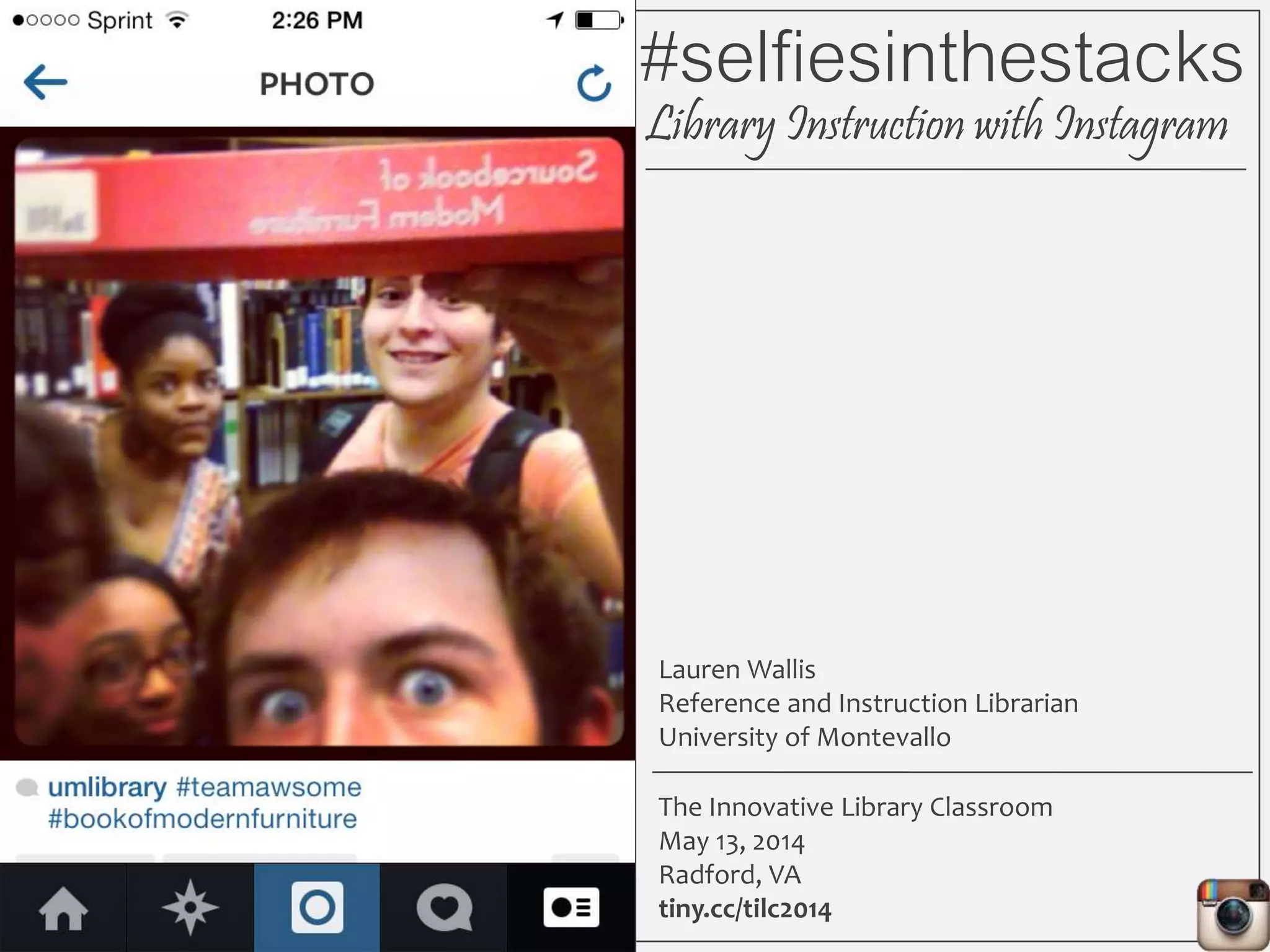
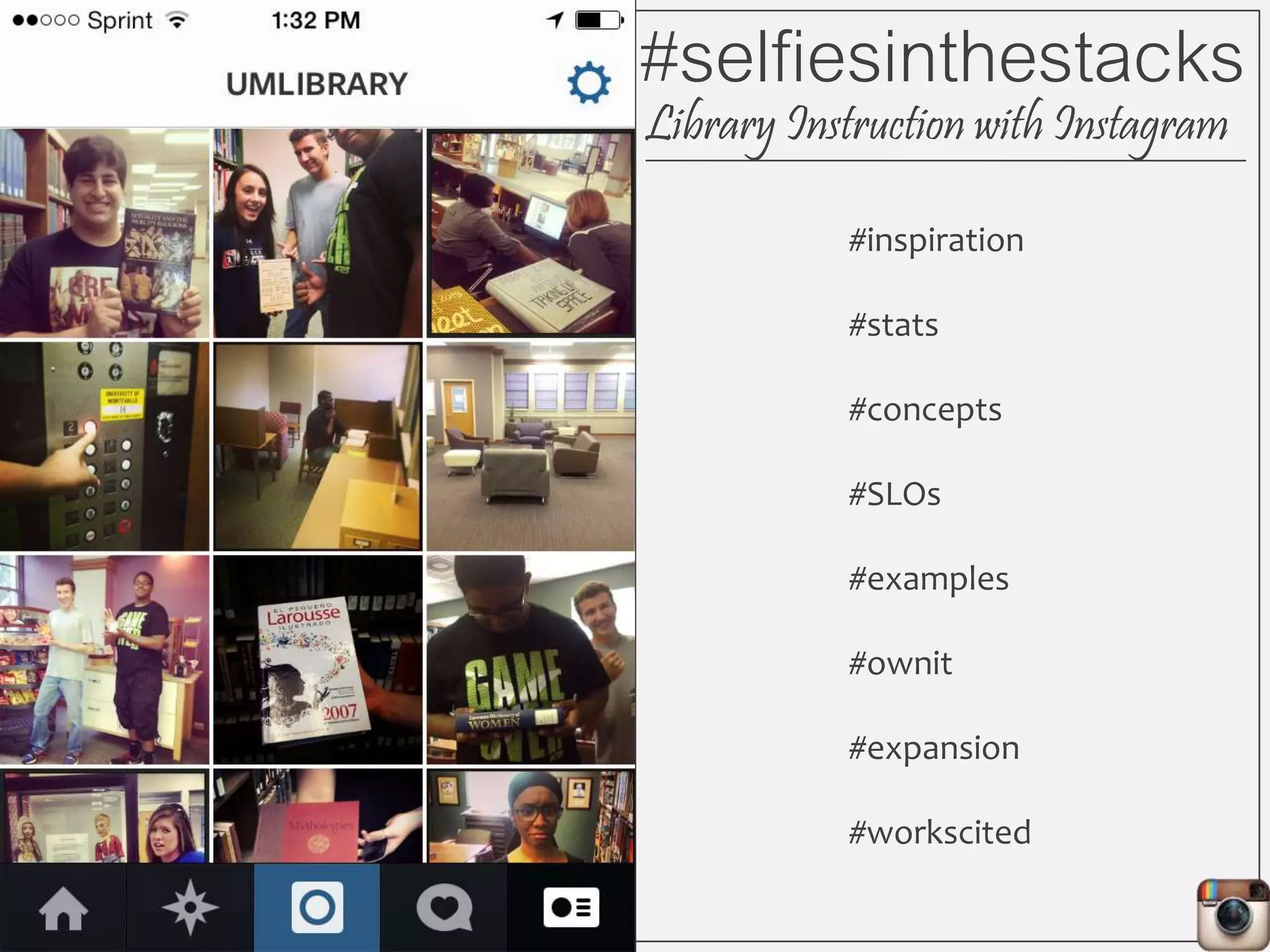
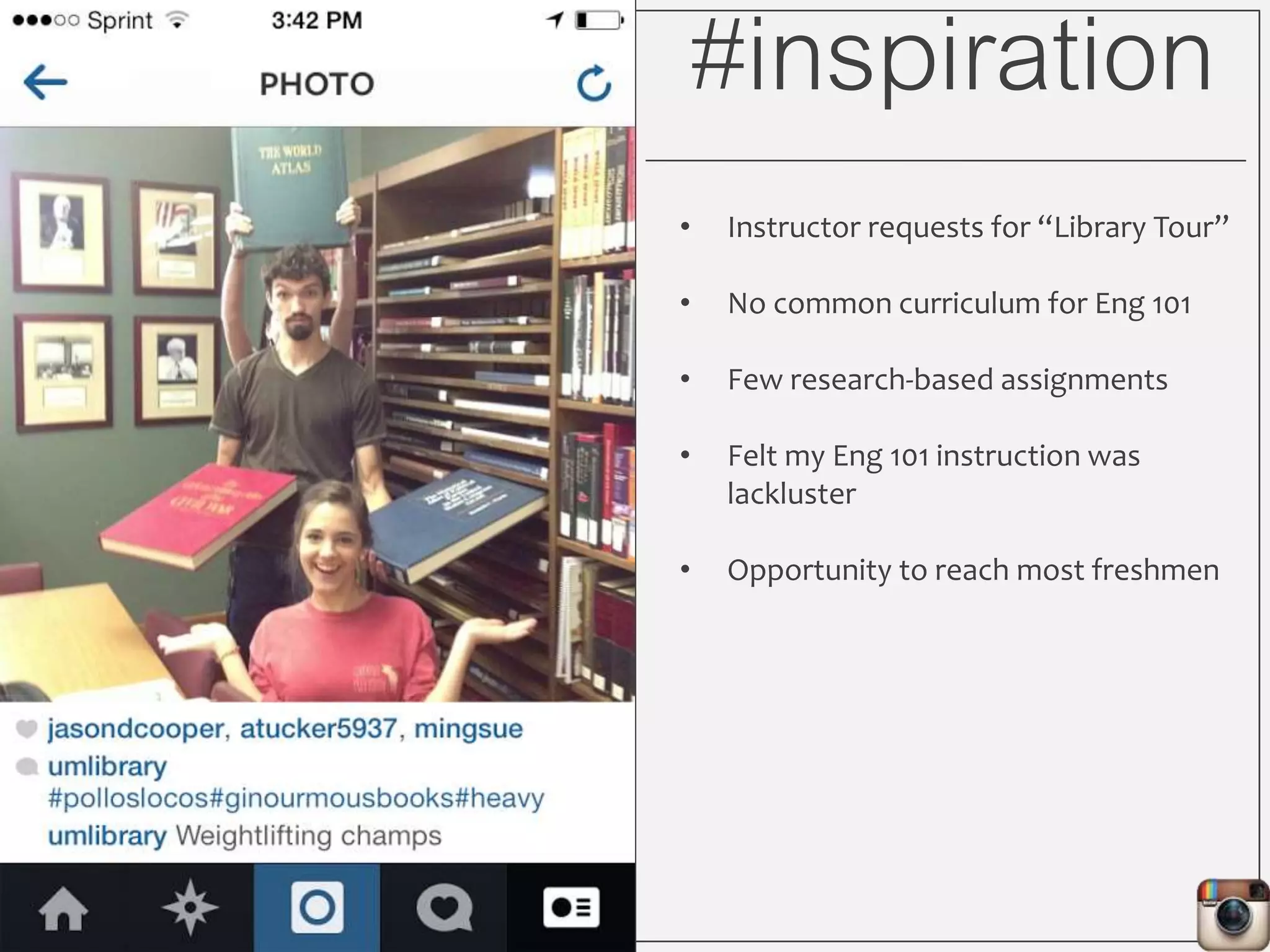
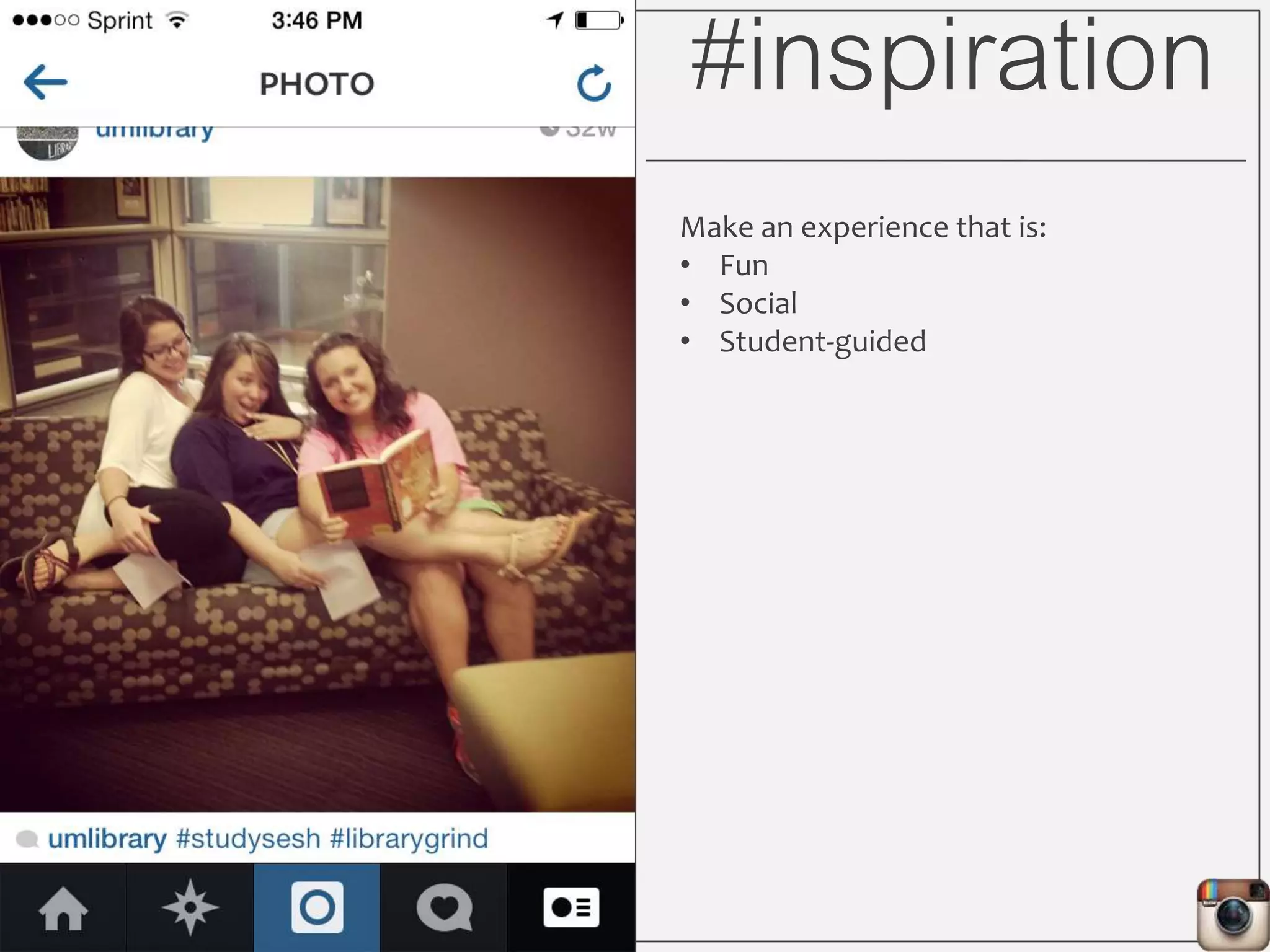
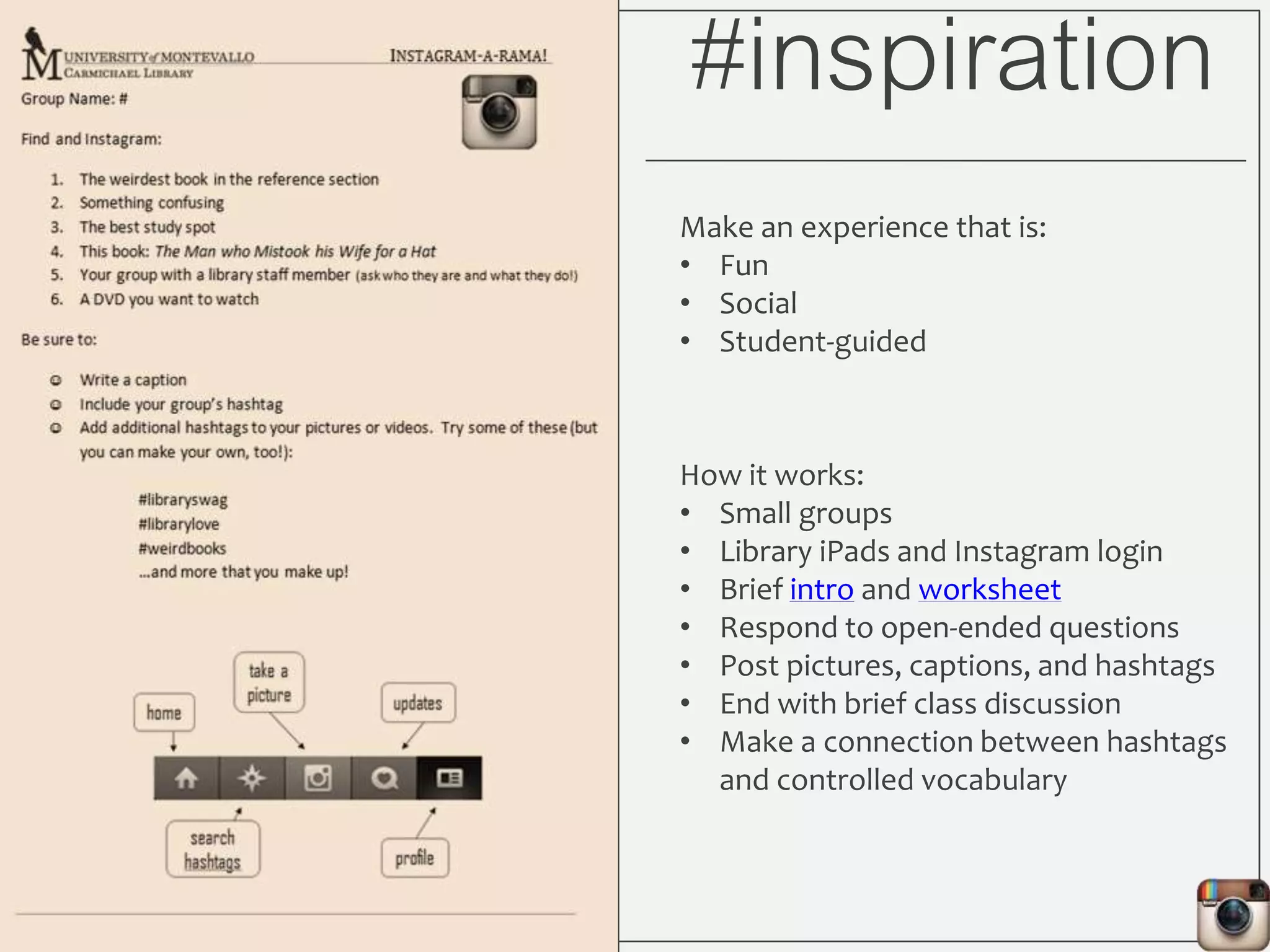
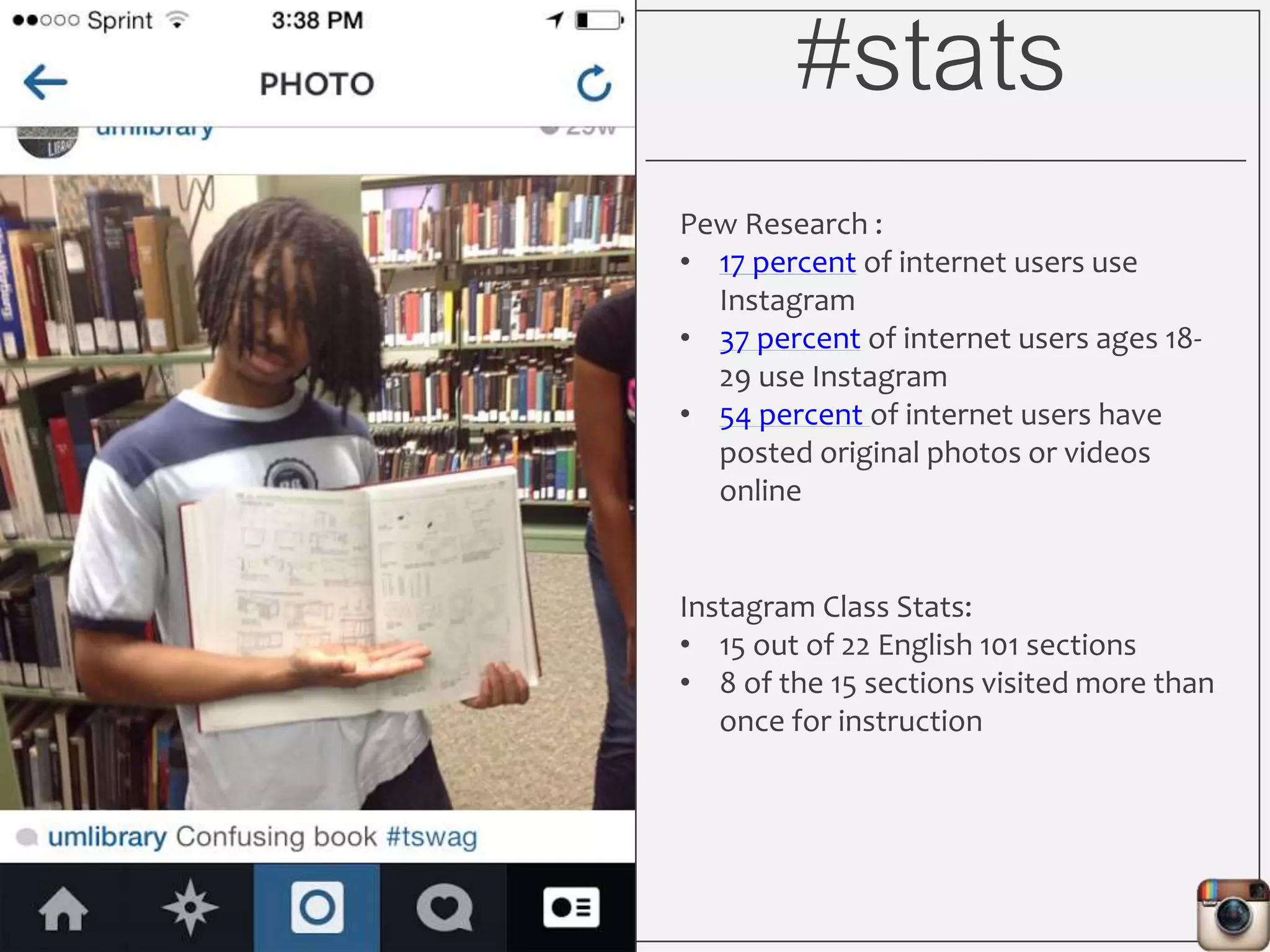
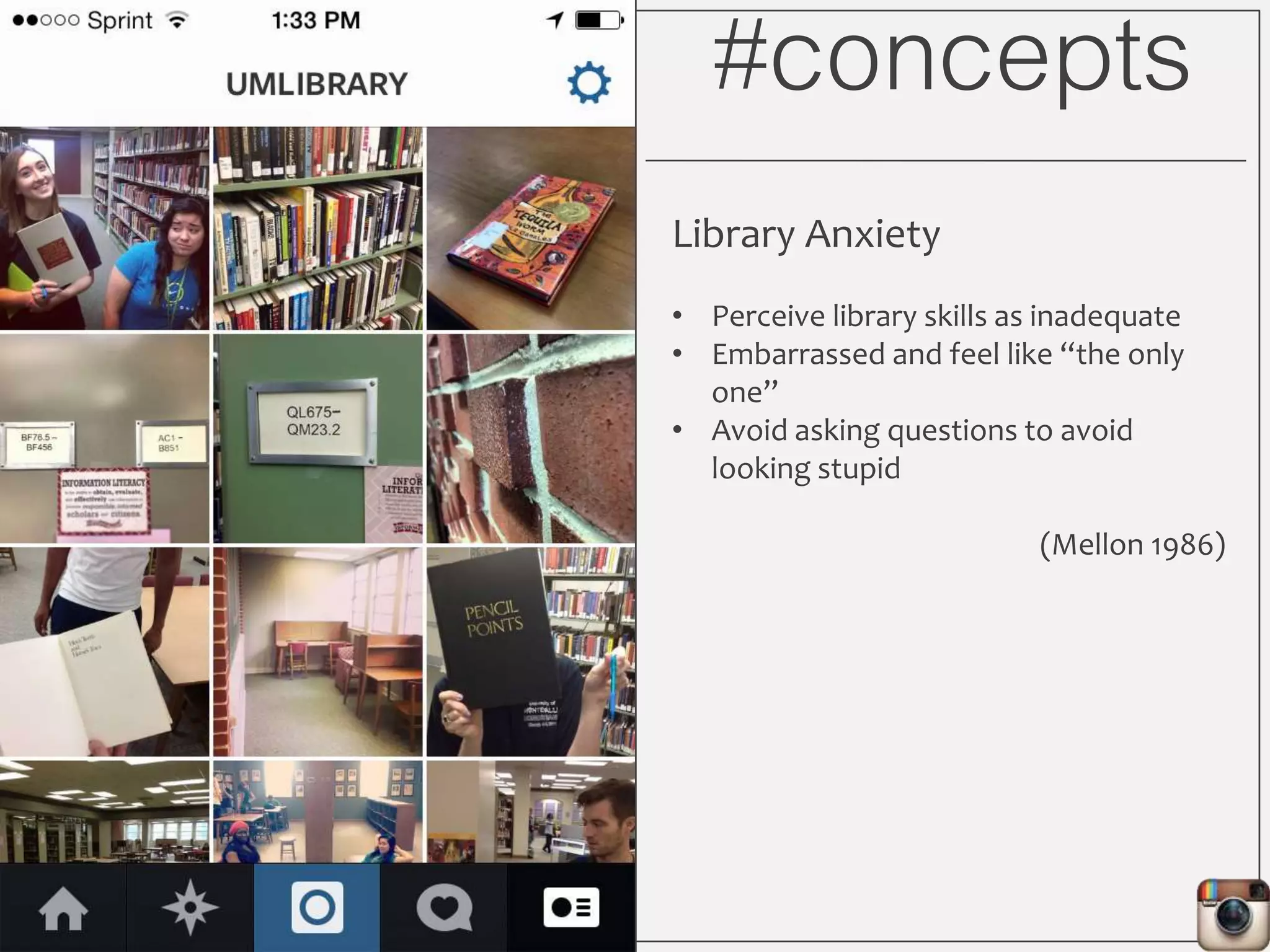
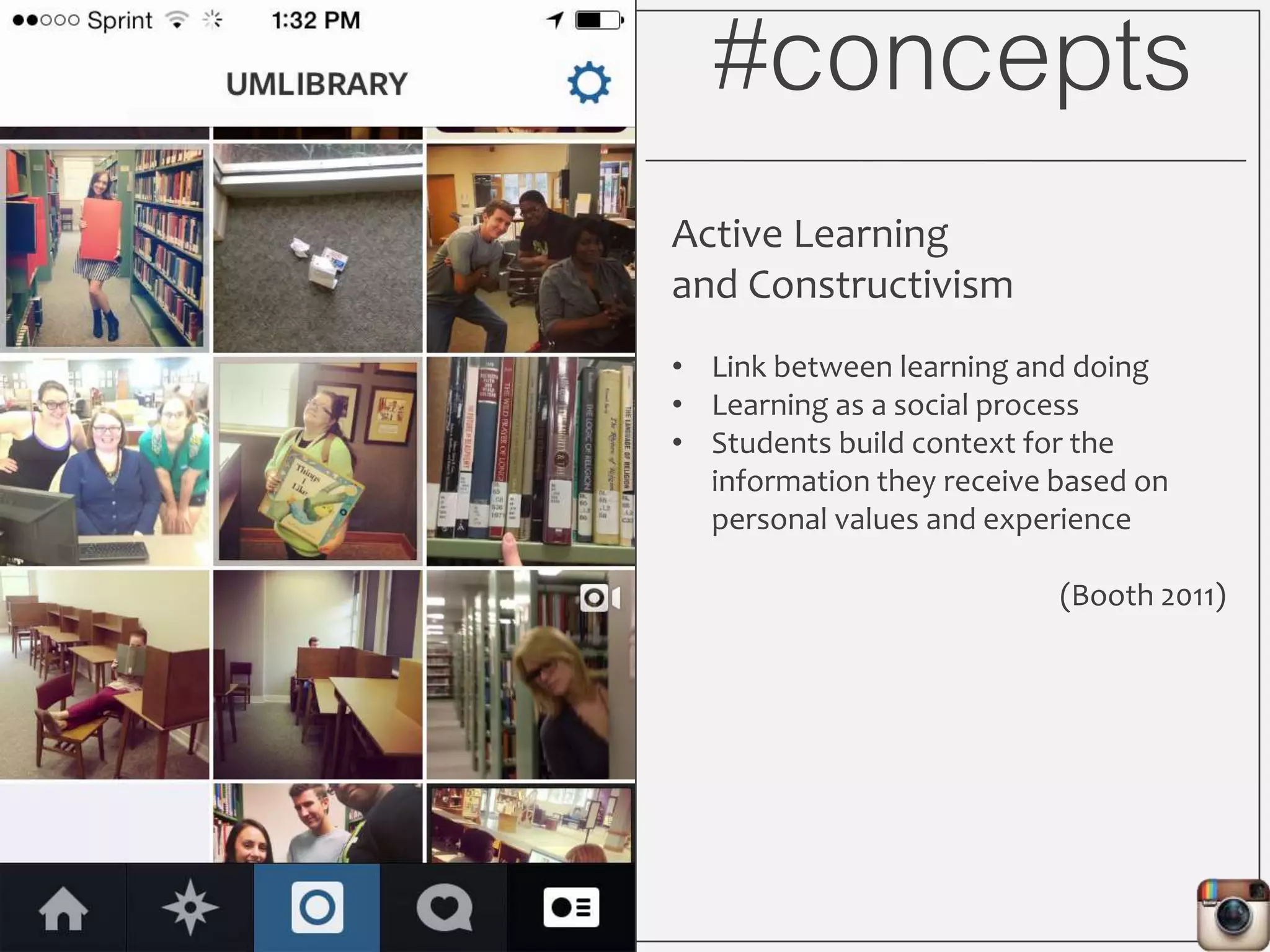
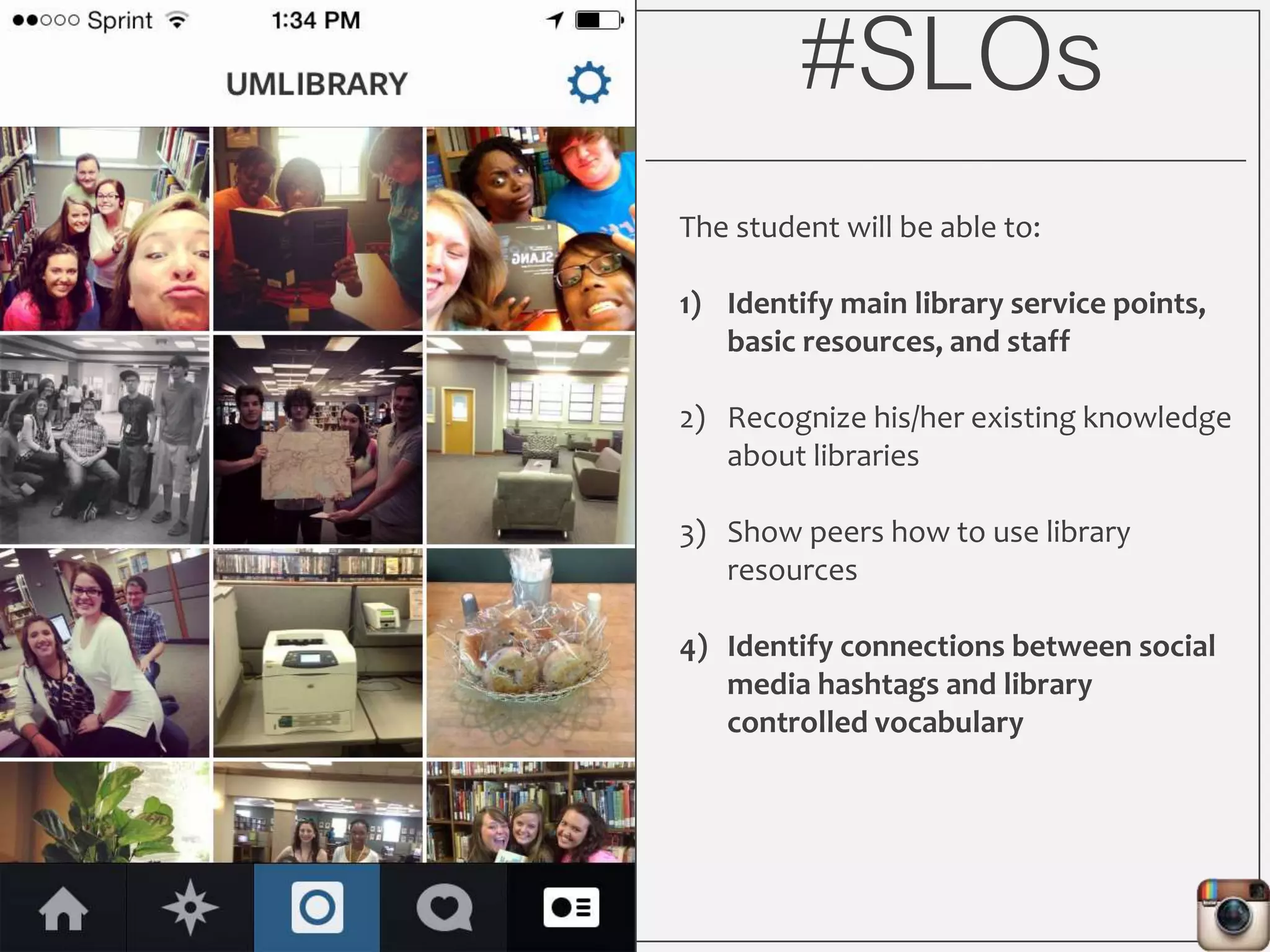
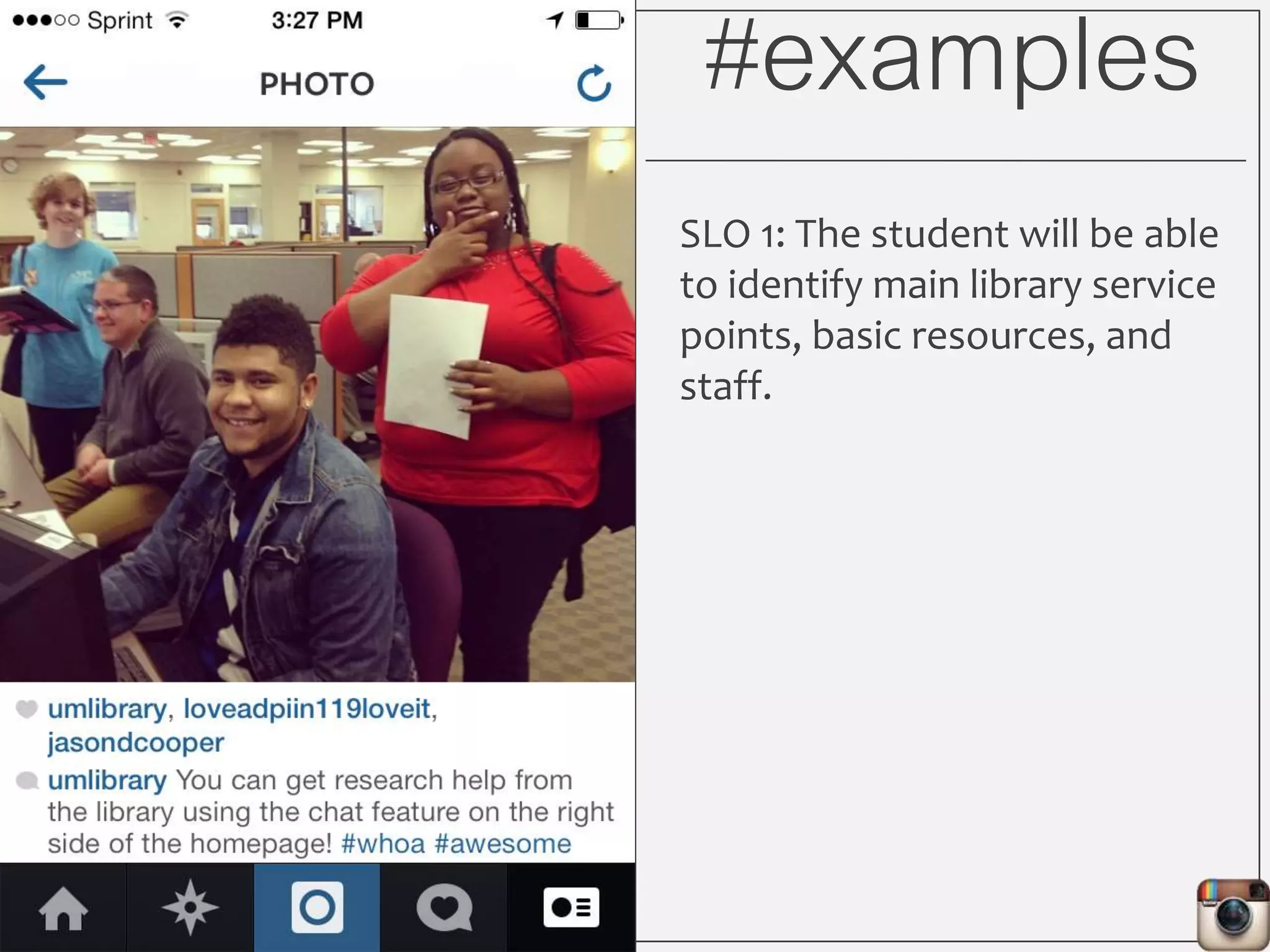
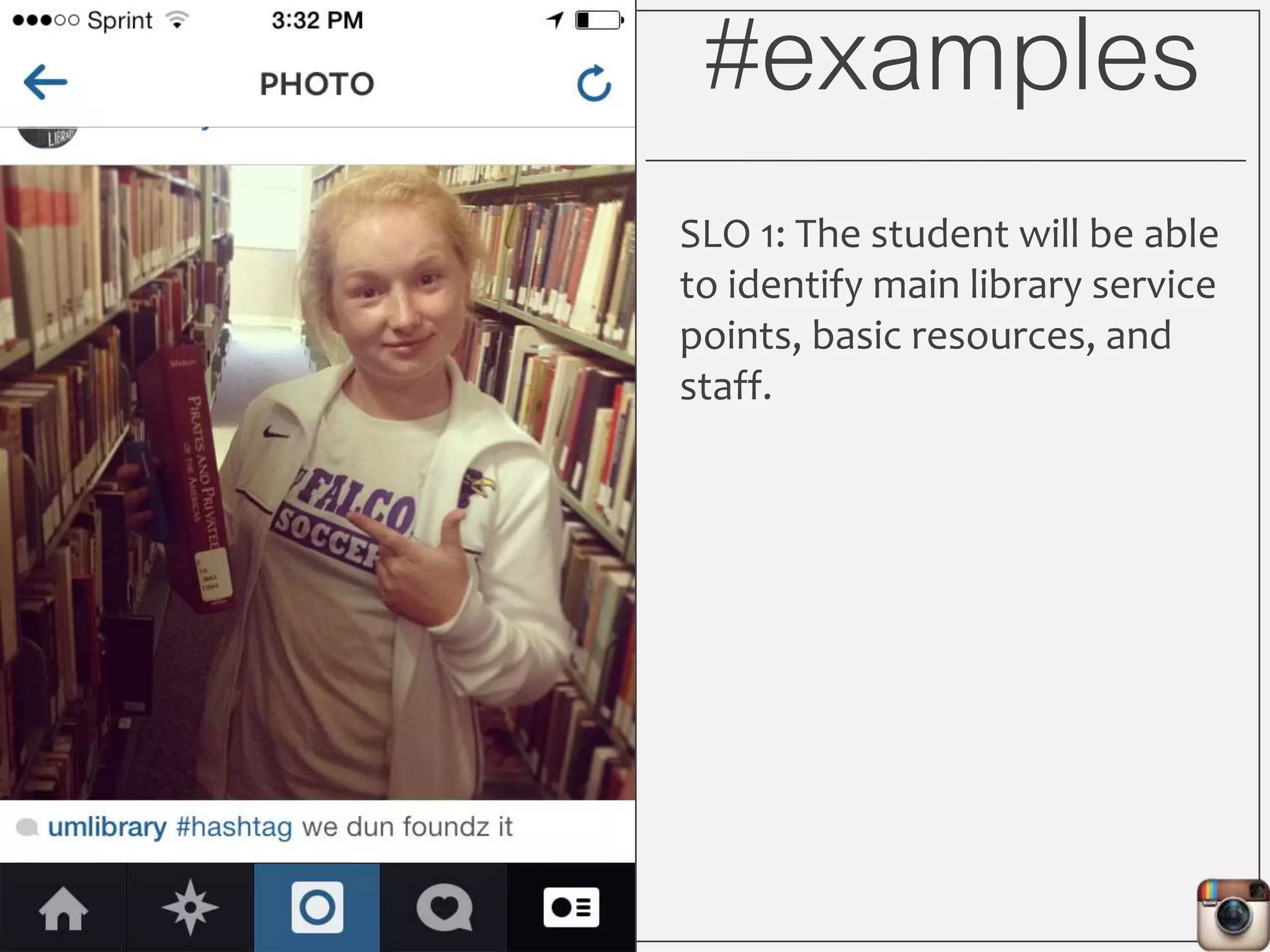
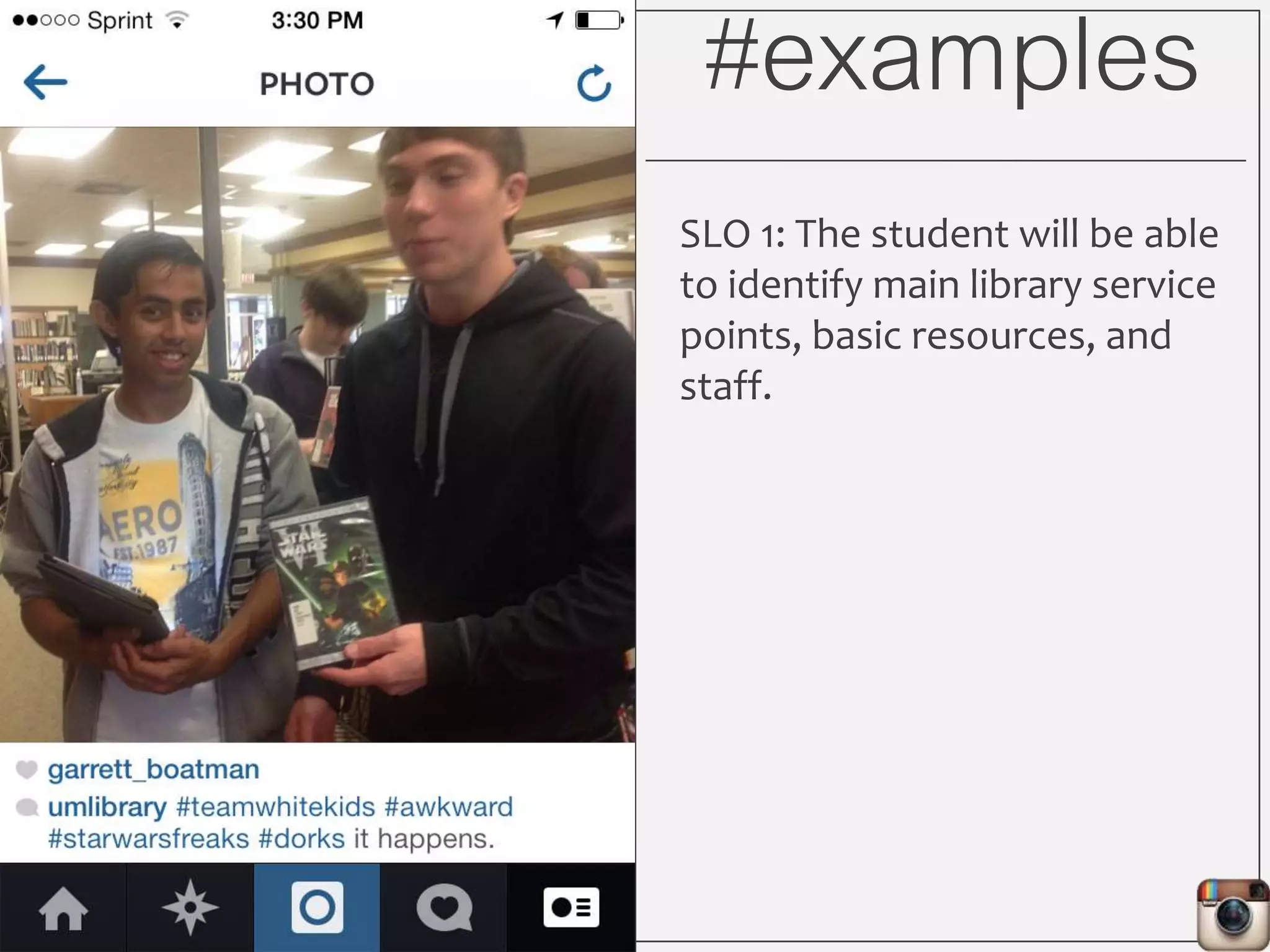
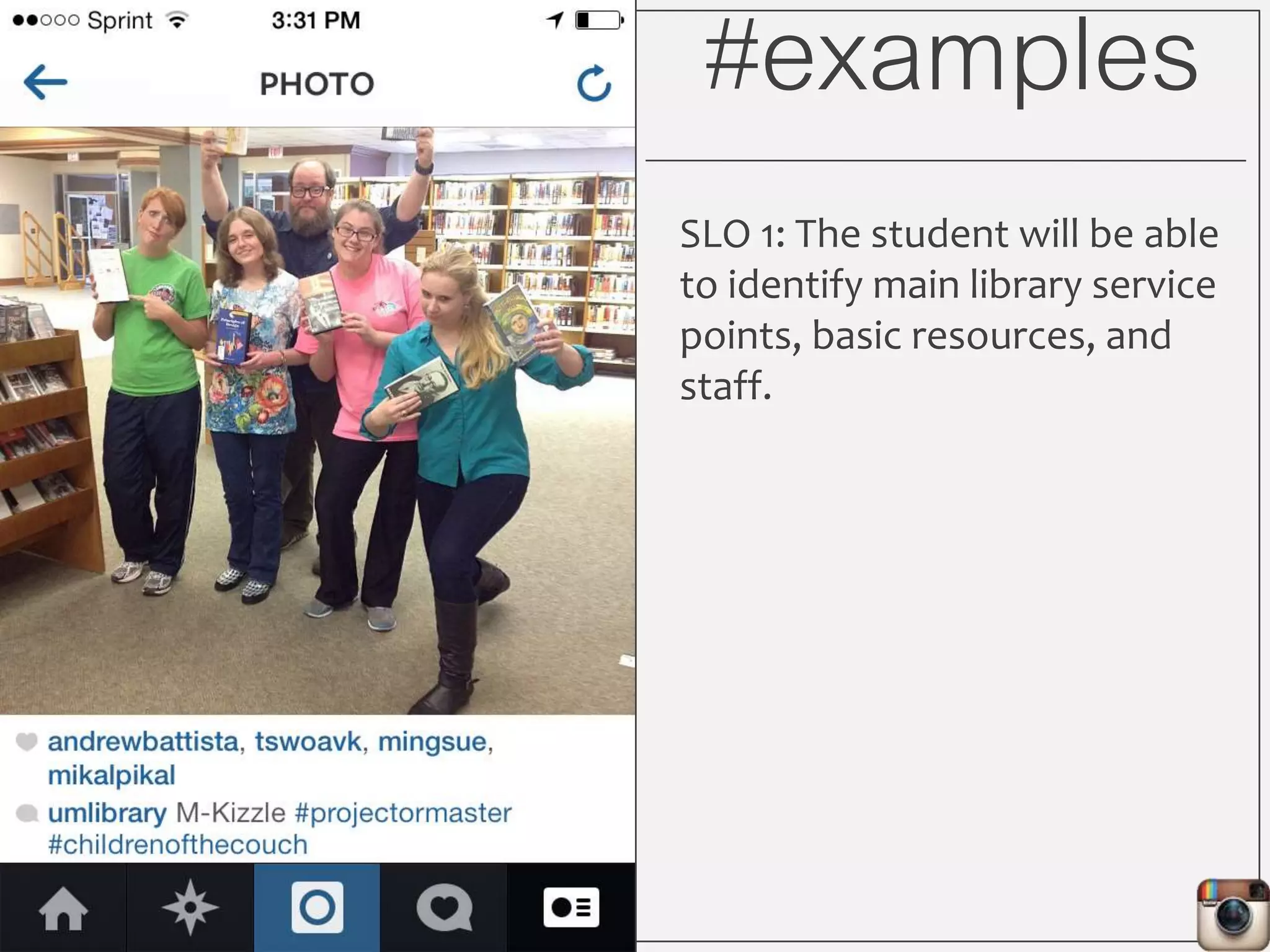
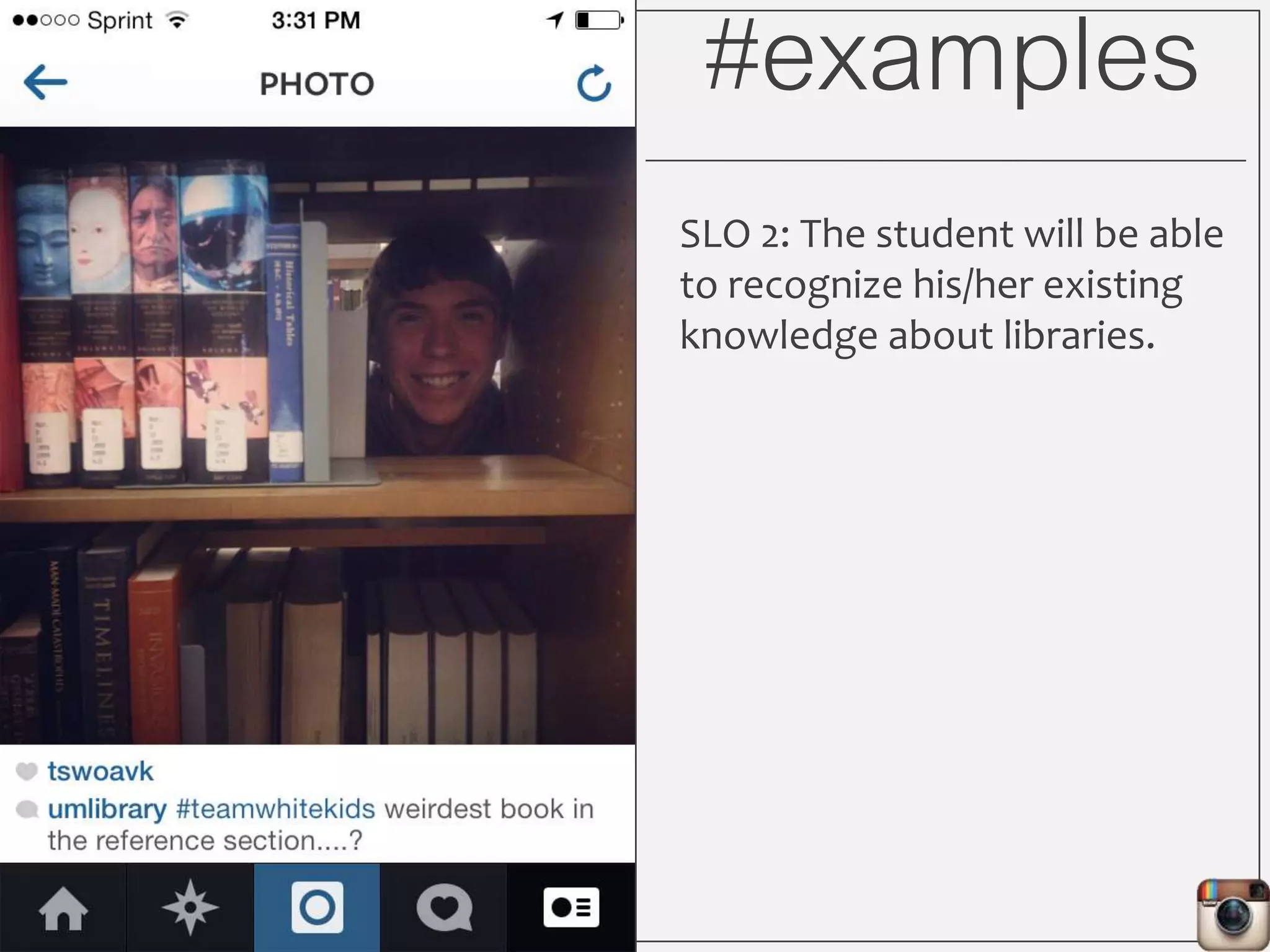
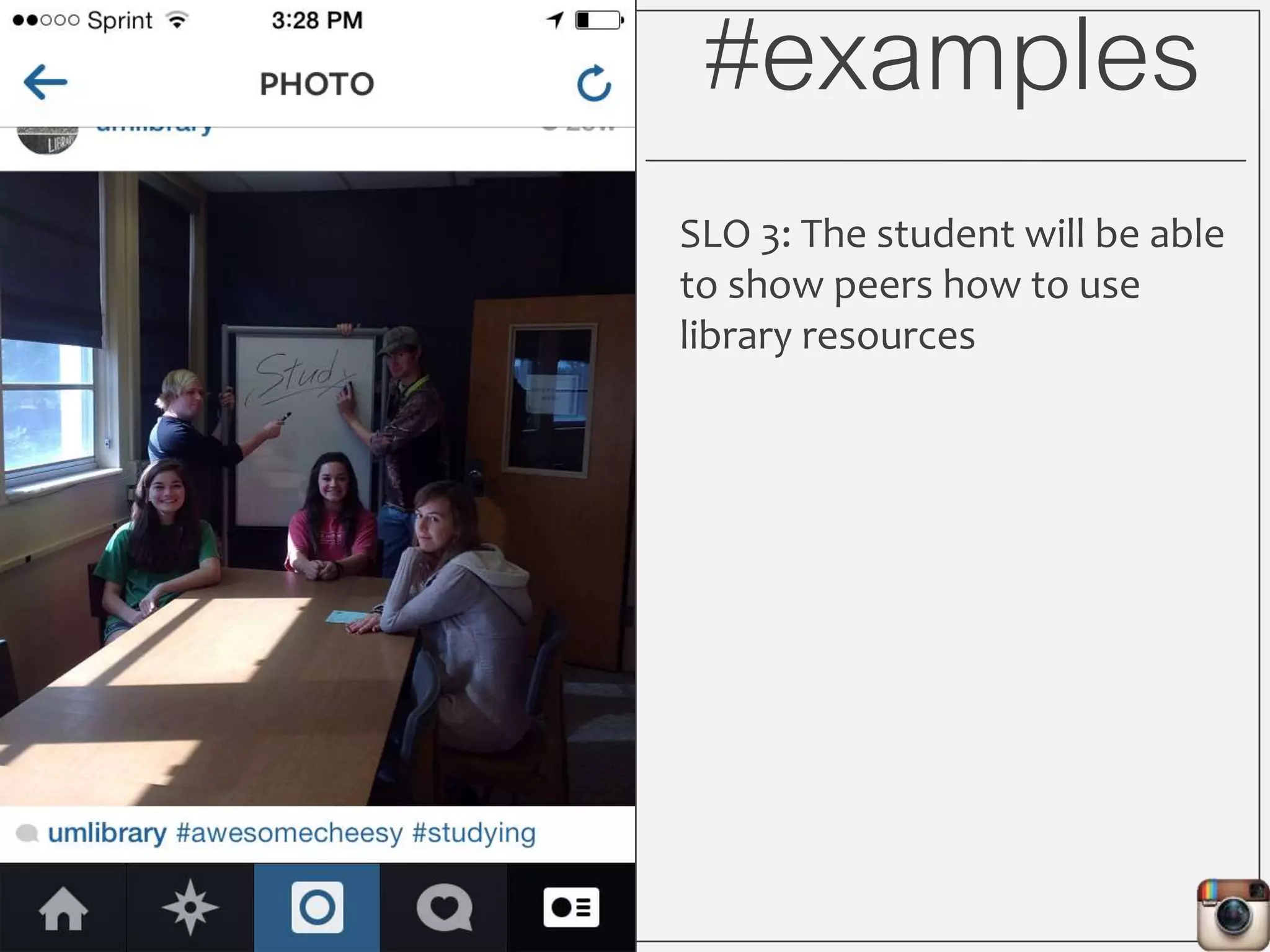
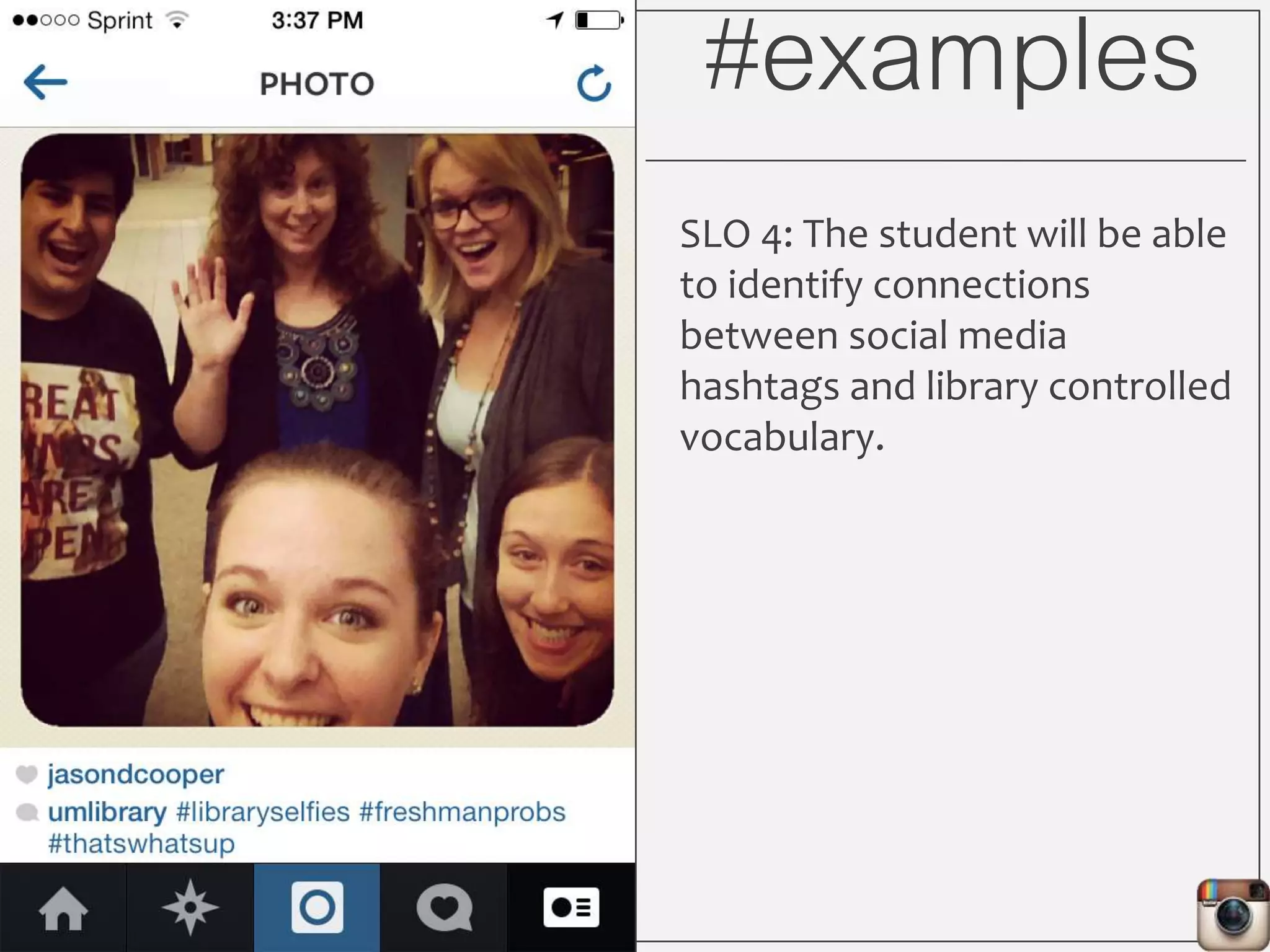
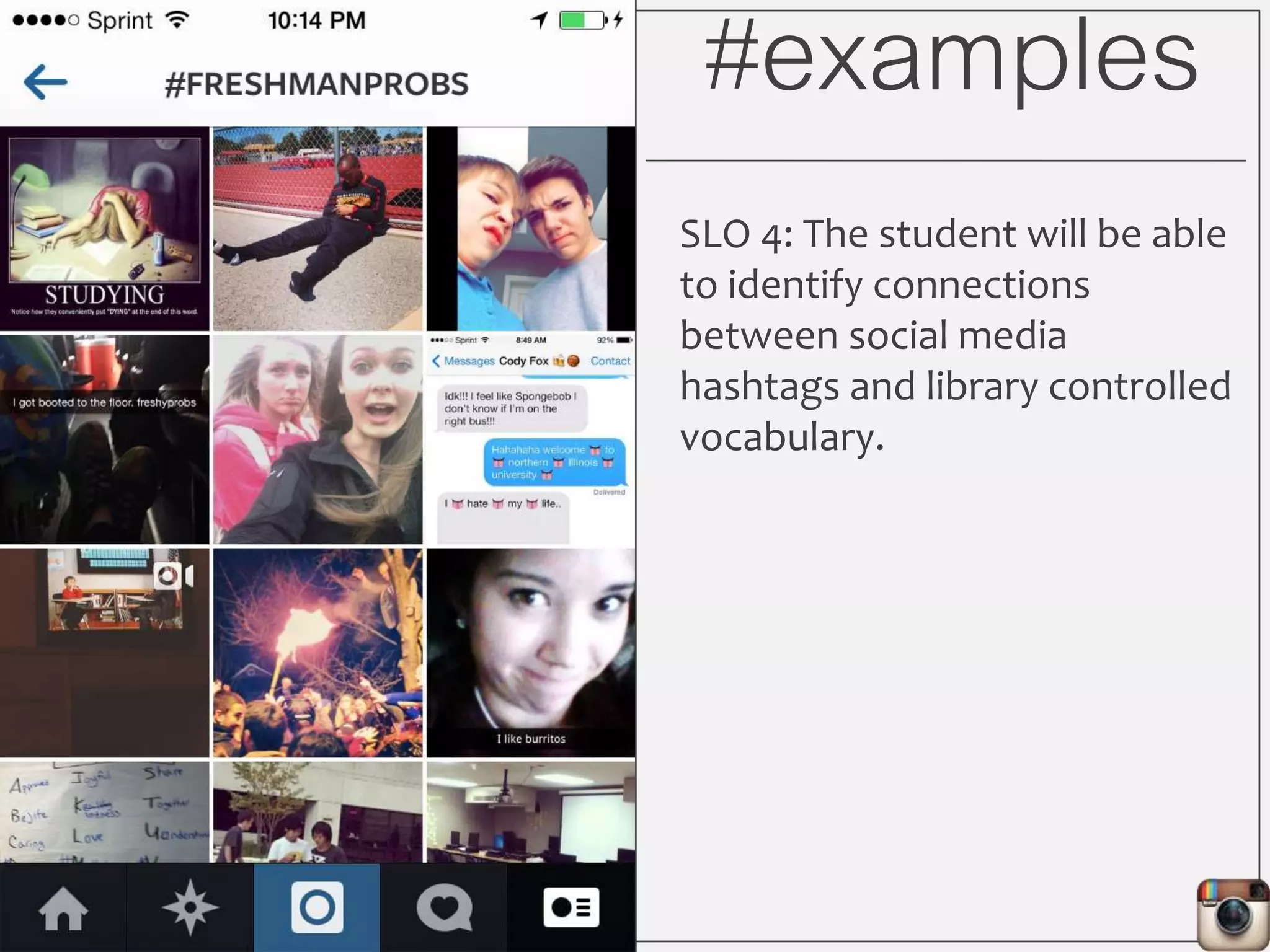
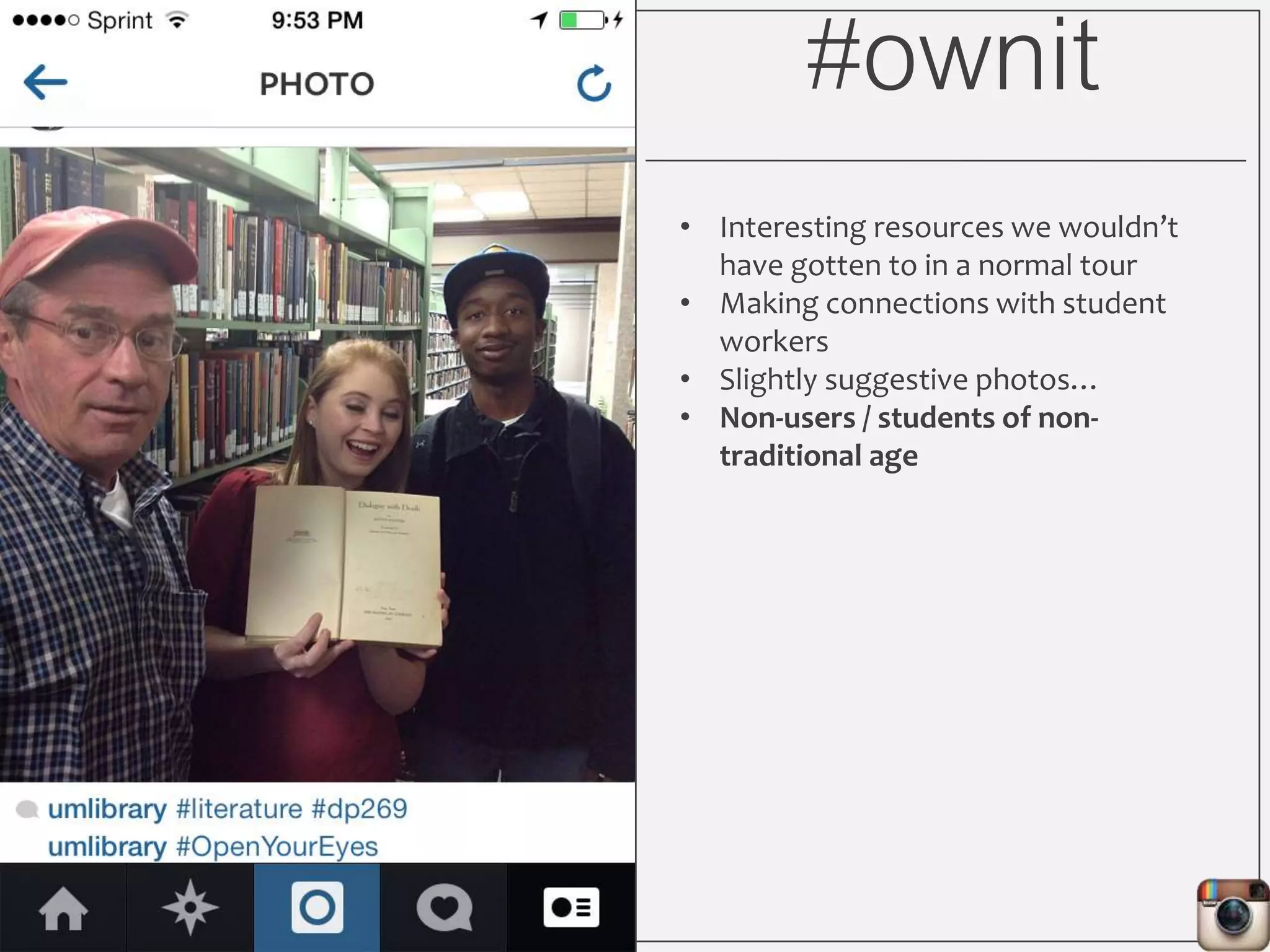
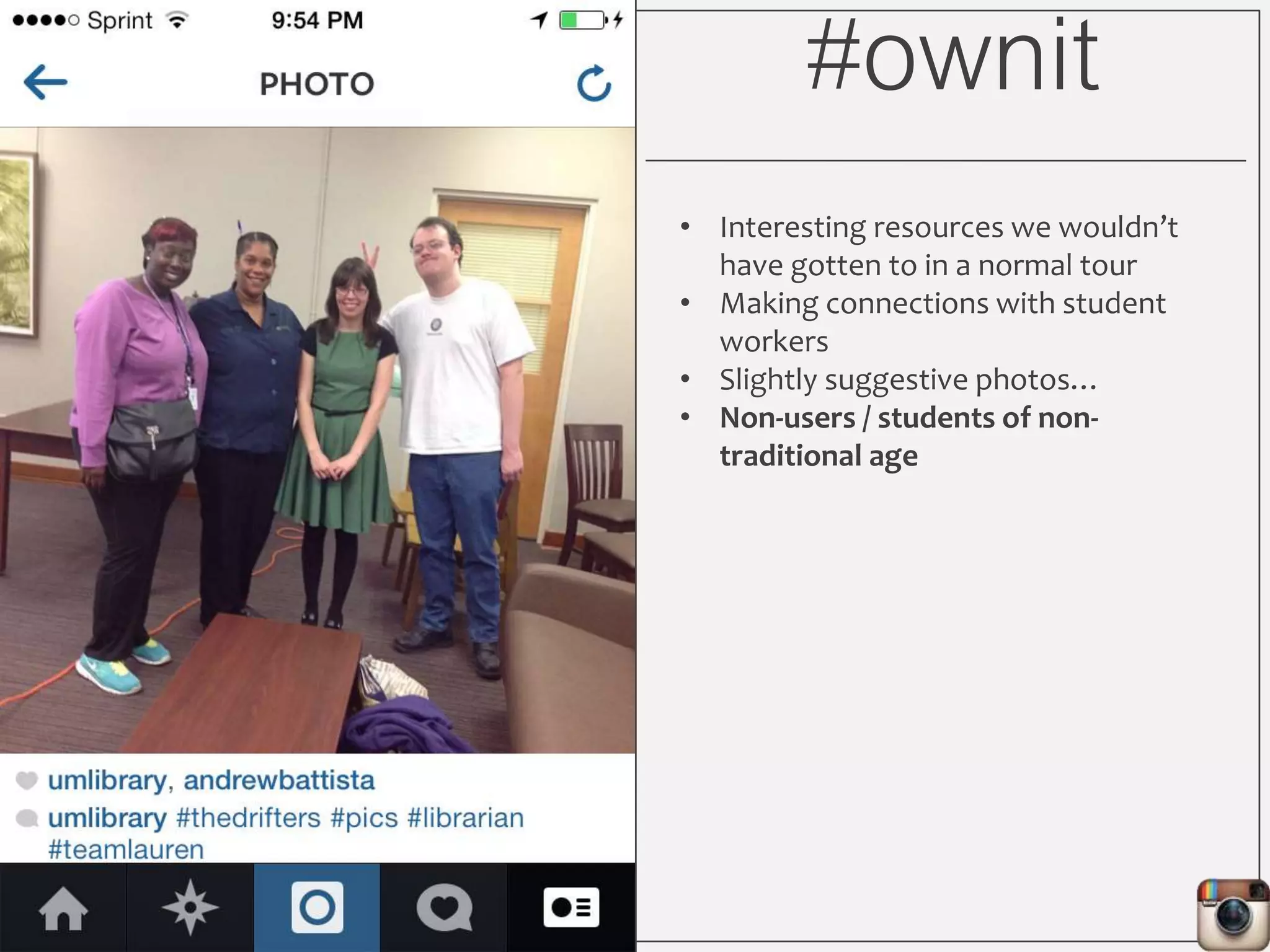
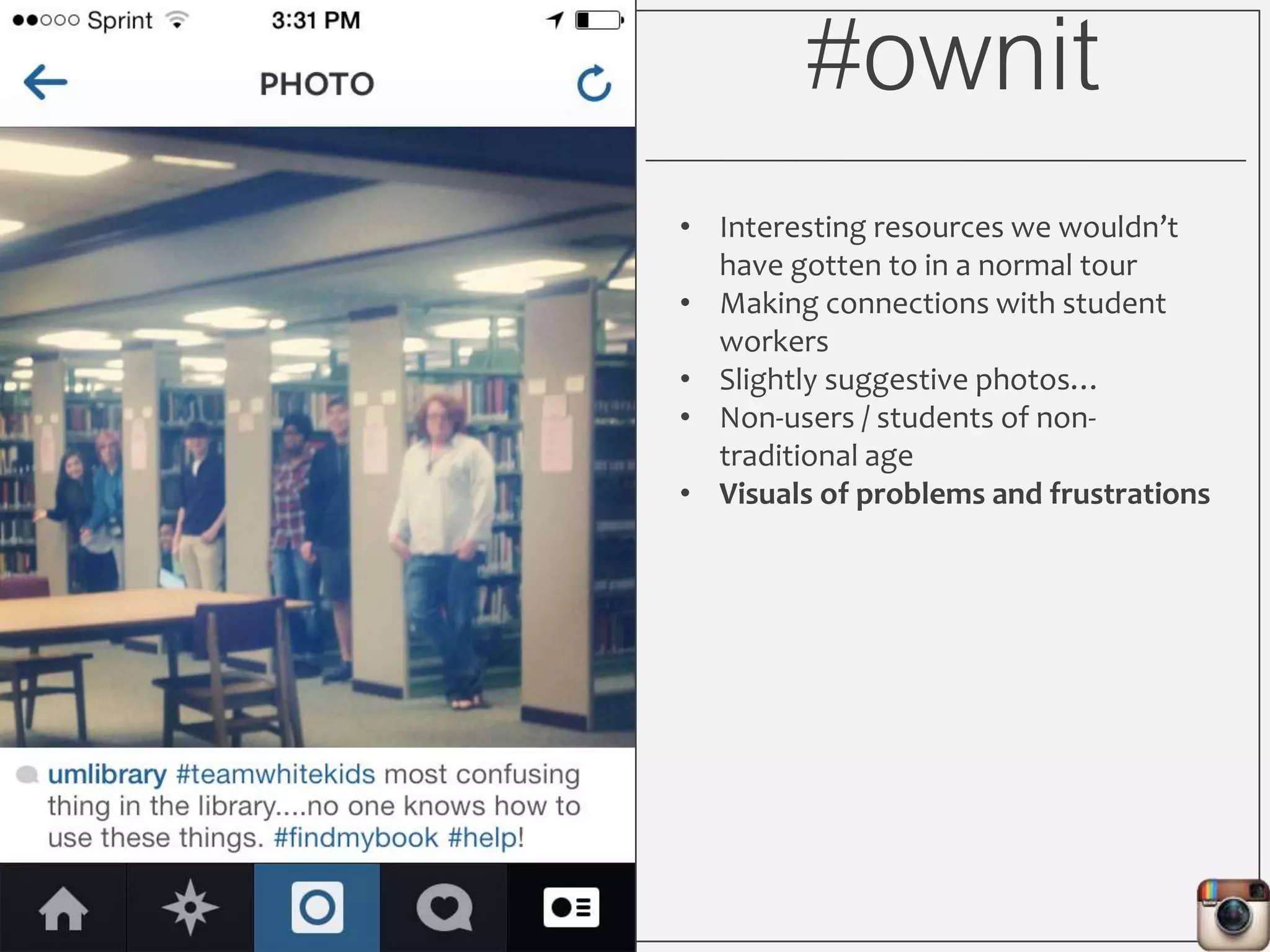
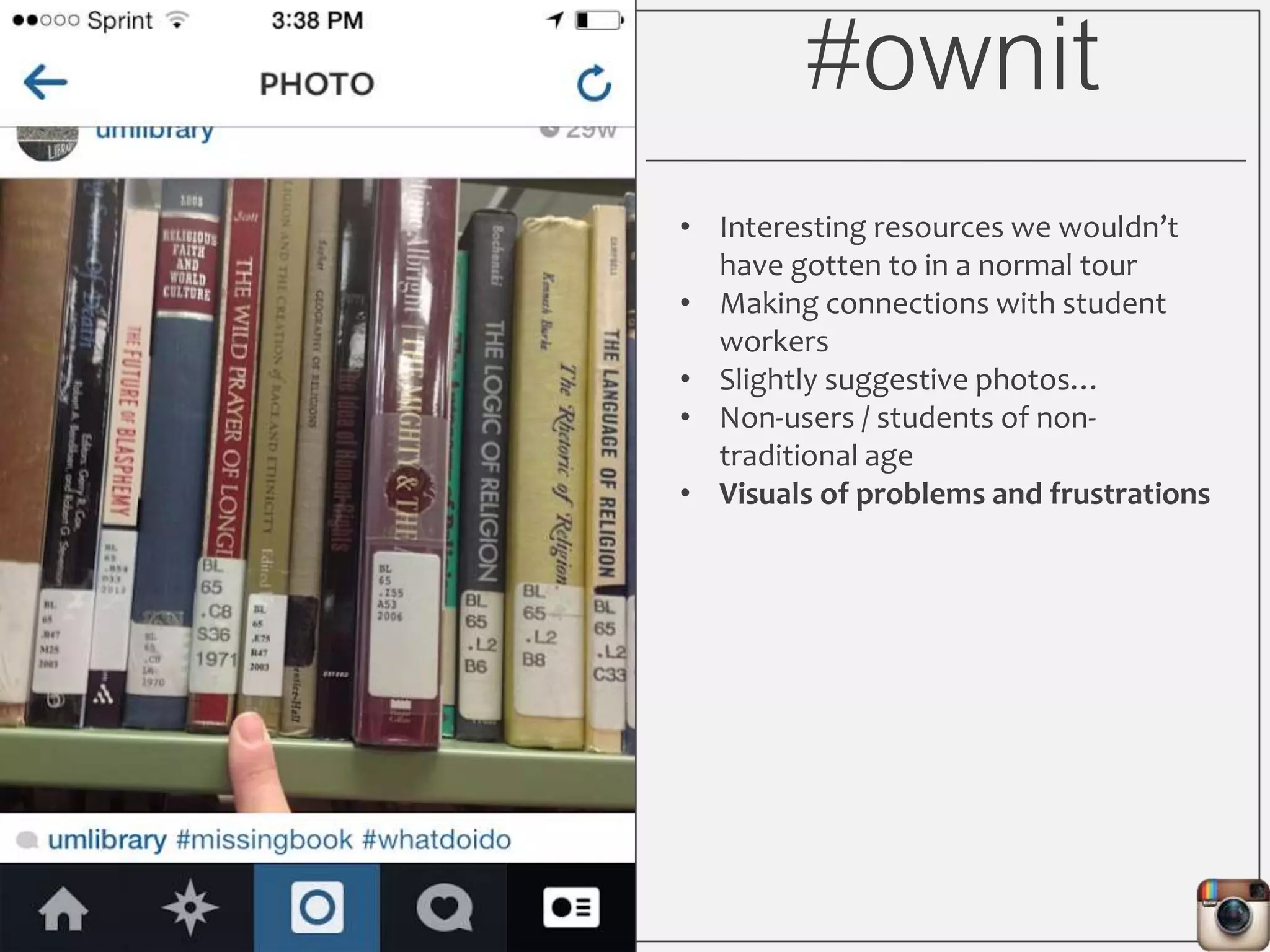
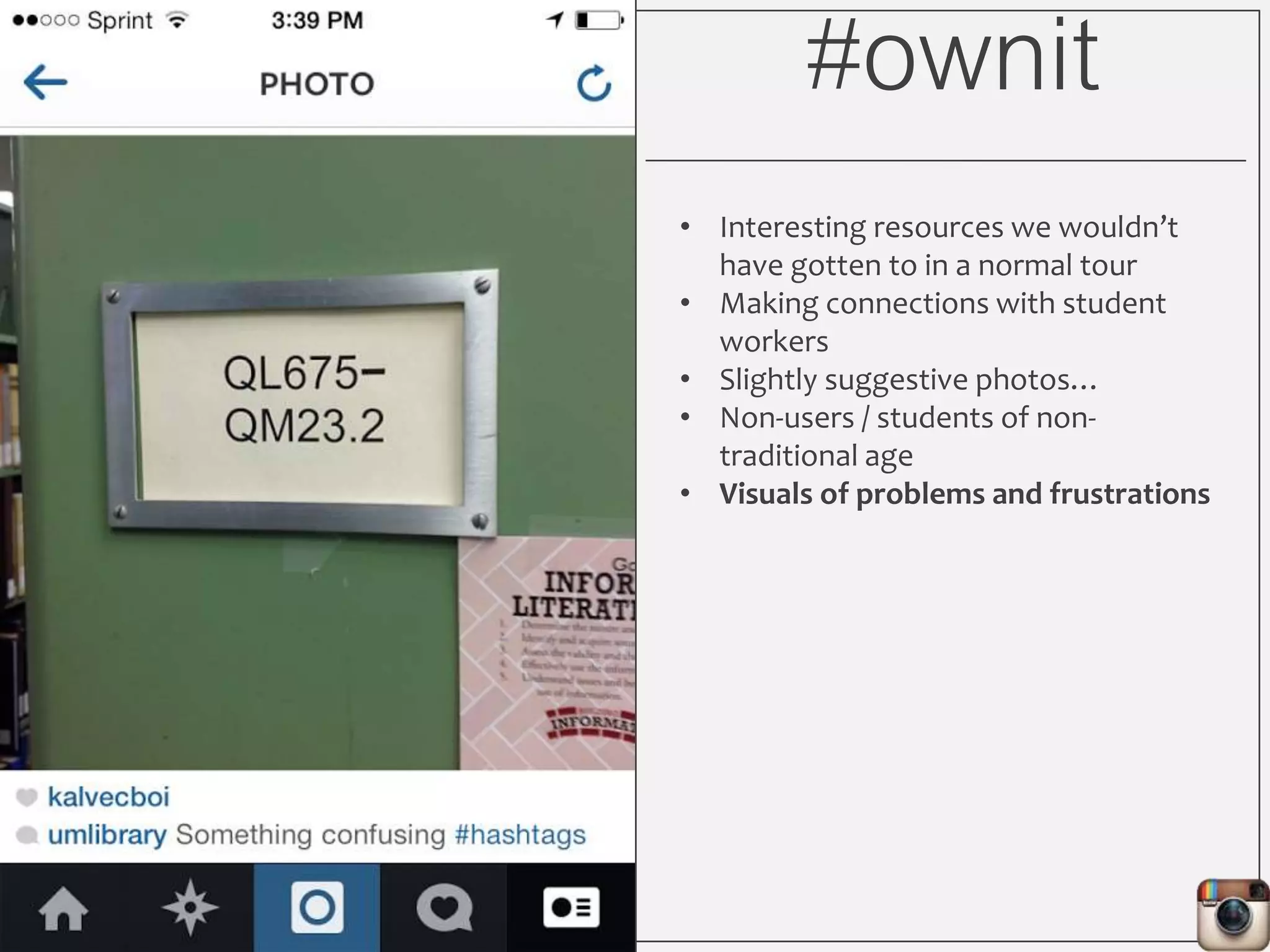
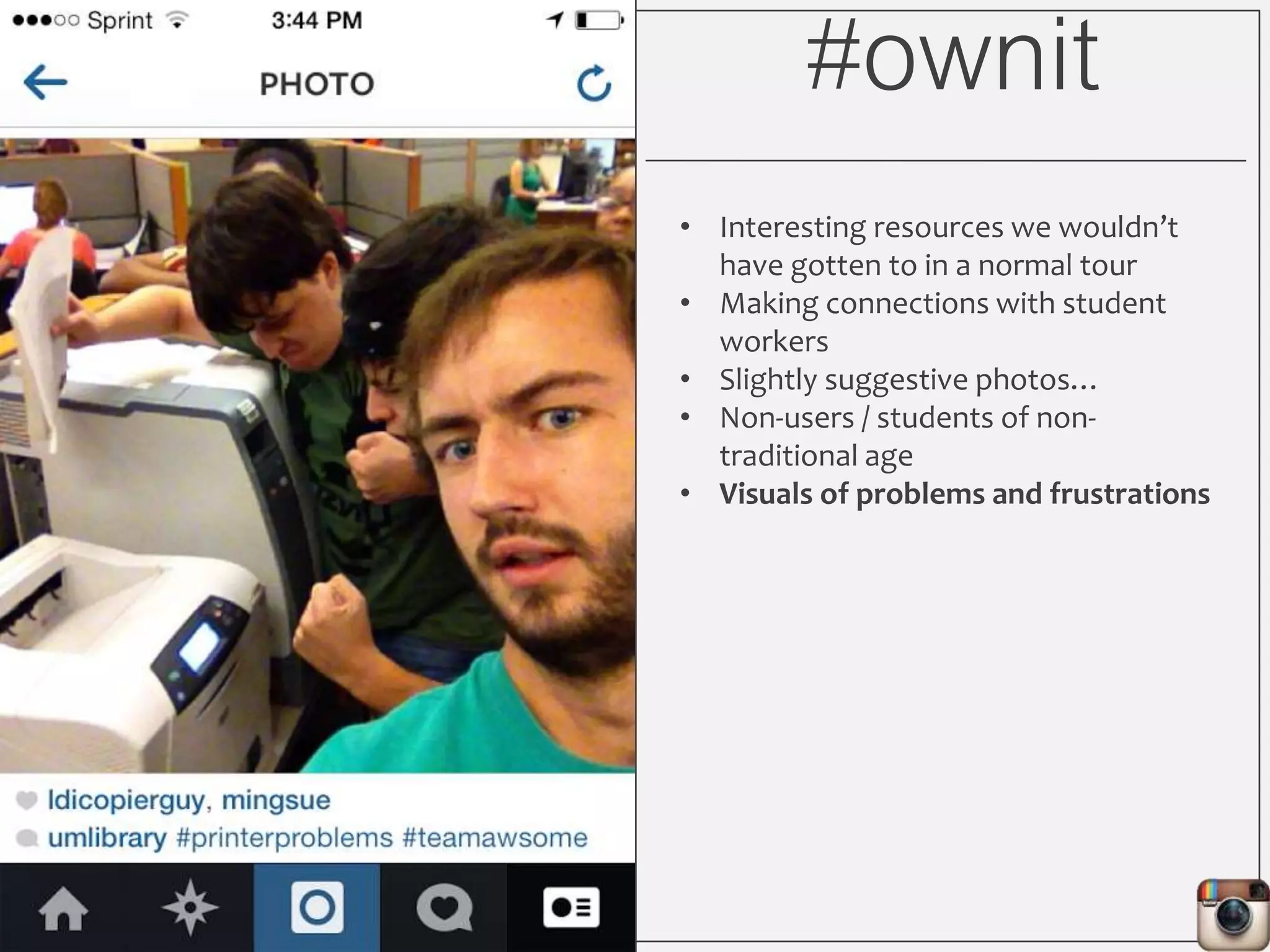
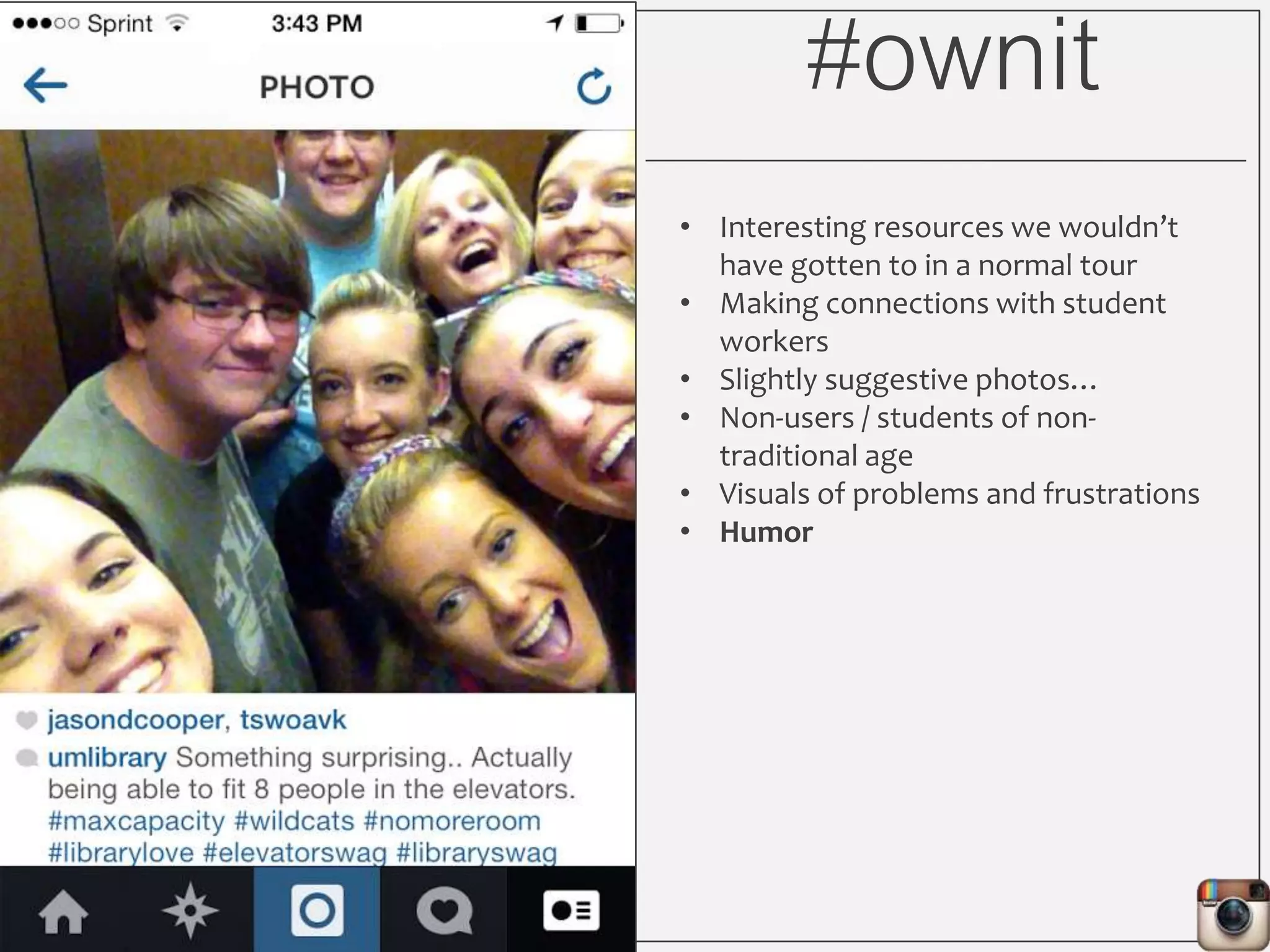
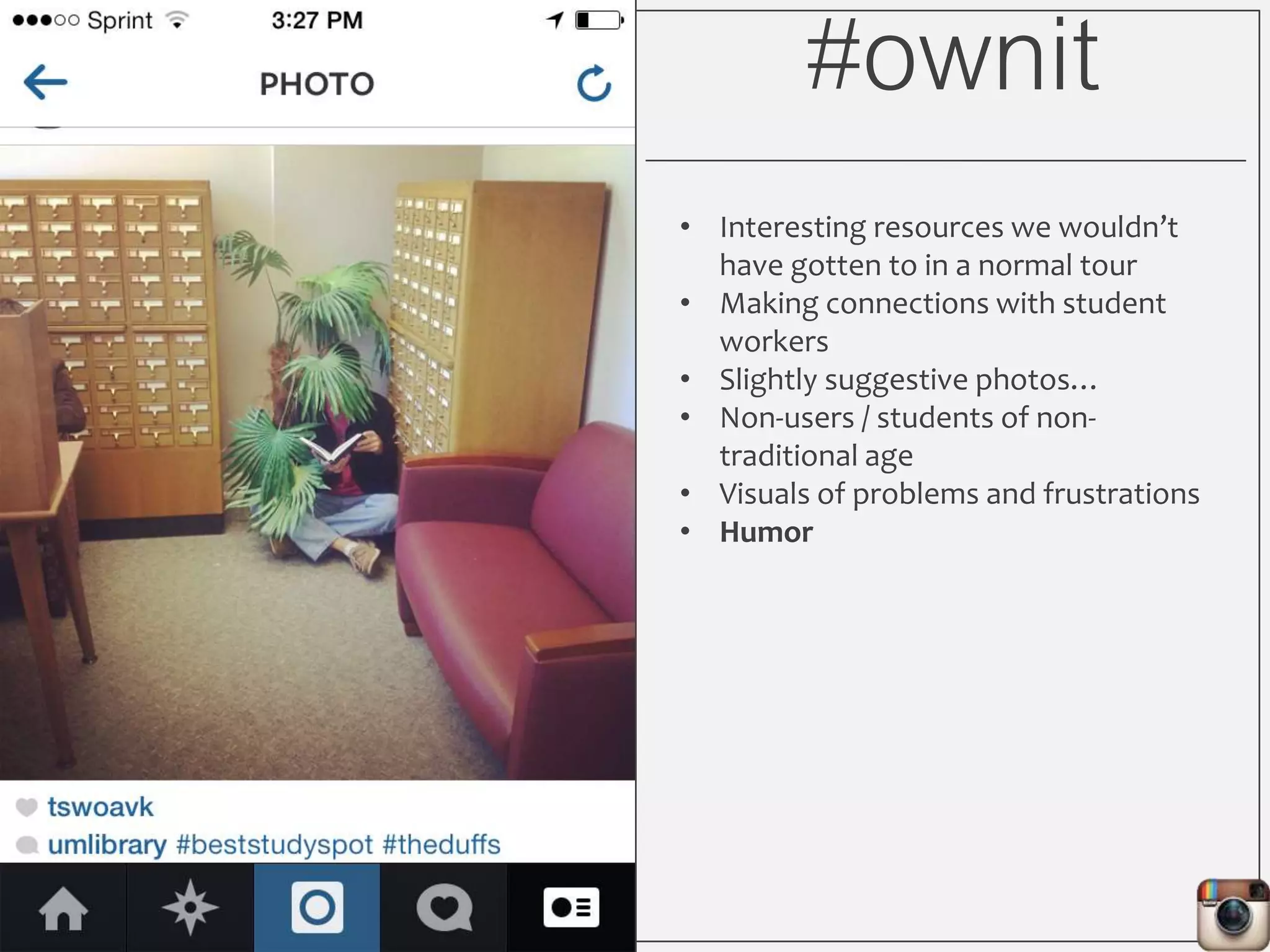
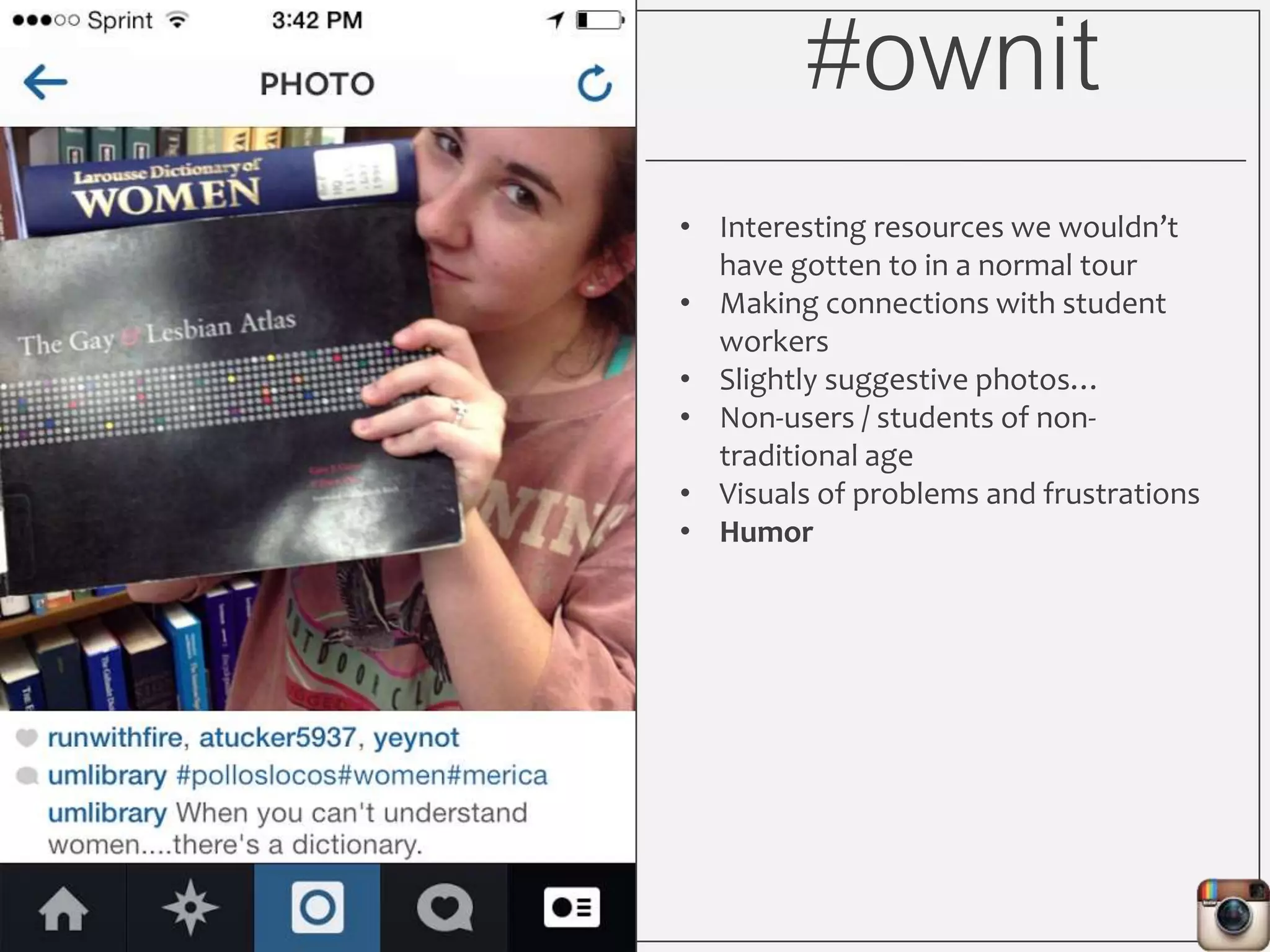
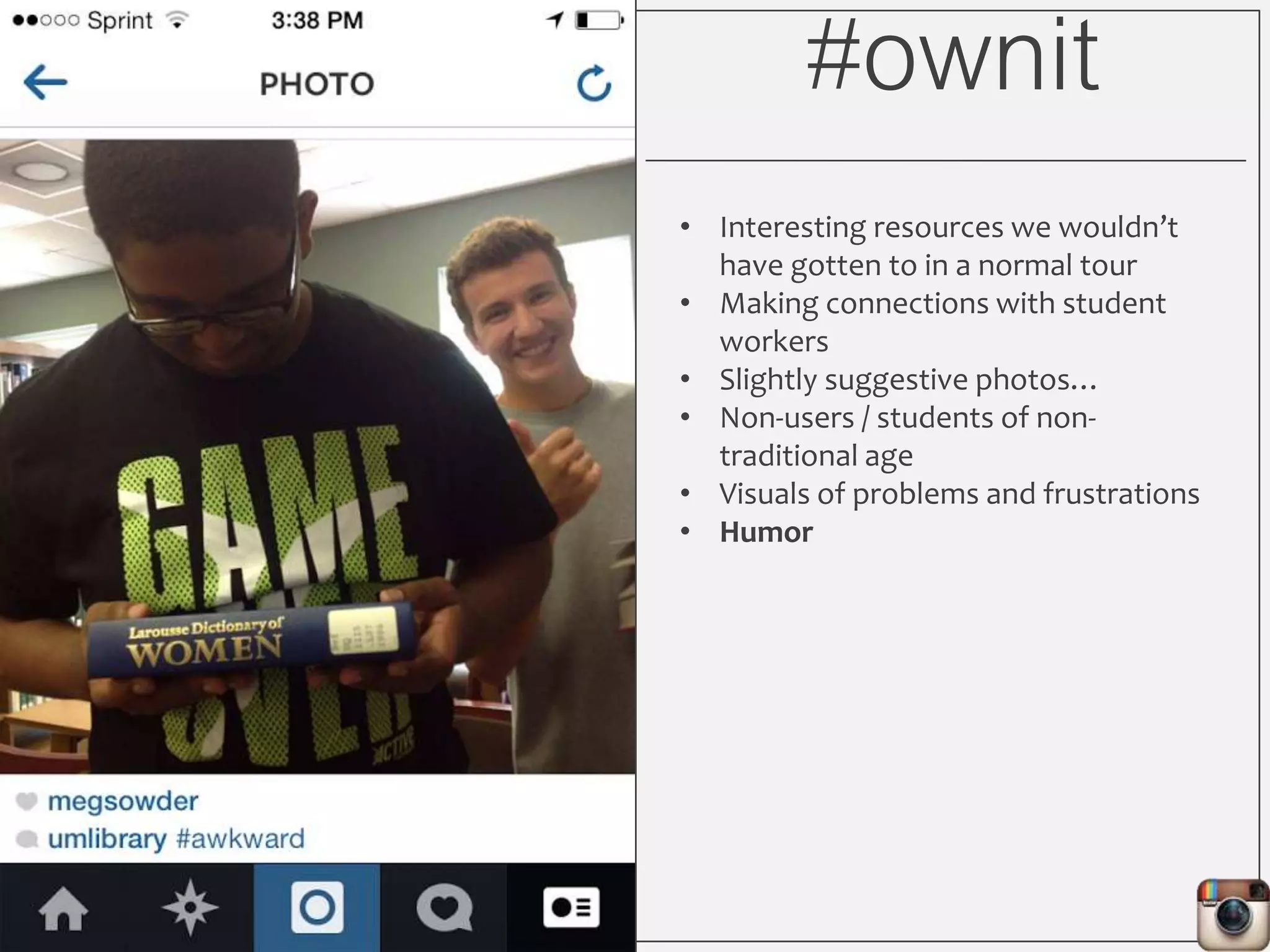
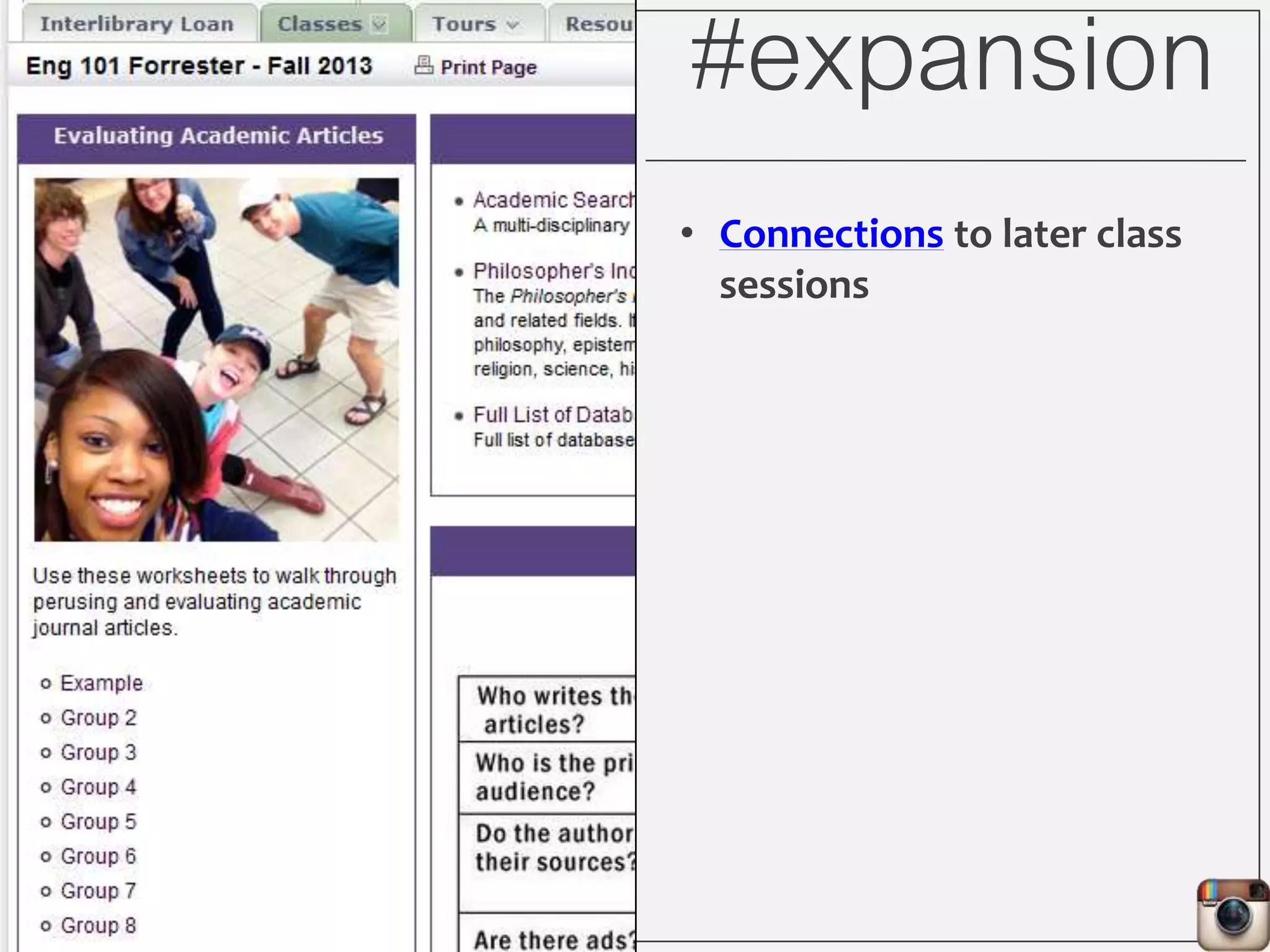
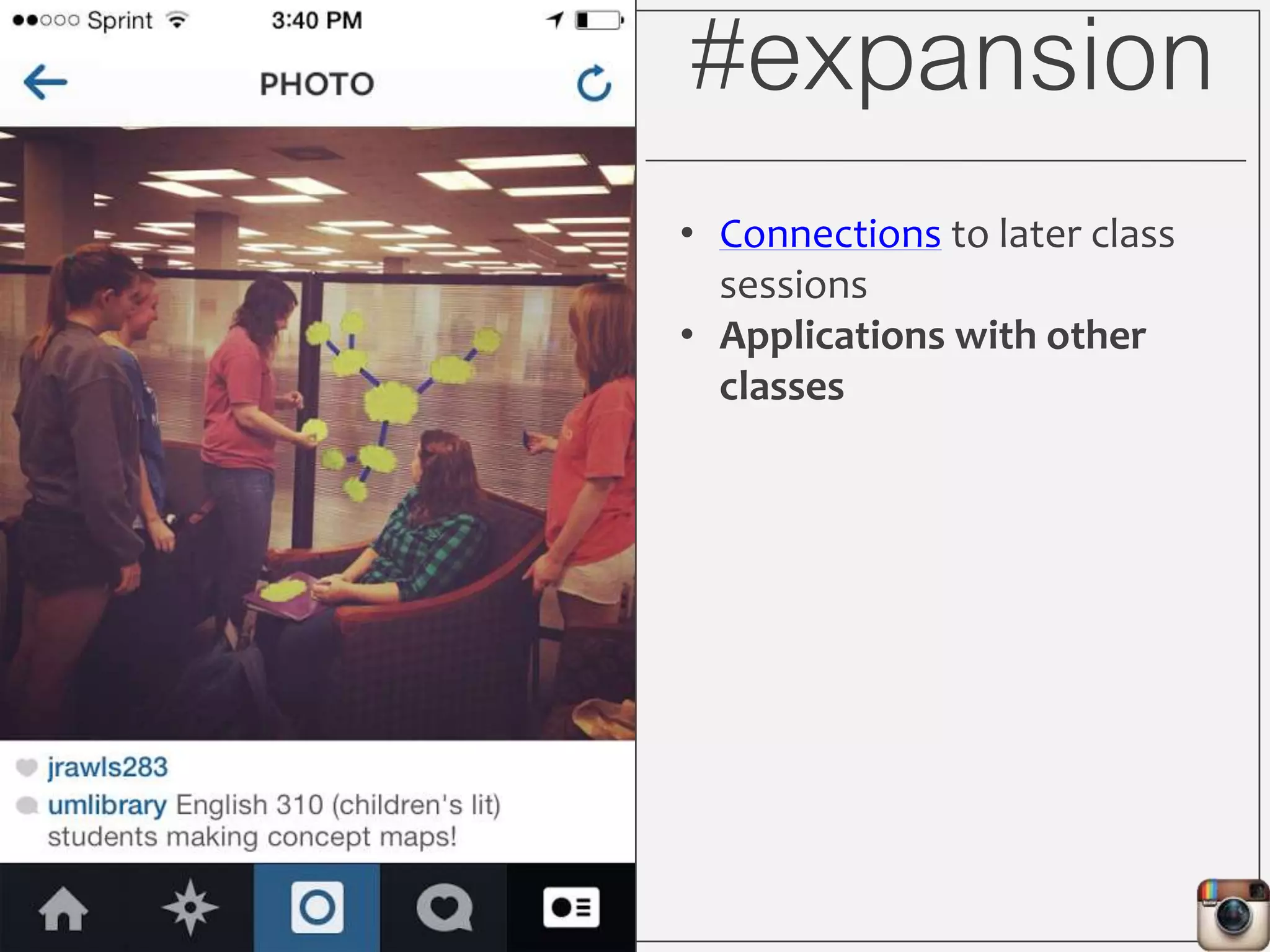
This document outlines Lauren Wallis' presentation on using Instagram for library instruction. She describes how she developed an Instagram library tour for freshman English students to make the experience fun, social, and student-guided. Wallis discusses the concepts of library anxiety, active learning, critical pedagogy, and metaliteracy that informed the project. She provides examples of student posts that addressed the learning outcomes and assessments that showed what students learned and still had questions about.