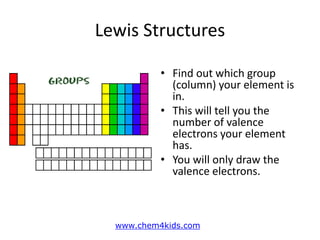
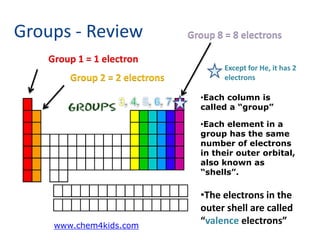
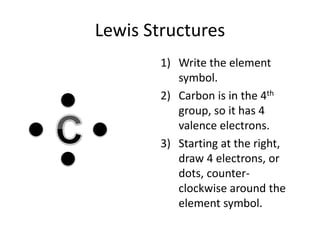
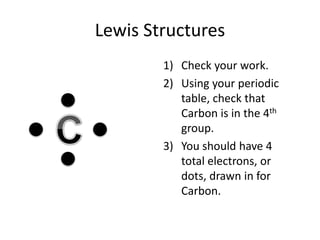
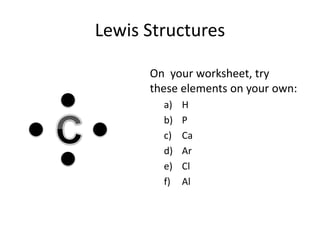
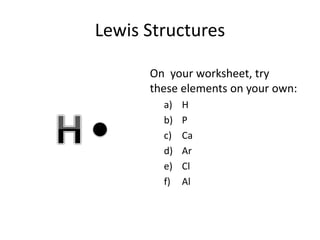
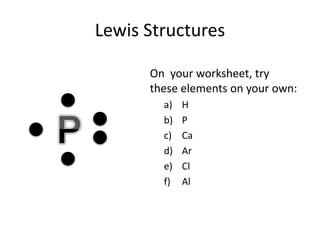
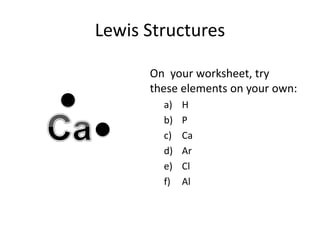
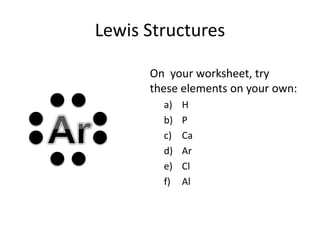
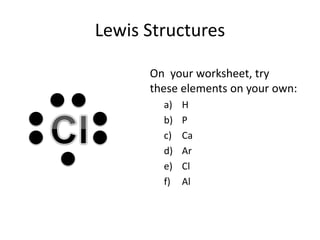
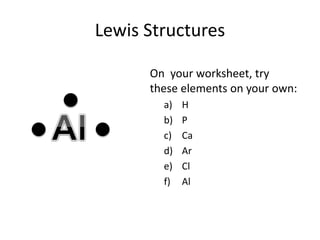
This document explains Lewis dot structures, a method developed by G.N. Lewis for representing valence electrons in atoms to predict bonding. It highlights the importance of valence electrons and the octet rule in forming stable compounds. The document also provides steps for drawing Lewis structures and includes practice elements for readers.