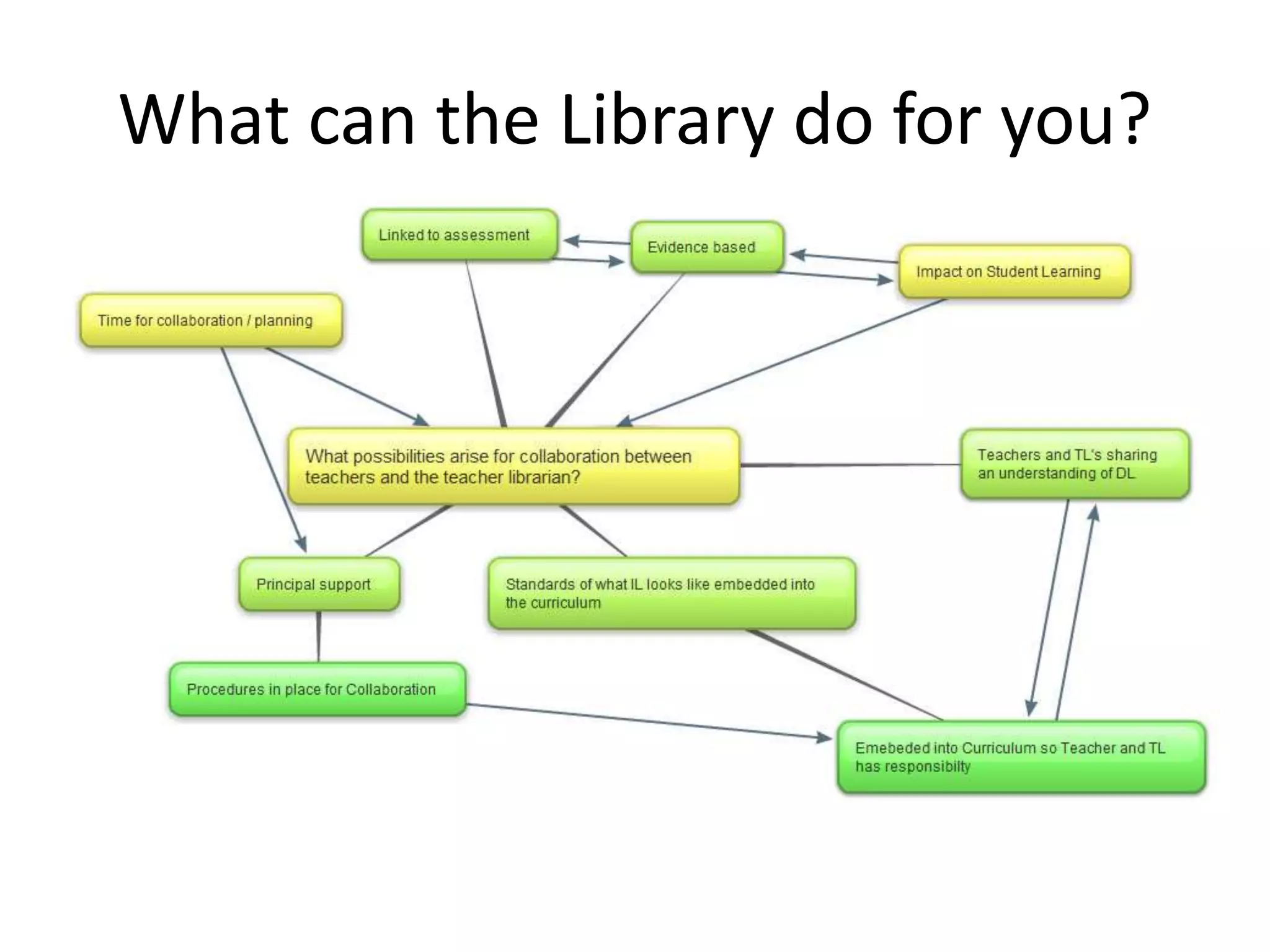
The document discusses the role of the library and librarian in supporting student learning outcomes. It suggests that librarians should collaborate with teachers to incorporate information literacy skills into the curriculum through guided inquiry projects. This requires flexible timetabling to allow for collaboration between teachers and librarians. Research shows that students benefit academically when teachers make use of the school library and partner with librarians in teaching literacy and research skills.