This document provides an introduction to linear programming, including:
- Linear programming originated during World War 2 to optimally allocate limited resources.
- It involves identifying decision variables, constraints as linear equations, non-negativity restrictions, and an objective function to maximize or minimize.
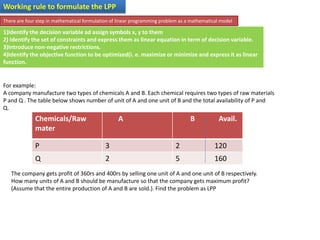
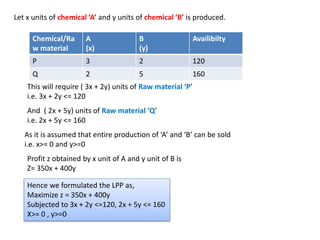
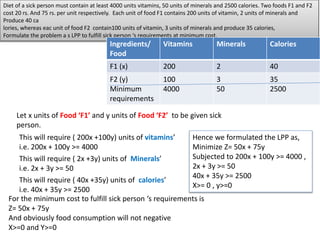
- Two examples of formulating linear programming problems (LPPs) are provided: determining the optimal product mix to maximize profit for a company, and minimizing the cost of a diet to meet a sick person's nutritional requirements.
- Graphical solution methods for LPPs include the iso-profit and corner point methods.