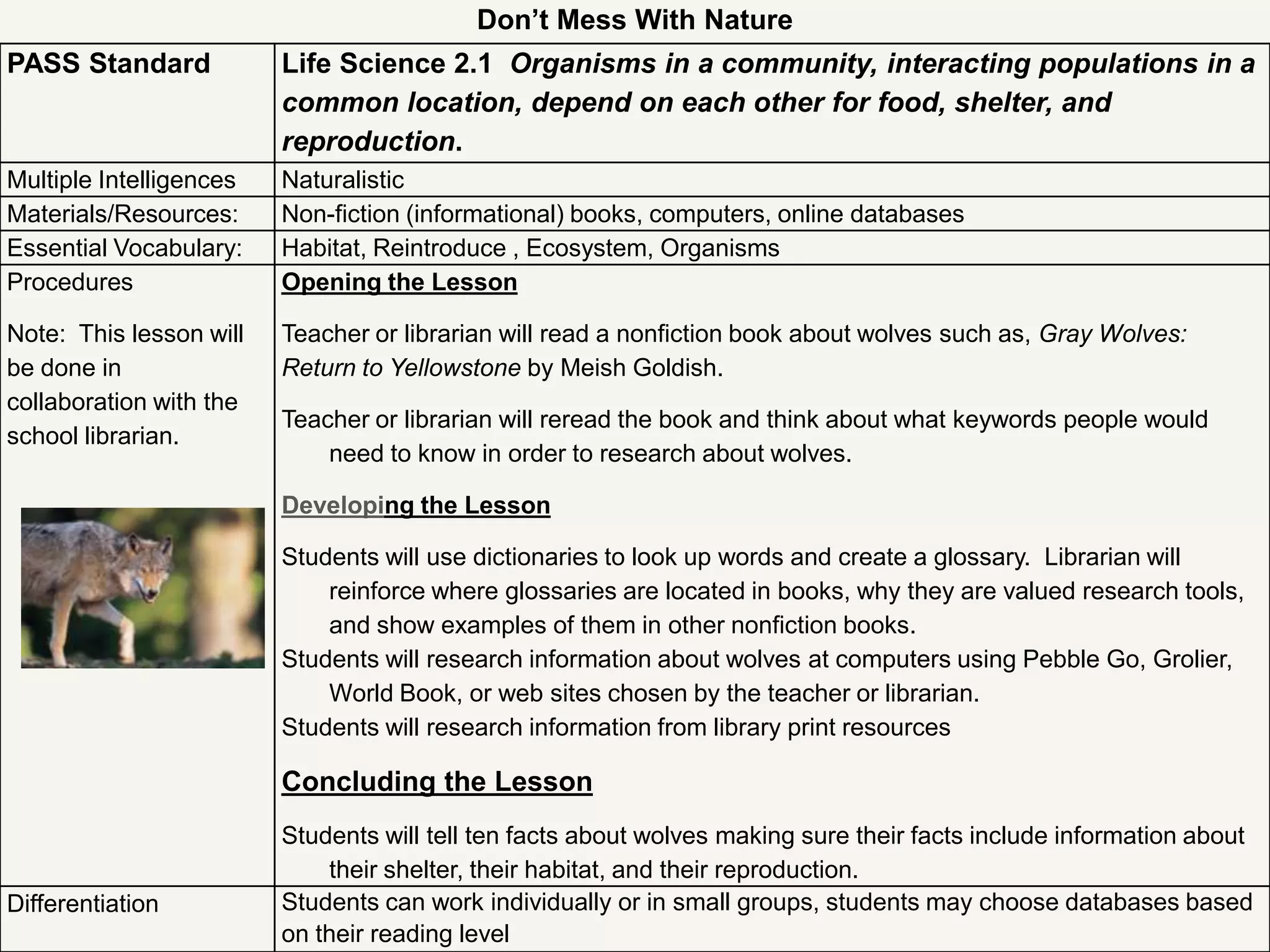
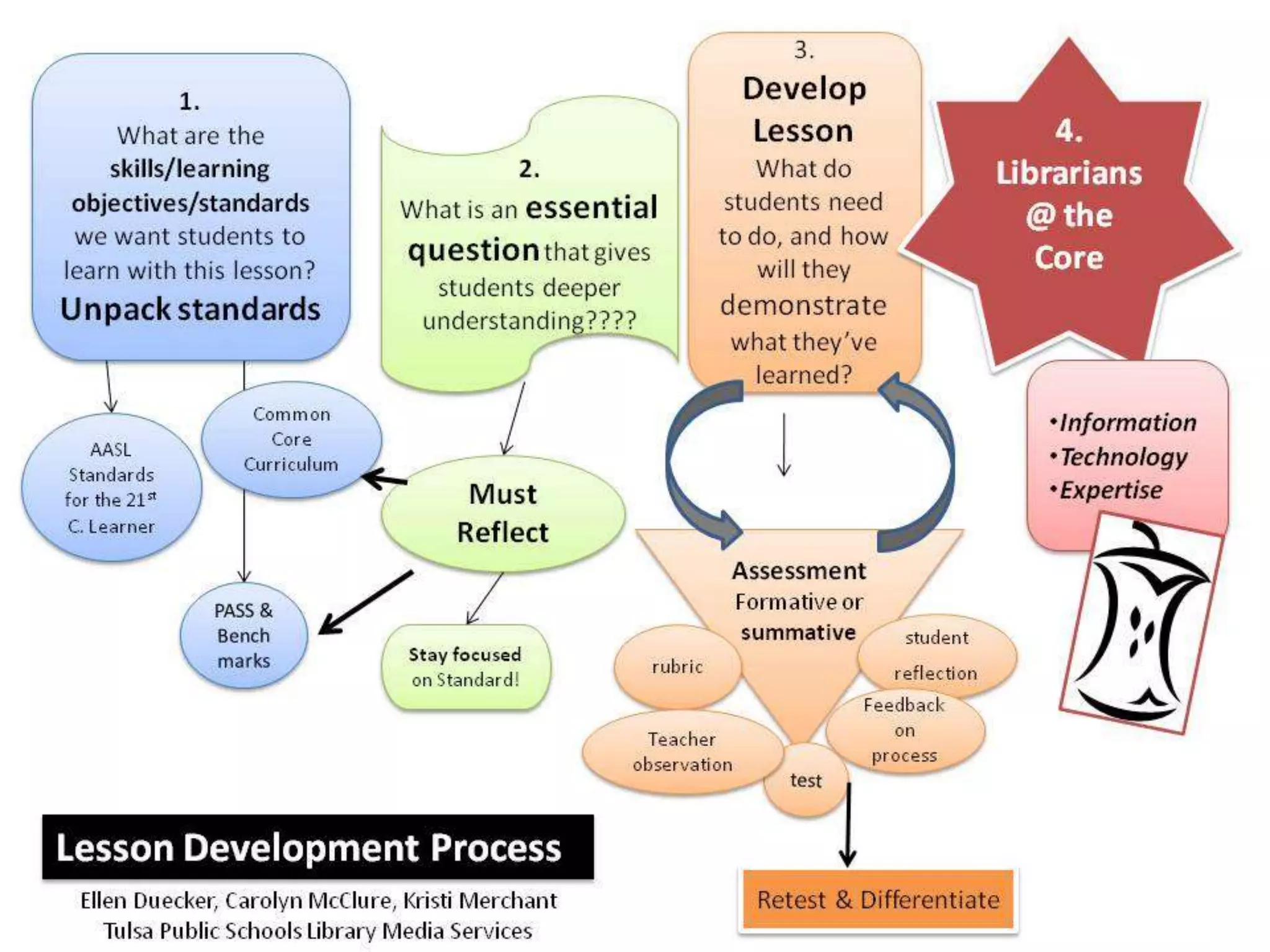
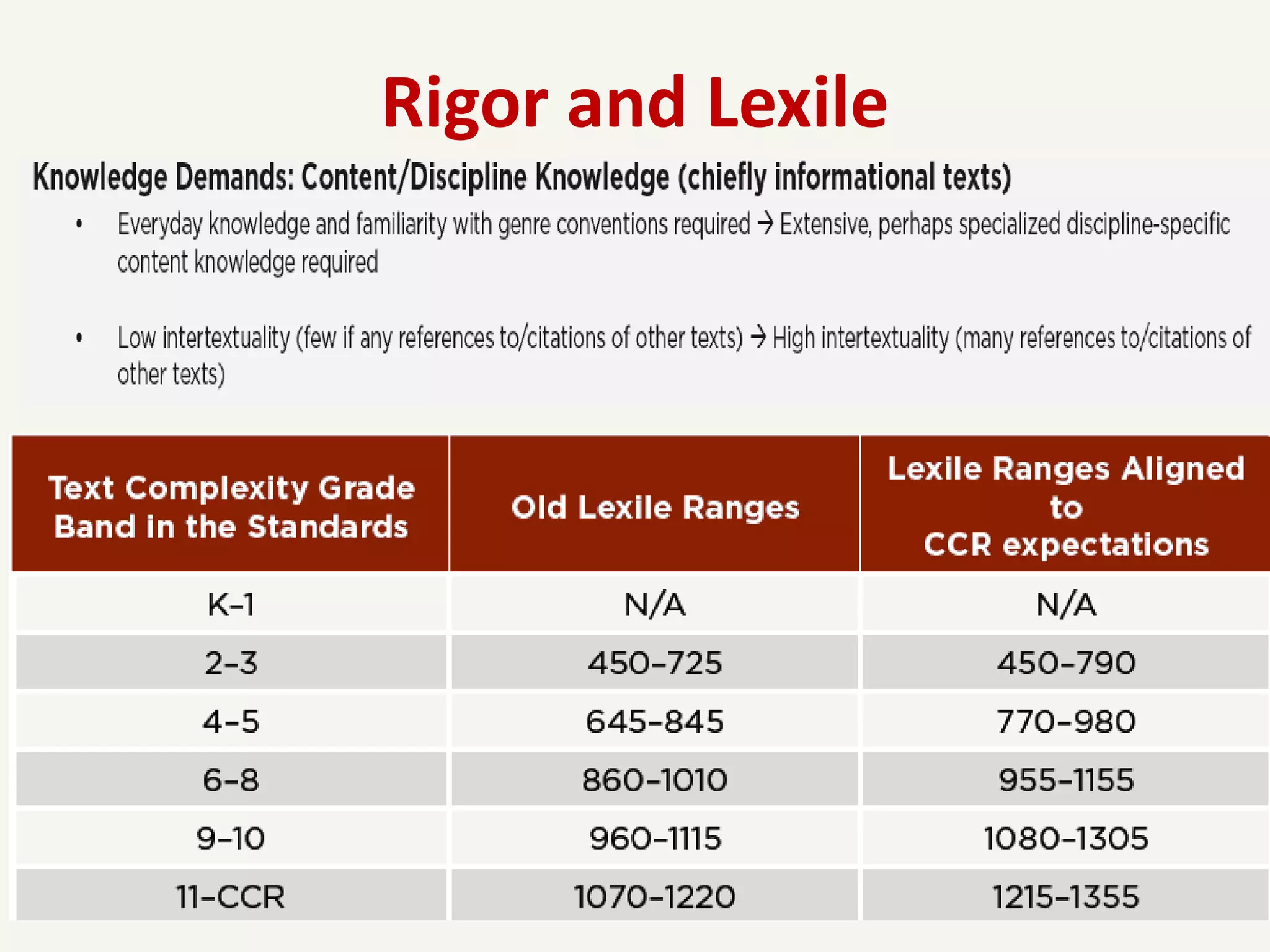
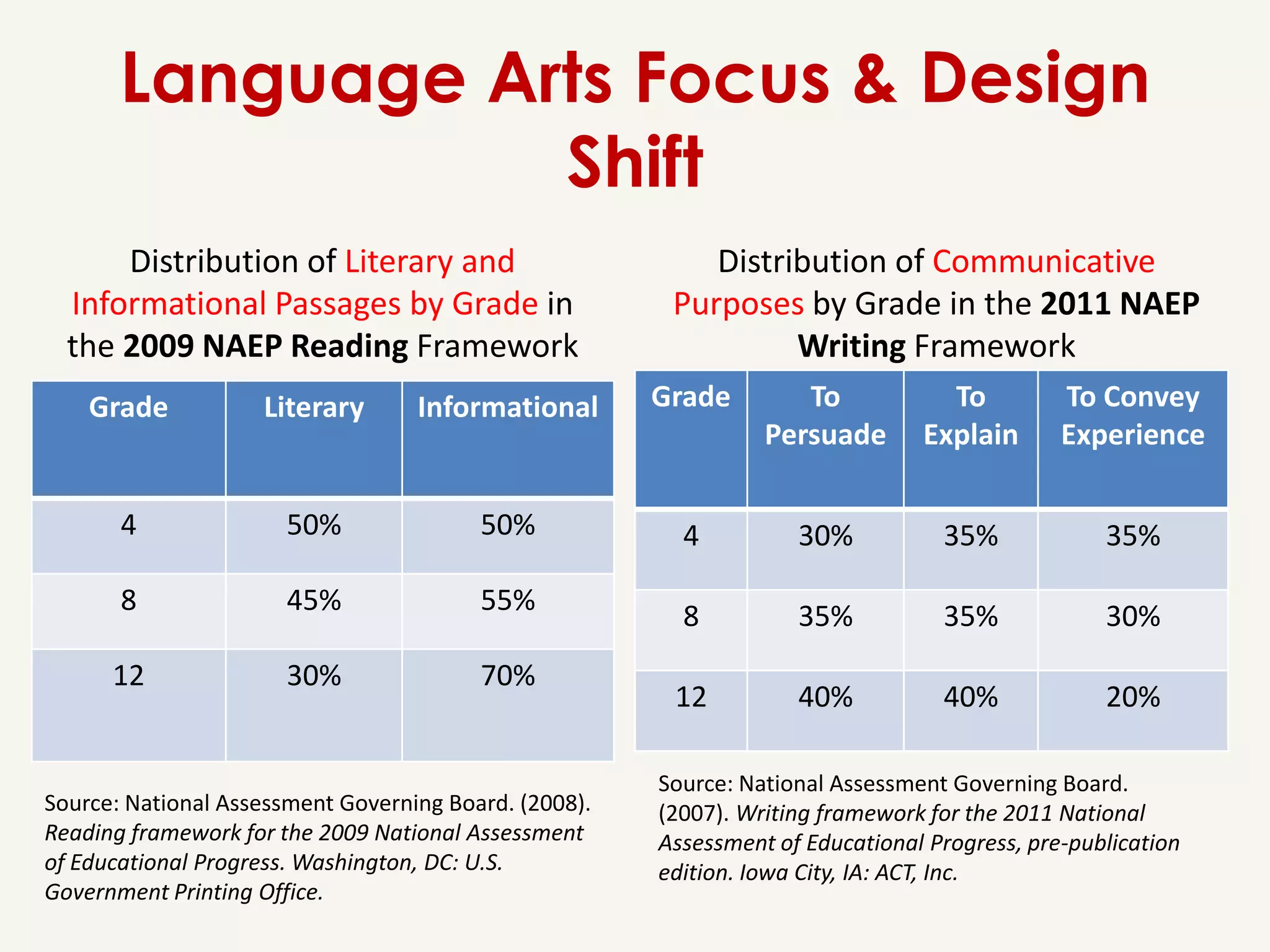
This document provides an overview of the Common Core State Standards for librarians. It begins with an introduction to the Common Core and some initial reactions people may have to it. It then discusses key aspects of the Common Core such as its focus on rigor, literacy across subject areas, and alignment of standards from kindergarten through 12th grade. The document provides examples of Common Core standards and performance tasks. It also explains how to analyze and "unwrap" the standards. Finally, it offers resources for librarians to learn more about implementing the Common Core.









![Sample CCSS Performance Task
Grade 3: Informational Texts
Students explain how the main idea that
Lincoln had “many faces” in Russell
Freedman’s Lincoln: A Photobiography is
supported by key details in the text.
[RI.3.2]
PARCC Partnership for Assessment of Readiness of
College and Careers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commoncorelibrariansencyclo-120206091517-phpapp02/75/Librarians-the-Core-12-2048.jpg)