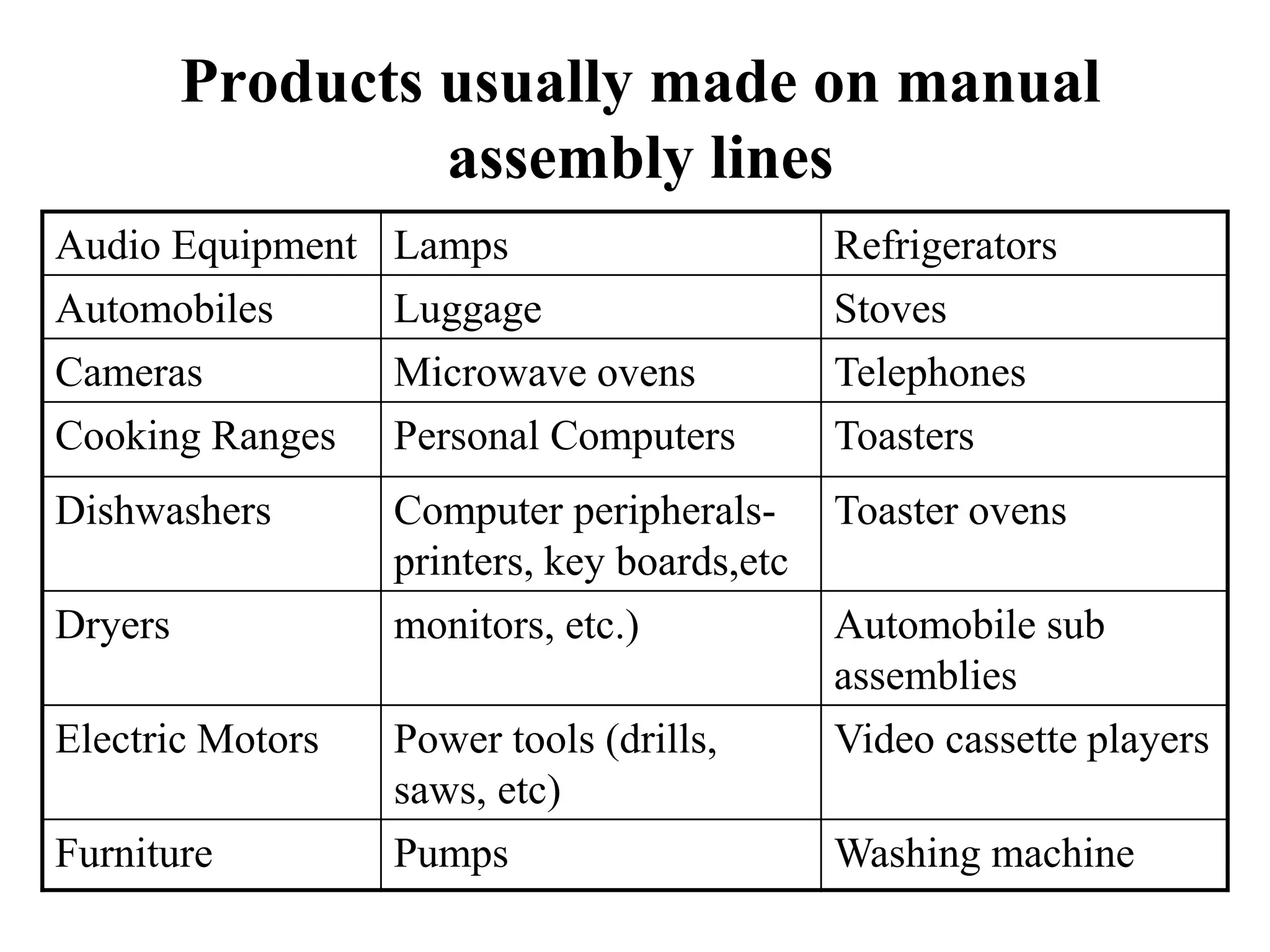
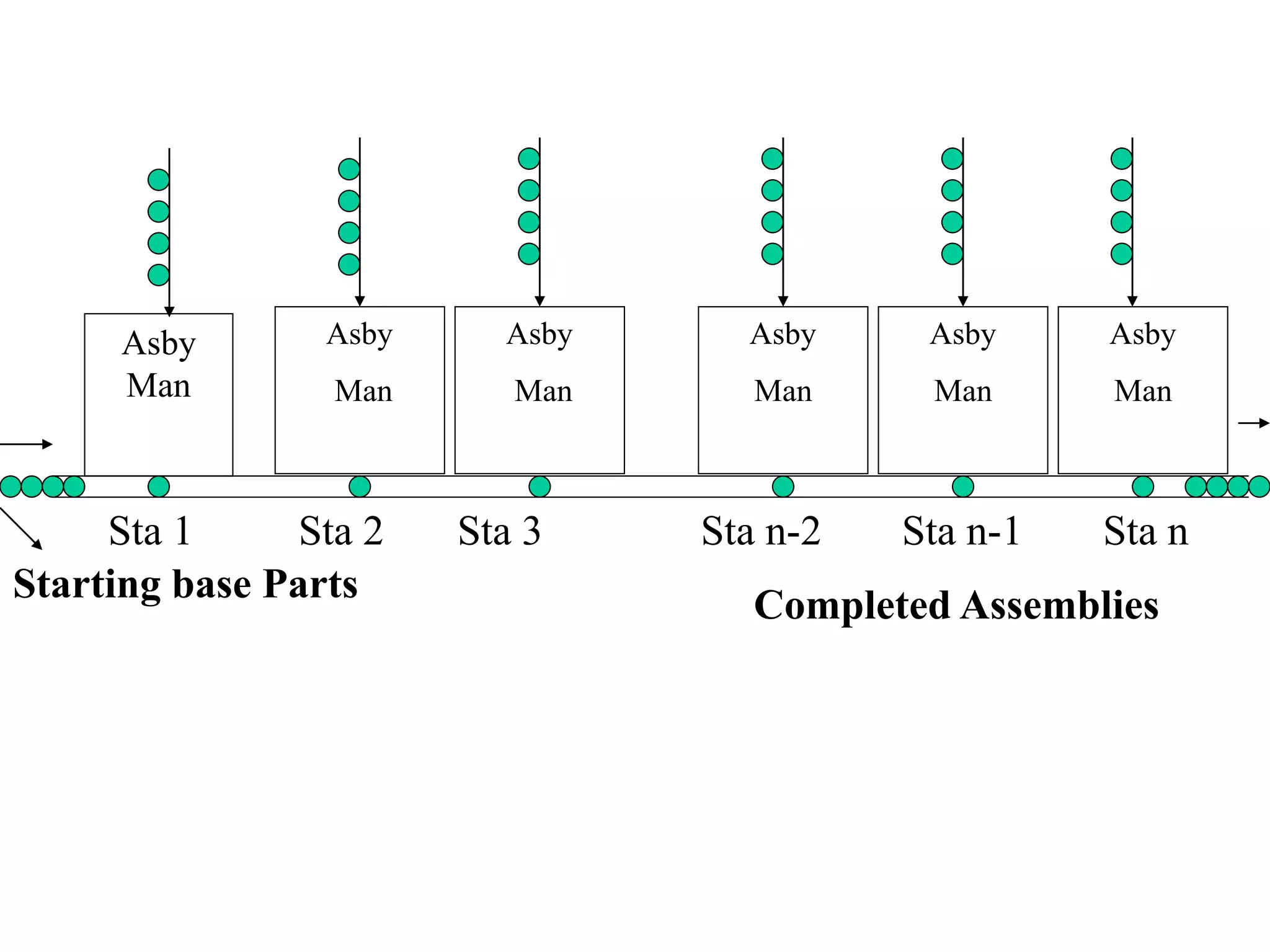
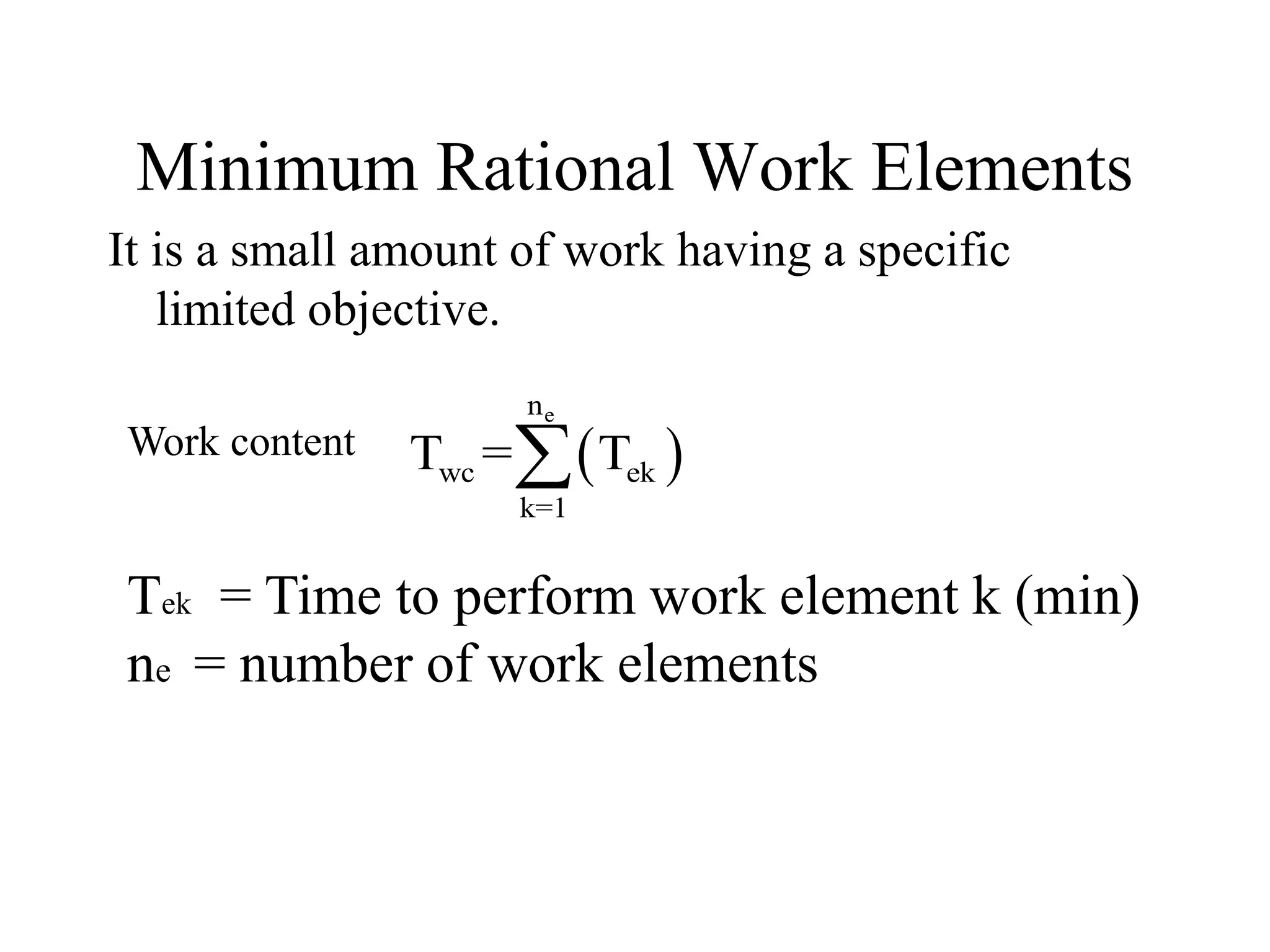
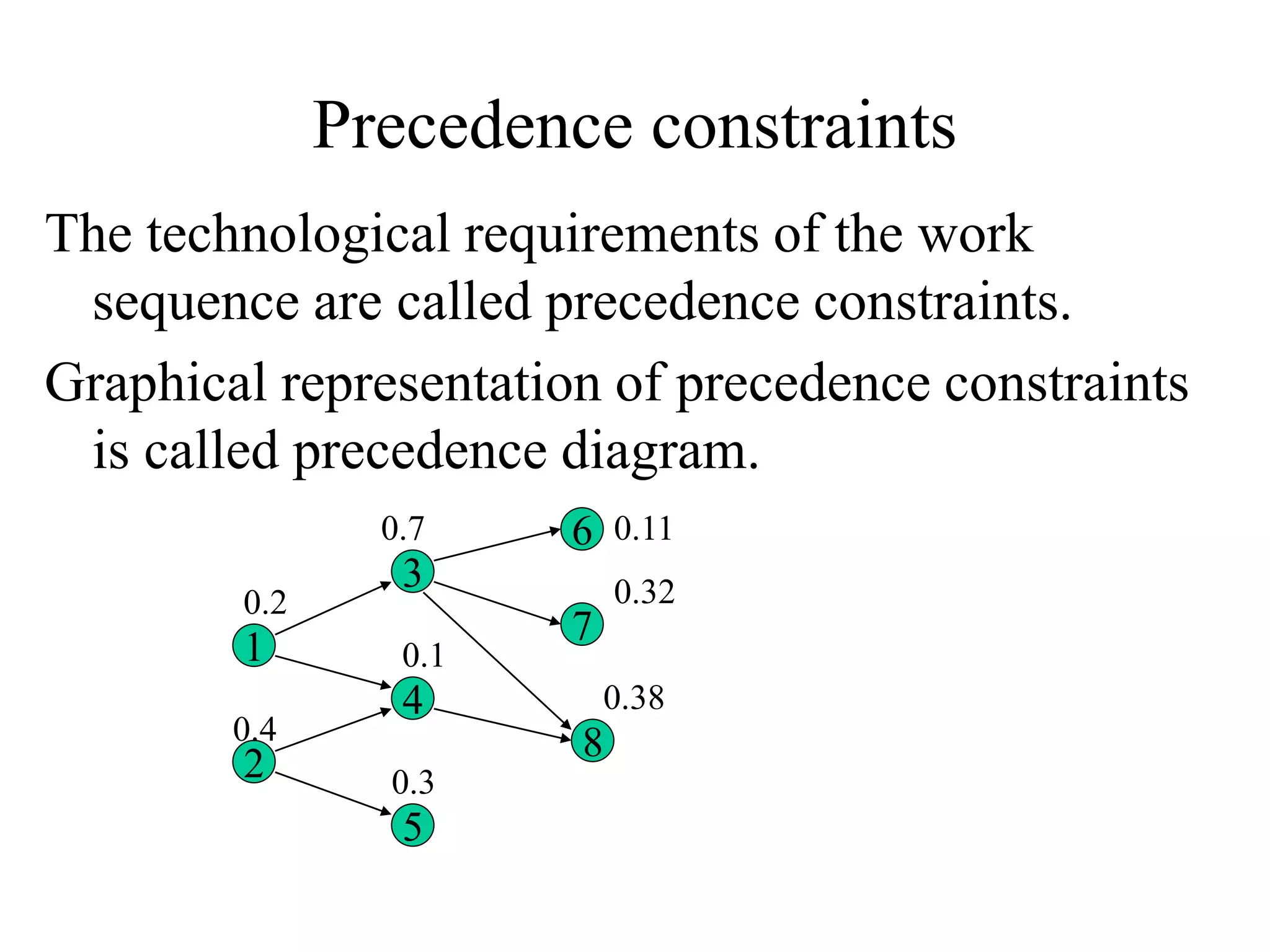
Manual assembly lines are used to assemble consumer products where demand is high or medium, products are identical or similar, and total work can be divided into small elements. They consist of sequential workstations where one or more workers complete tasks. Line pacing is important to maintain production rates, assigning tasks to be completed within each cycle time. Proper line balancing algorithms are used to evenly distribute work among stations, such as the Largest Candidate Rule. Factors like precedence constraints and minimum rational work elements are considered.