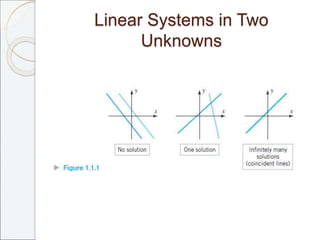
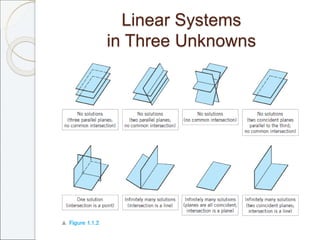
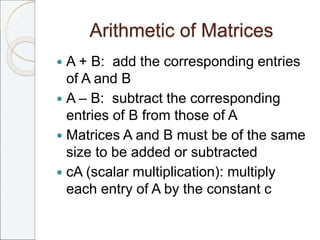
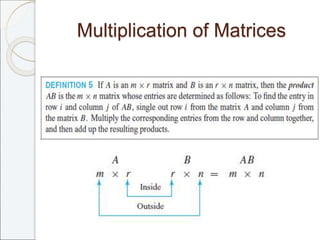
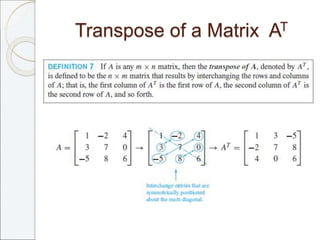
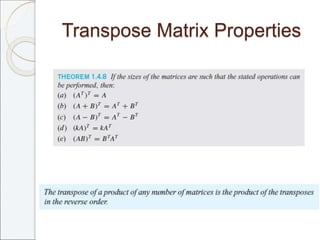
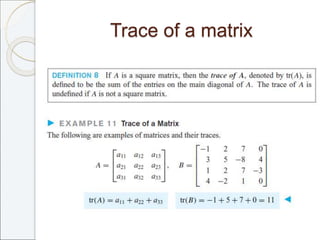
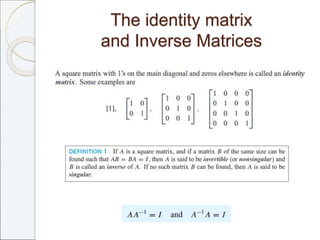
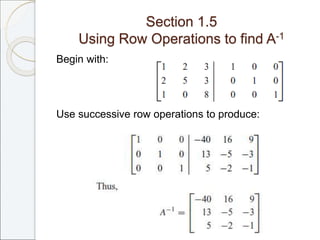
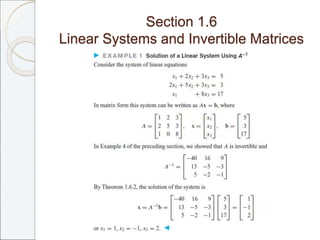
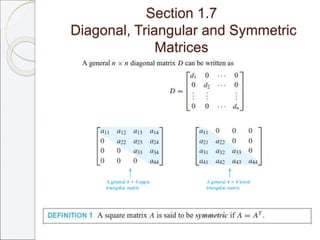
This document outlines the contents of Chapter 1 from the textbook "Elementary Linear Algebra" by Howard Anton. The chapter covers systems of linear equations and matrices. It introduces Gaussian elimination to solve systems of linear equations and defines matrix operations such as addition, scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication. It also discusses properties of matrices including inverses, diagonal matrices, and symmetric matrices. Key topics are solving systems of linear equations using Gaussian elimination, defining matrices and basic matrix operations, properties of invertible matrices, and special types of matrices.