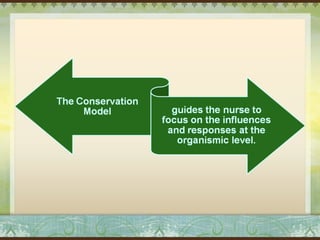
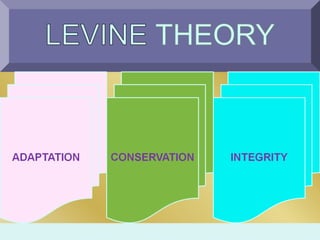
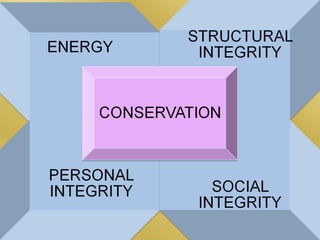
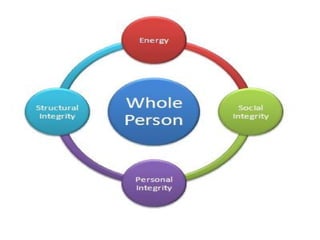
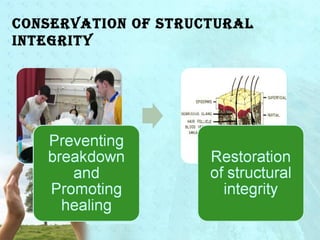
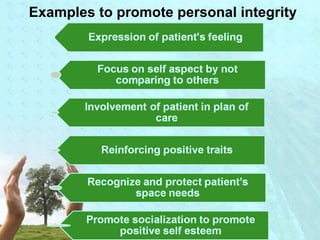
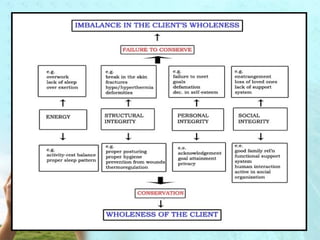
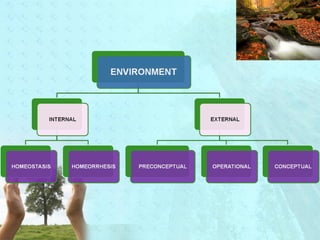
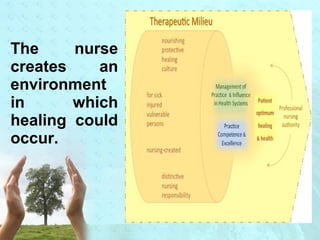
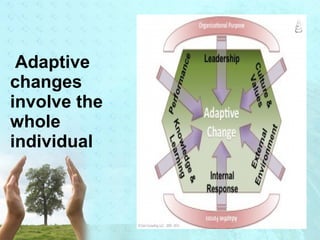
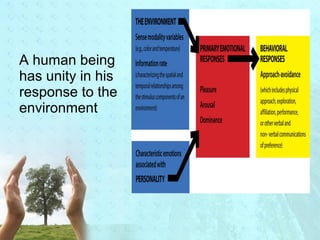
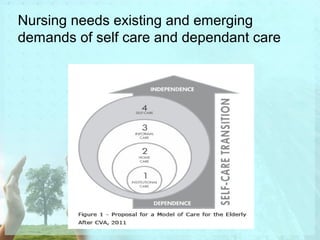
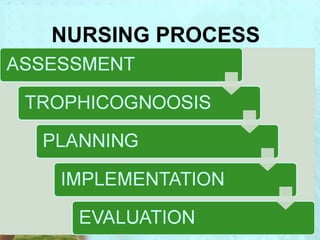
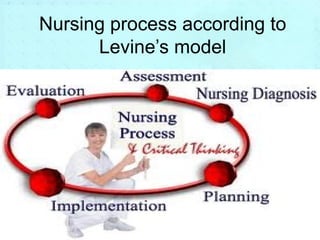
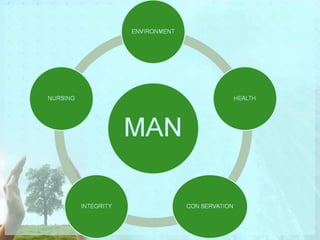
Myra Levine's conservation model of nursing focuses on helping patients adapt to stressors through four principles: conservation of energy, structural integrity, personal integrity, and social integrity. The nursing process involves comprehensive assessment of challenges in these areas, developing a care plan to address needs, implementing interventions, and evaluating responses. Key concepts are that humans strive for wholeness through orderly adaptation to environmental changes and the nurse's role is to create an environment facilitating healing.