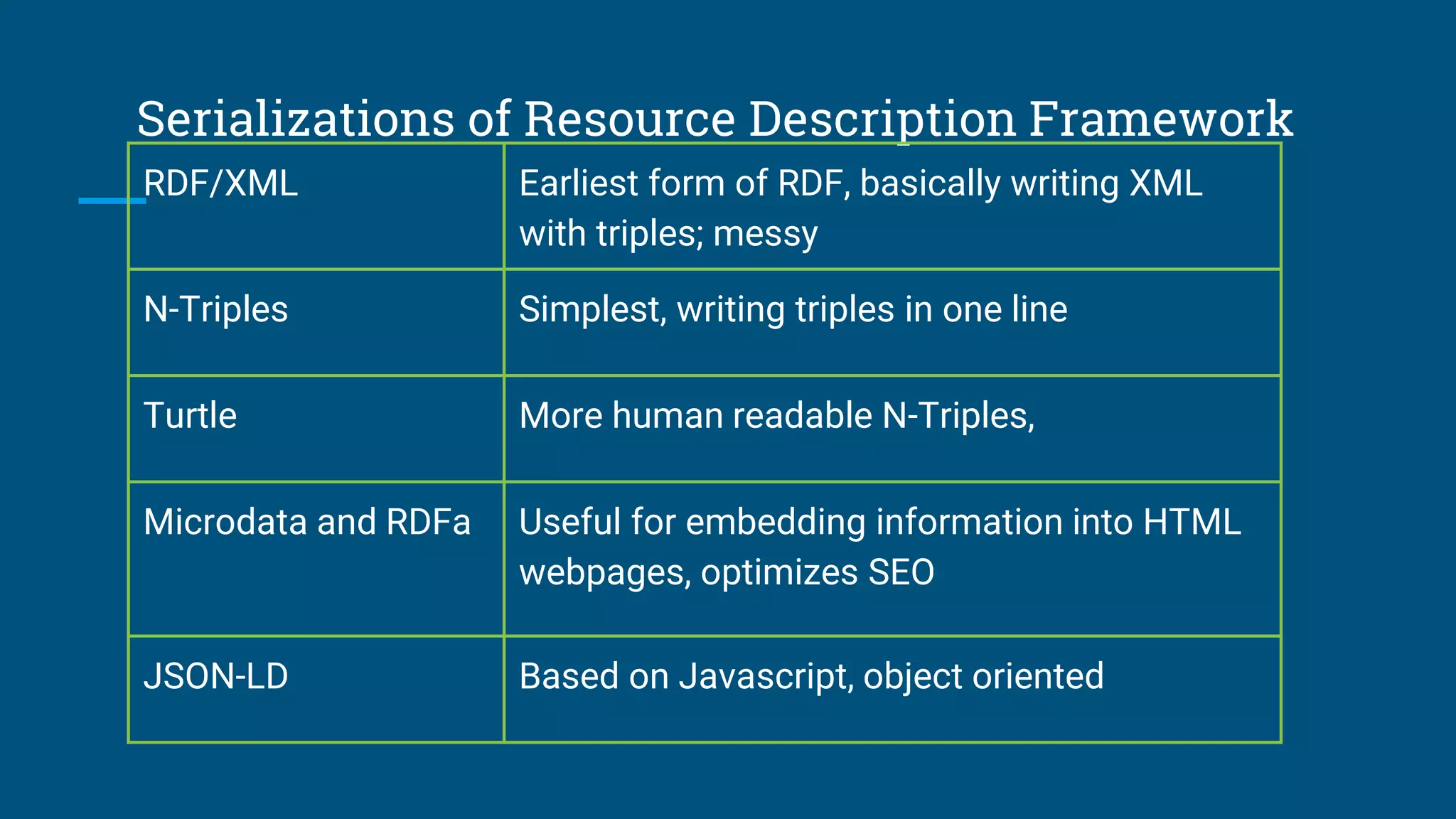
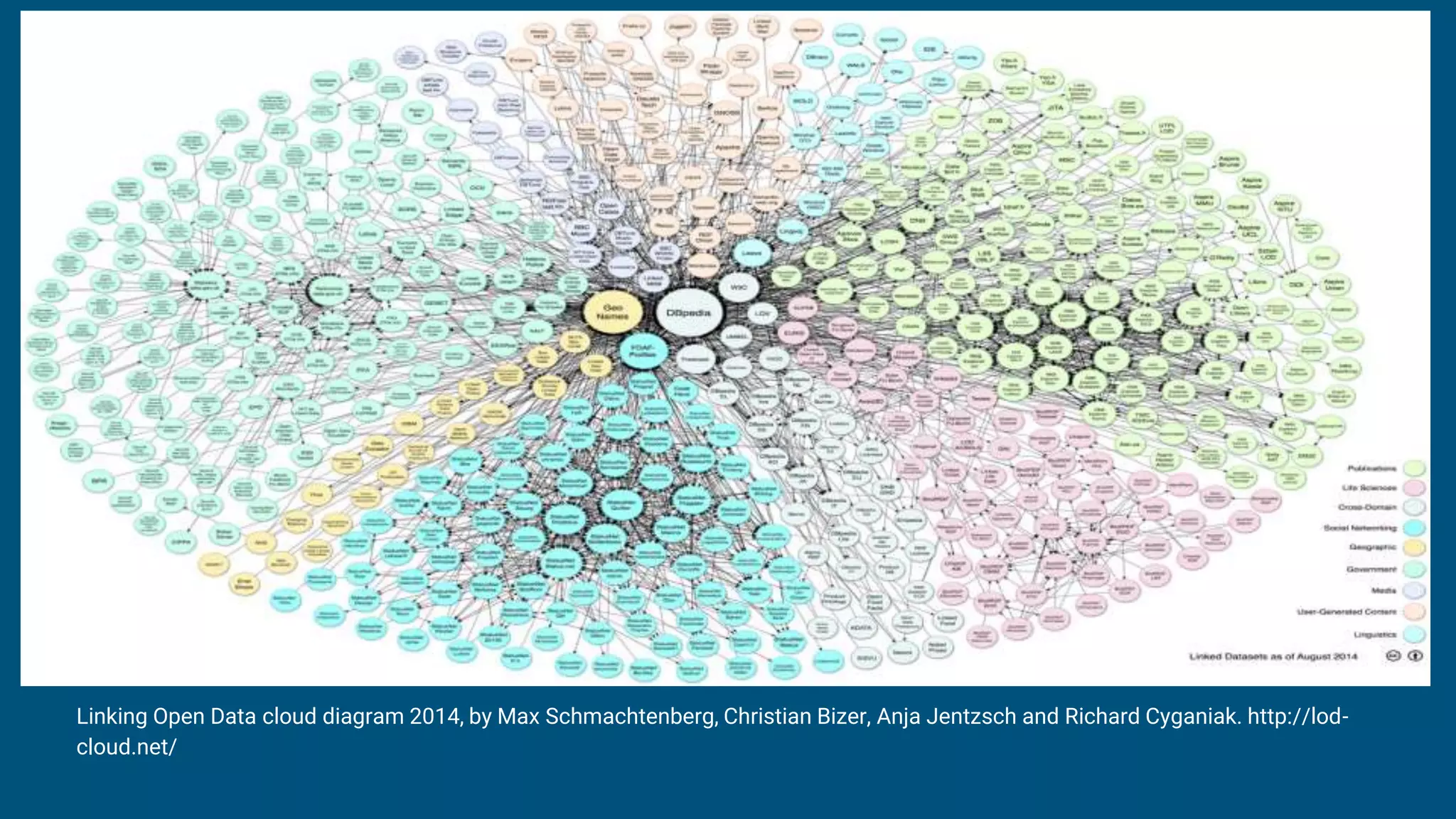
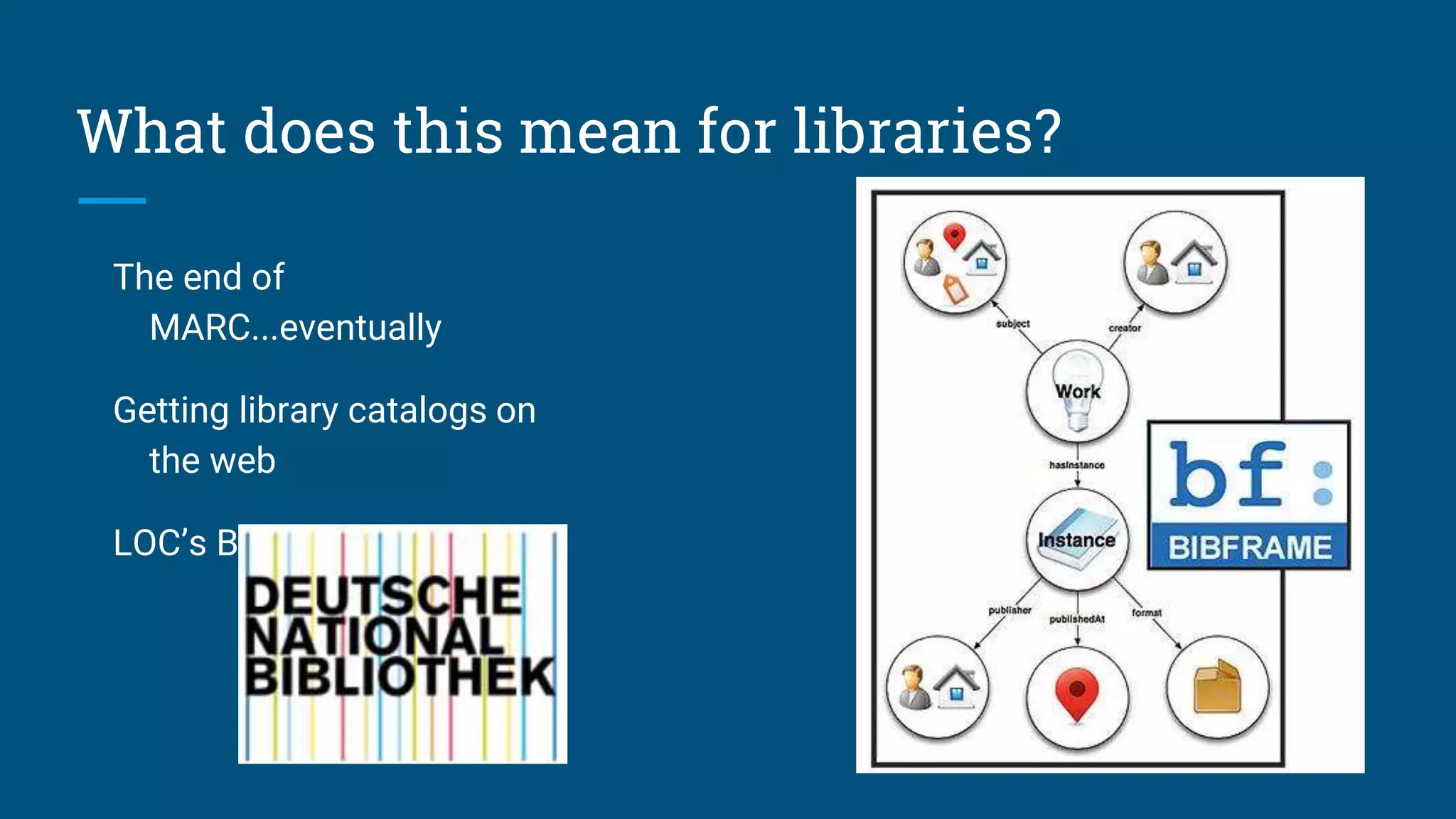
The document outlines the fundamentals of linked data, emphasizing best practices for publishing structured data on the web using URIs and standards like RDF and SPARQL. It discusses various linked data vocabularies and examples of RDF triples, along with their applications in improving web searches. It also addresses potential challenges related to privacy and the adoption of linked data in libraries, especially concerning the transition from MARC to more modern frameworks like BibFrame.