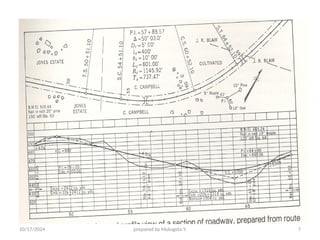
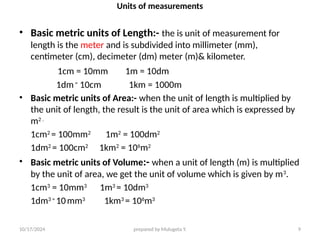
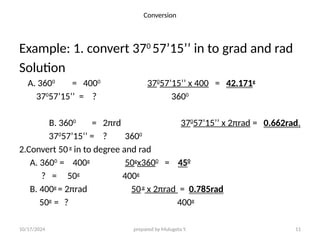
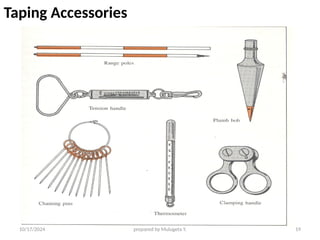
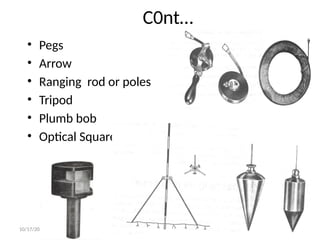
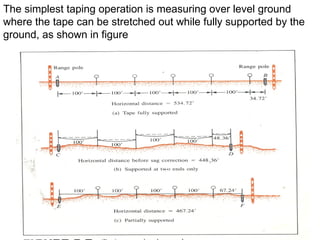
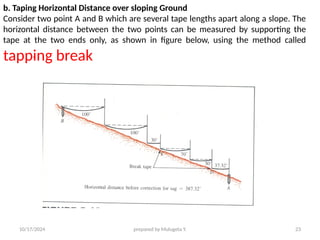
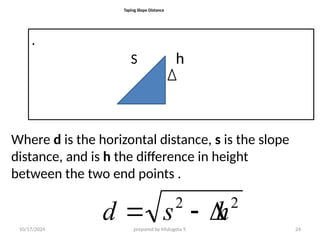
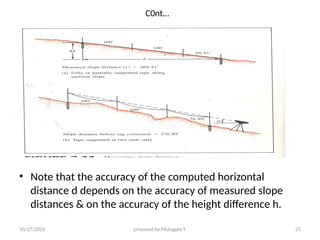
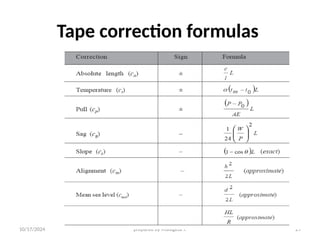
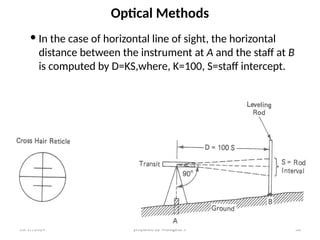
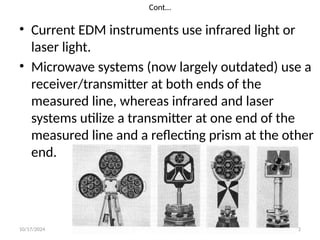
The document outlines essential definitions and processes of surveying, emphasizing its importance in measuring distances, angles, and elevations for infrastructure projects. It categorizes surveying into types, classifications based on purpose and instruments, and describes basic measurements and methods for distance measurement. Additionally, it discusses potential errors in linear measurements and advancements in electronic distance measurement technology.