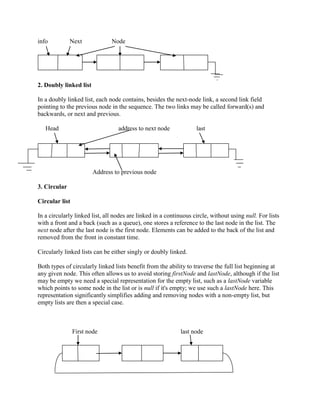
The document discusses different types of linked lists, including linear, doubly, and circular linked lists. Linear linked lists contain nodes with an information field and a next pointer. Doubly linked lists contain previous and next pointers. Circular linked lists form a continuous circle without a null pointer, with the next node after the last being the first. Key operations on linked lists include searching, insertion, and deletion. Linked lists allow for dynamic memory allocation and efficient insertion/deletion compared to arrays.

![Operations on linked list:
1. Searching
2. Insertion
3. Deletion
1. Searching for node from linked list
Algorithm: Search_node(Start, Data)
[Searches for data, start ptr to first node]
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Accept linked list and data
Step 3: Set temp=Start
Step 4: While link [temp] not equal to Null [check till end]
If info [temp] =Data, then
Write: “Found Successfully”
Exit [if found, stop]
[End of if]
Set Temp=Link [tamp] [pointer is incremented to next]
[End of while]
Step 5: Write: “Not Found”
Step 6: Exit [stop]
Types of linked list:
1. Linear
2. Doubly
3. Circular
1. Linear linked list
Contained within itself the address of the next items such an explicit ordering gives rise to a data
structure, which is known as a linear linked list.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linklistassi-120927062659-phpapp02/85/Link-list-assi-2-320.jpg)