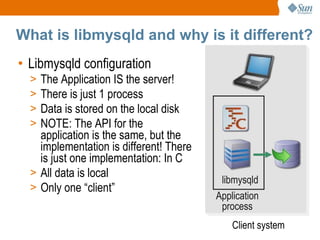
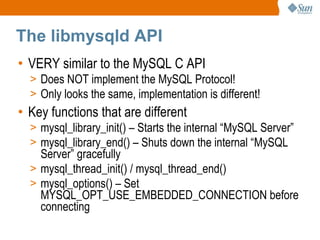
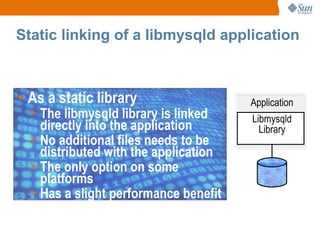
The document discusses libmysqld, a MySQL embedded database library that allows integrating a MySQL database directly into an application. It summarizes the key differences between libmysqld and the traditional MySQL client-server model, including that libmysqld runs the database within the application process rather than as a separate server process. It also provides an overview of how to initialize, configure and program with the libmysqld API, limitations compared to the traditional MySQL server, and resources for further information.






![The mysql_library_init() parameters Argument count (argc) Arguments (argv) – Like the parameters to mysqld, the first argument (as in argv[0] beging name of the program) being ignored. A list of option file sections to read If a -- defaults-file or any other argument with an option file is passed, the config files section specifies whicg sections in this file to read The last section name is NULL If no option file is passed, this argument may be NULL.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmysqldintroduction-090428040339-phpapp01/85/Libmysqld-Introduction-14-320.jpg)
![static char *server_options[] = { "mysql_test", "--datadir=C:/mydata", NULL}; static char *server_groups[] = { "libmysqld_server", NULL}; int main(argc, argv) { MYSQL mysql; mysql_library_init(sizeof(server_options)/ sizeof(char *) – 1, server_options, (char **) server_gropus); mysql = mysql_init(NULL); mysql_options(mysql, MYSQL_OPT_USE_EMBEDDED_CONNECTION, NULL); mysql_real_connect(mysql, NULL, NULL, NULL, "test", 0, NULL, 0); Initializing a libmysqld application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmysqldintroduction-090428040339-phpapp01/85/Libmysqld-Introduction-15-320.jpg)





![Resources and contacts Email me at: [email_address] Read my blog at: http://karlssonondatabases.blogspot.com/ MySQL Forum for Embedded systems: http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?58 Contribute to the community with samples and ideas, we need more of those for libmysqld http://forge.mysql.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmysqldintroduction-090428040339-phpapp01/85/Libmysqld-Introduction-26-320.jpg)
![Questions? [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmysqldintroduction-090428040339-phpapp01/85/Libmysqld-Introduction-27-320.jpg)