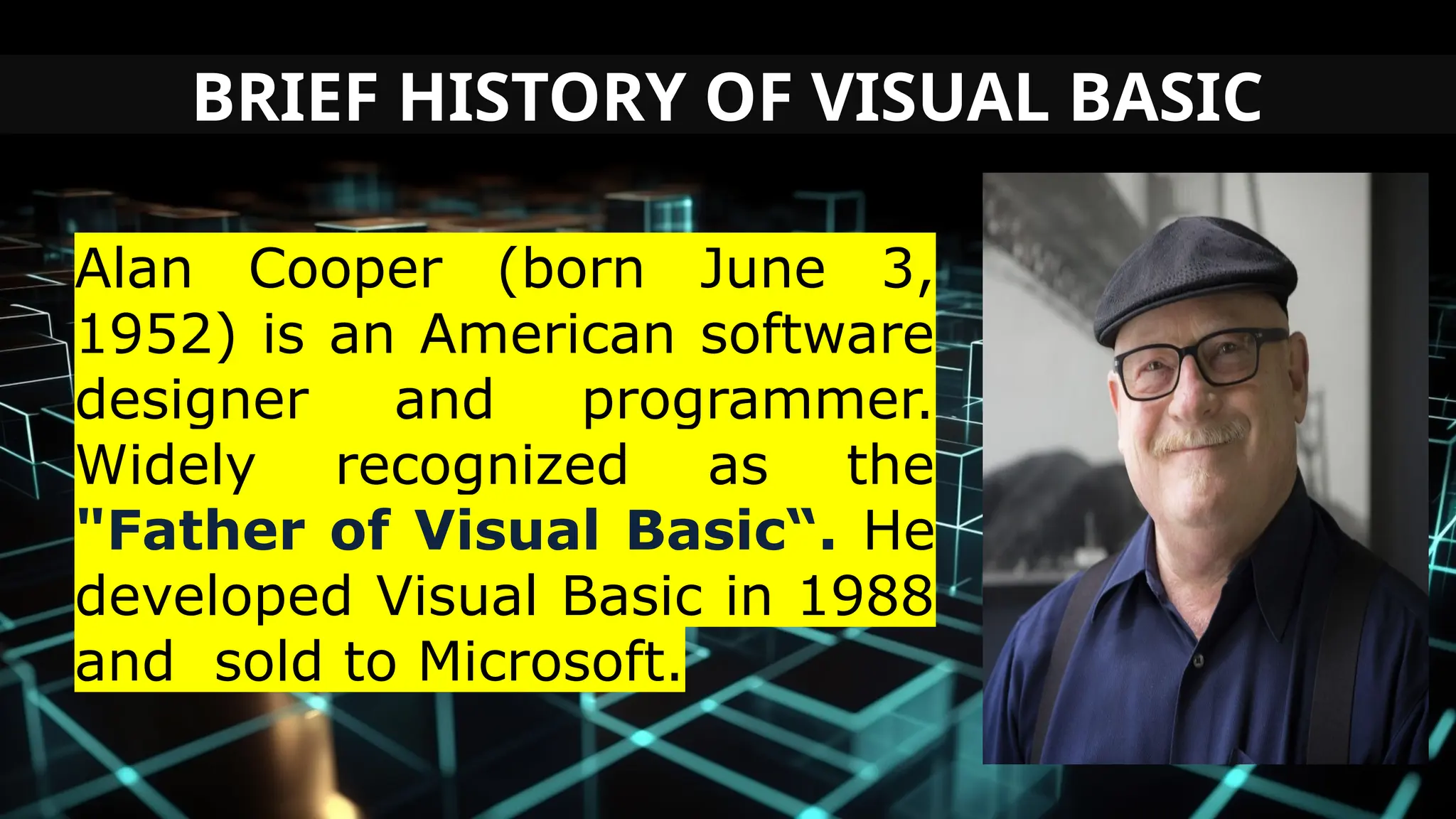
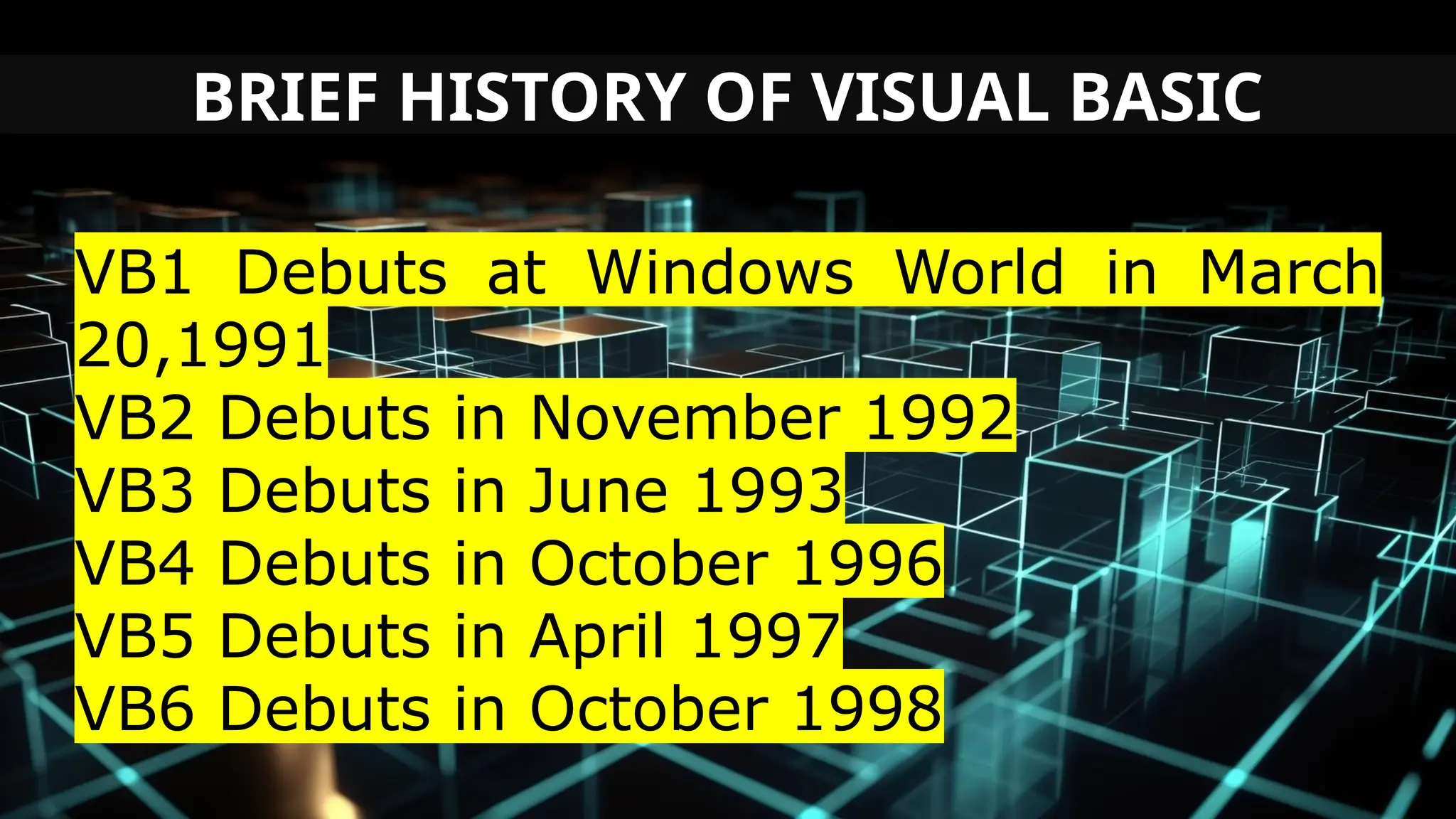
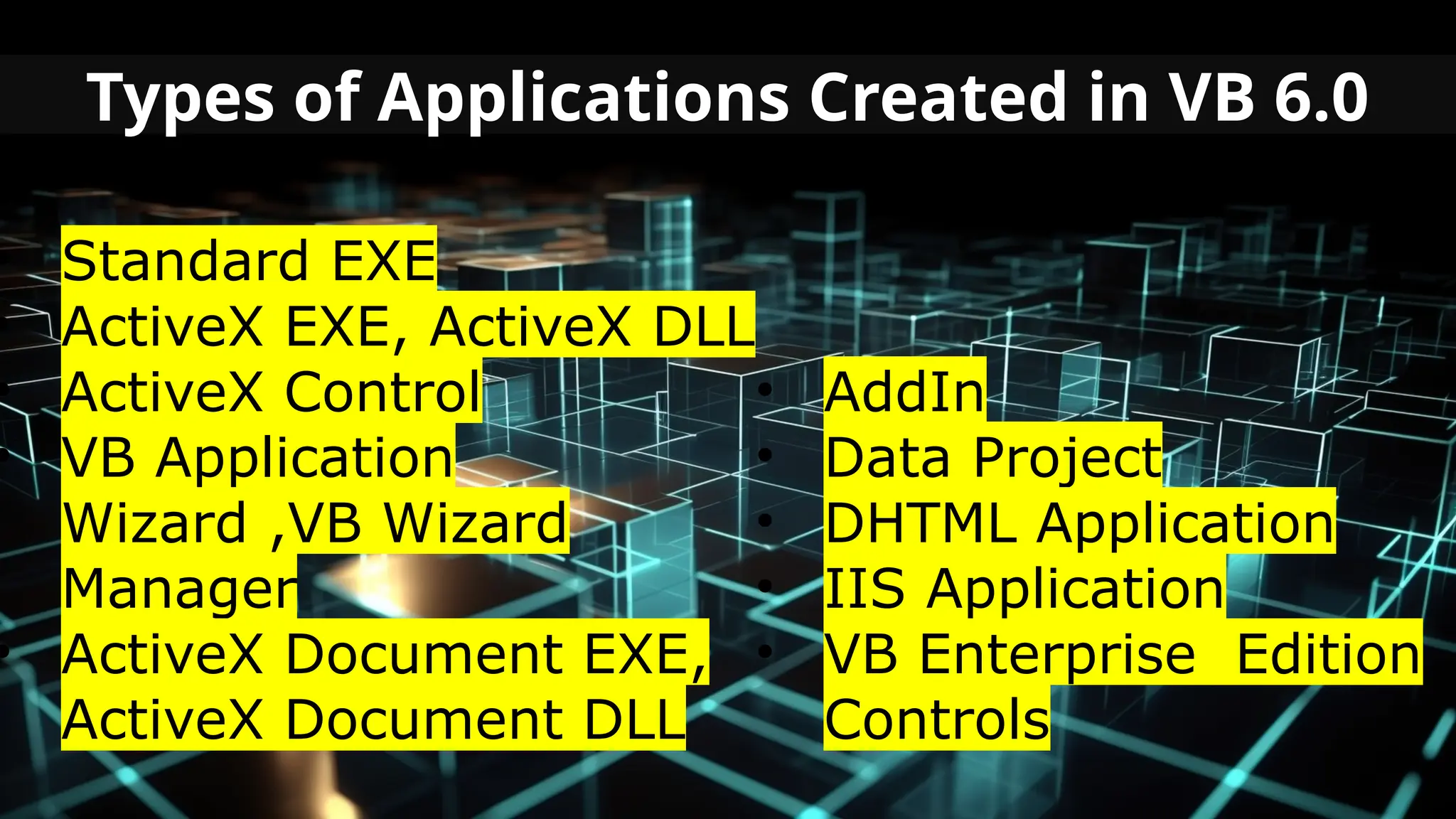
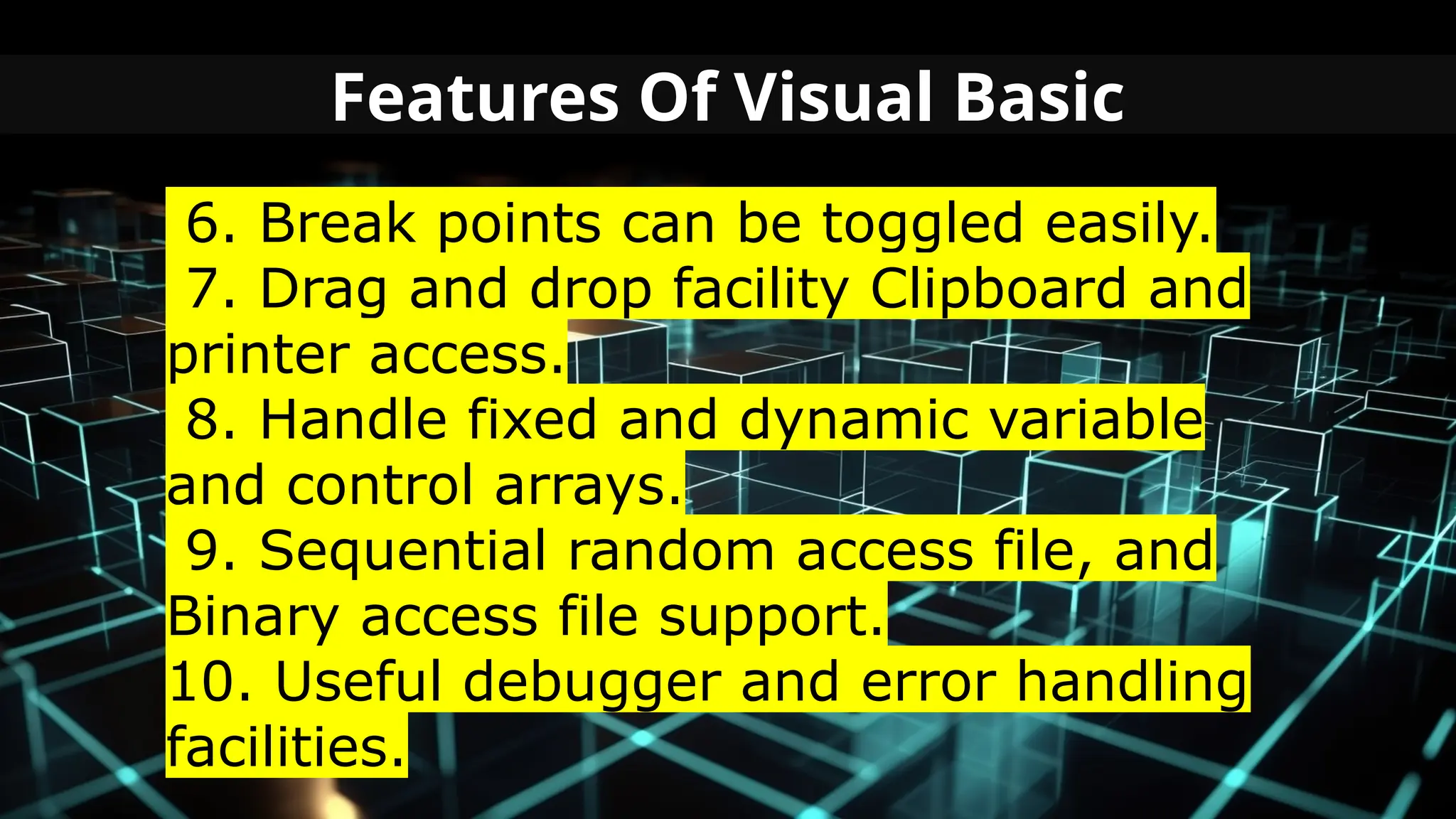
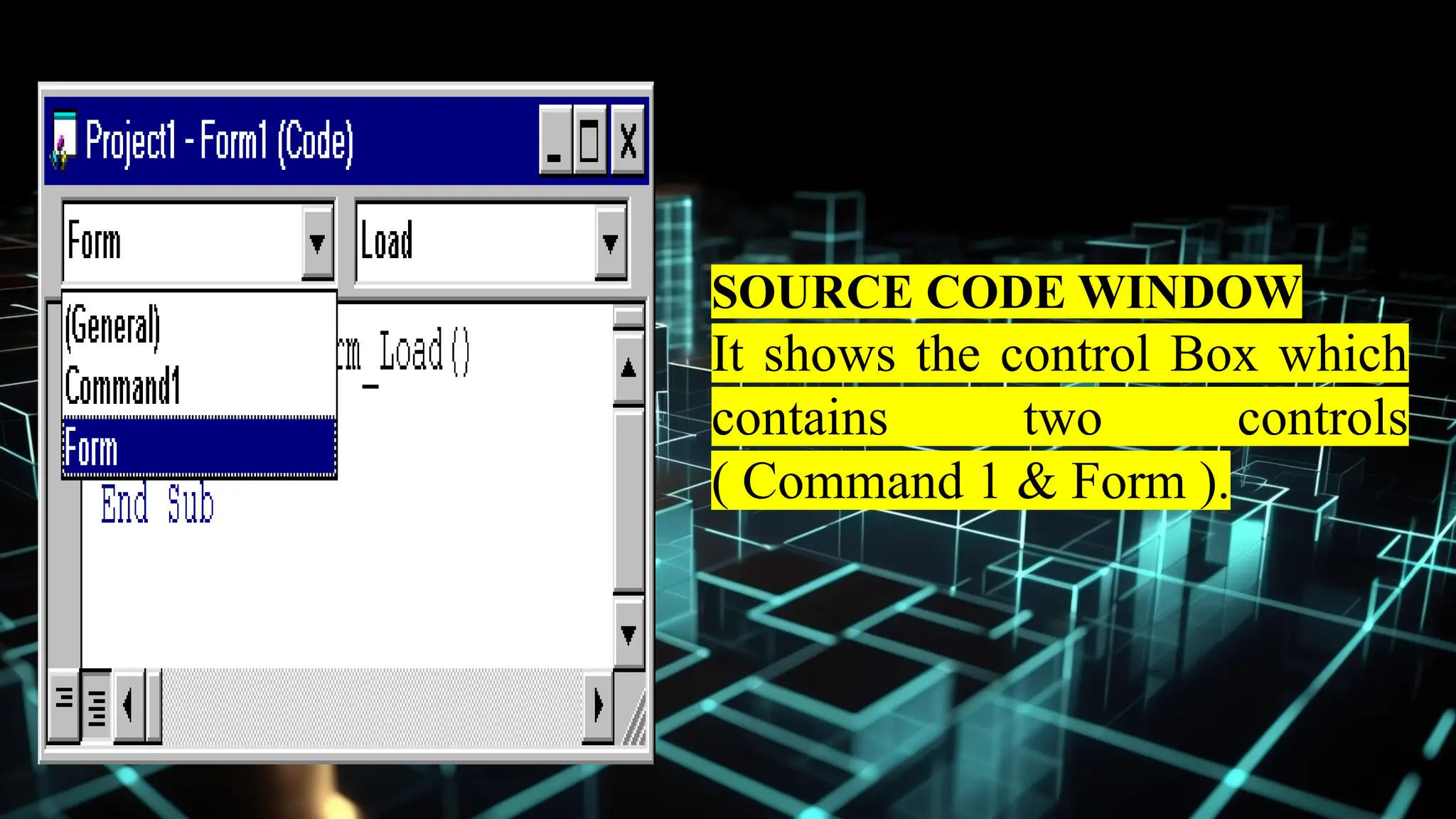
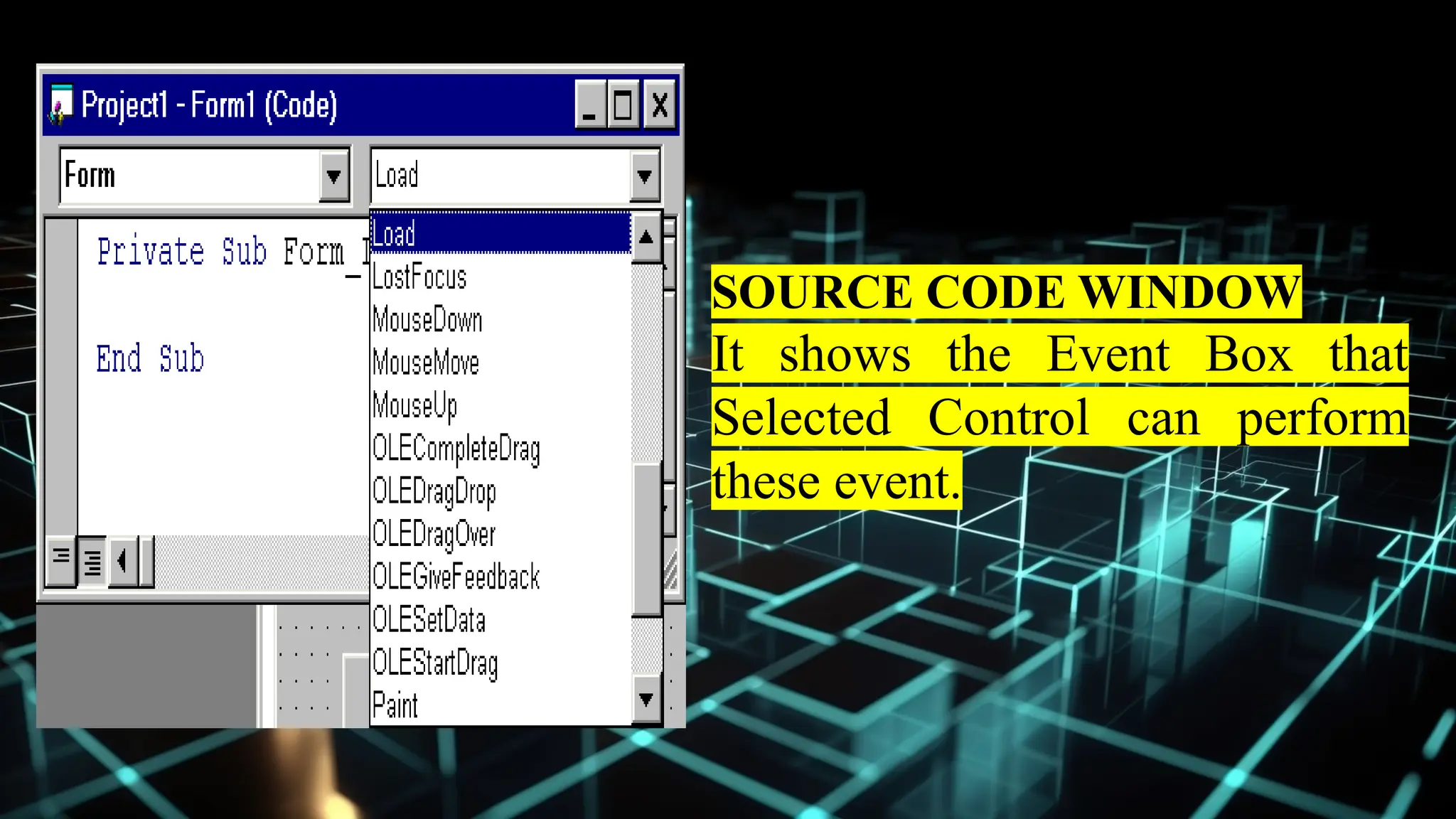
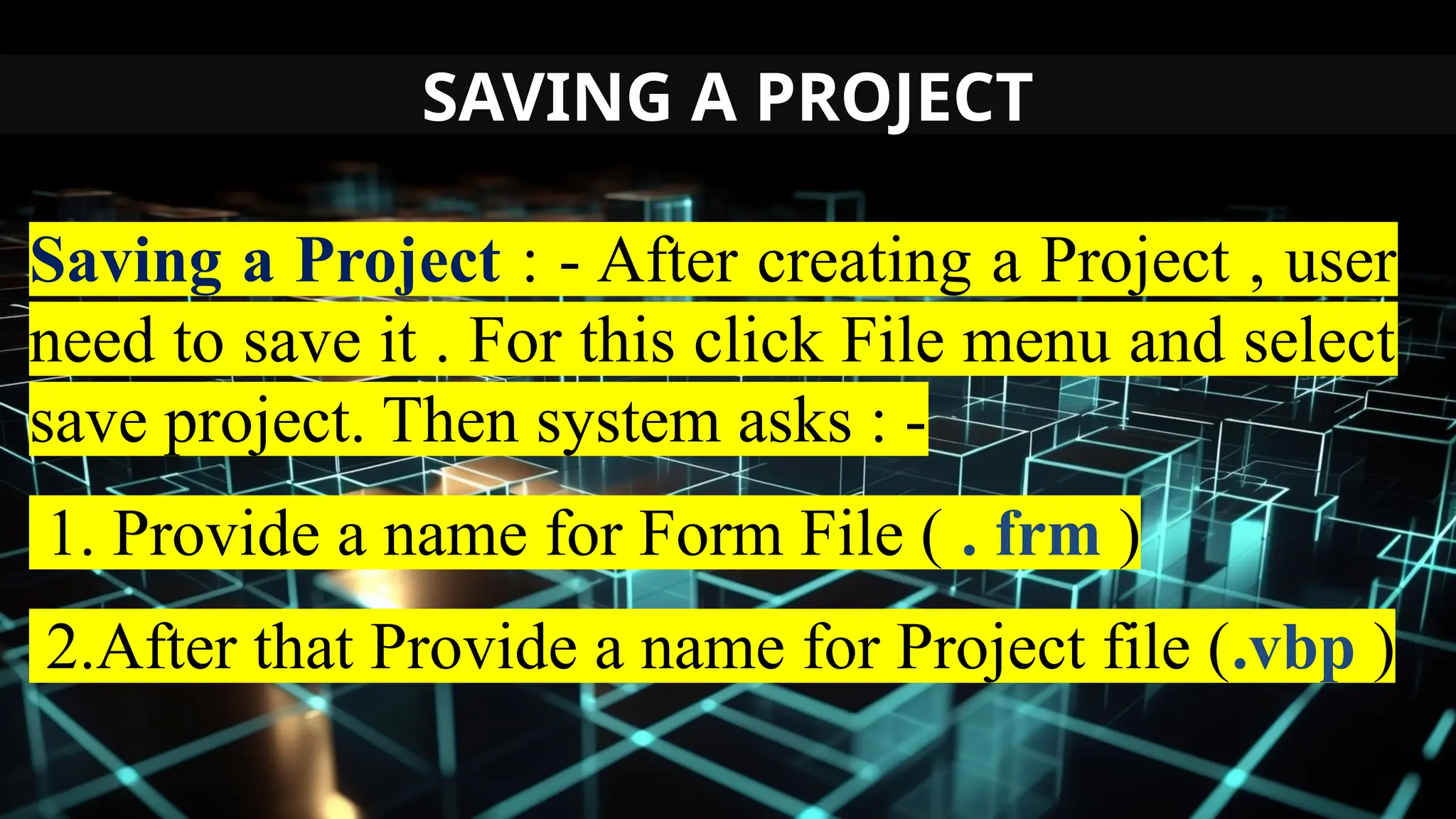
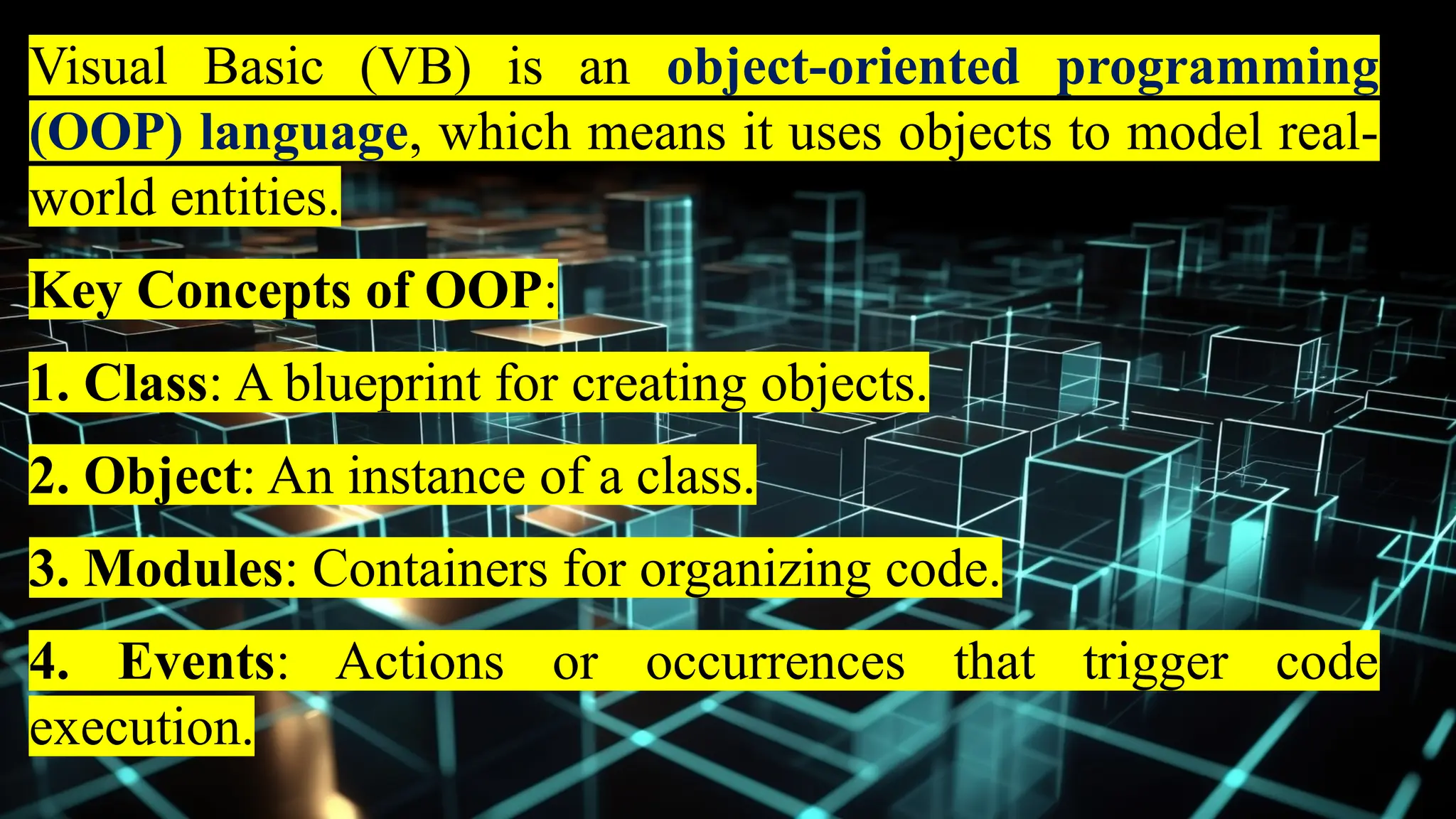
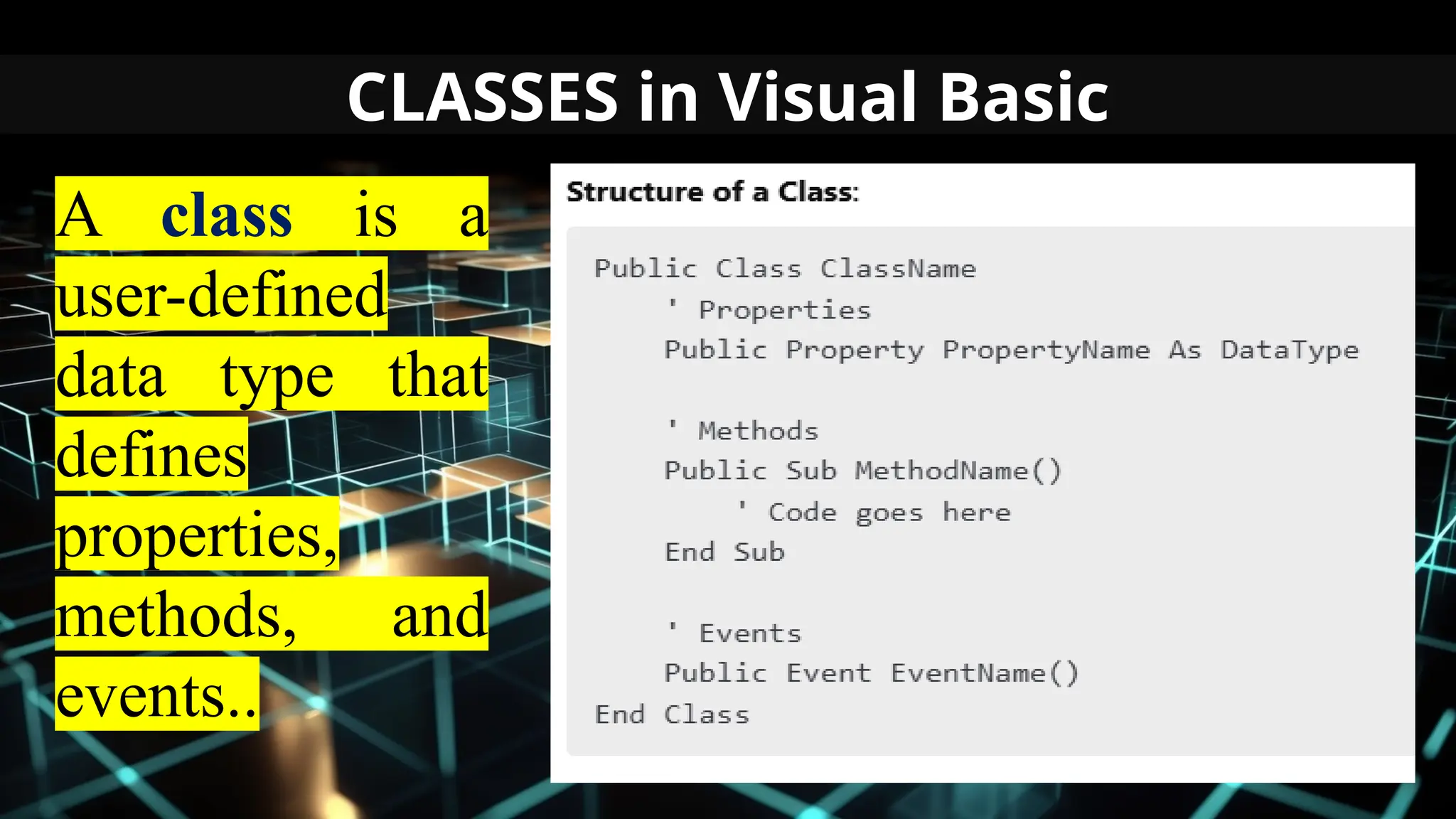
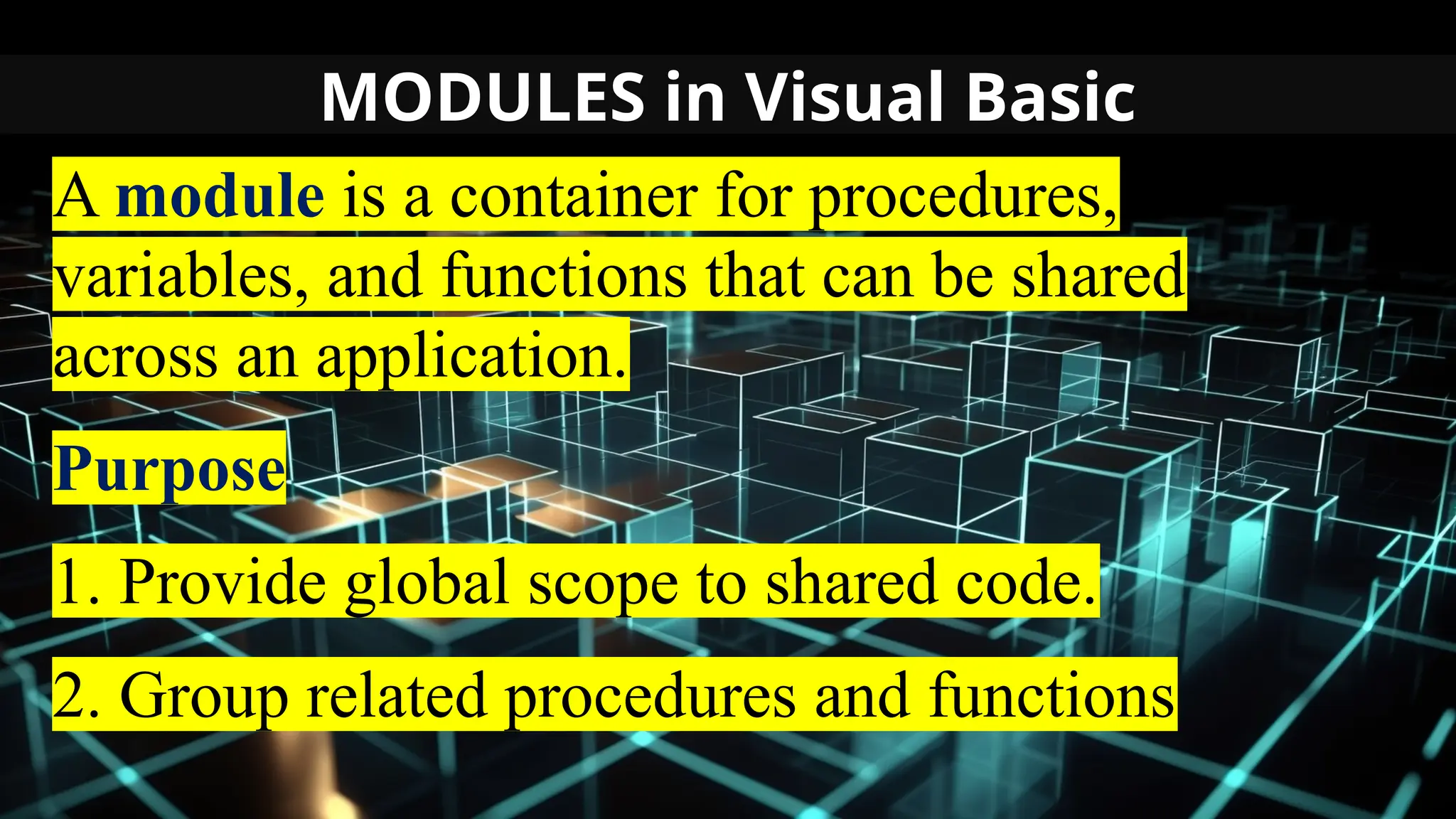
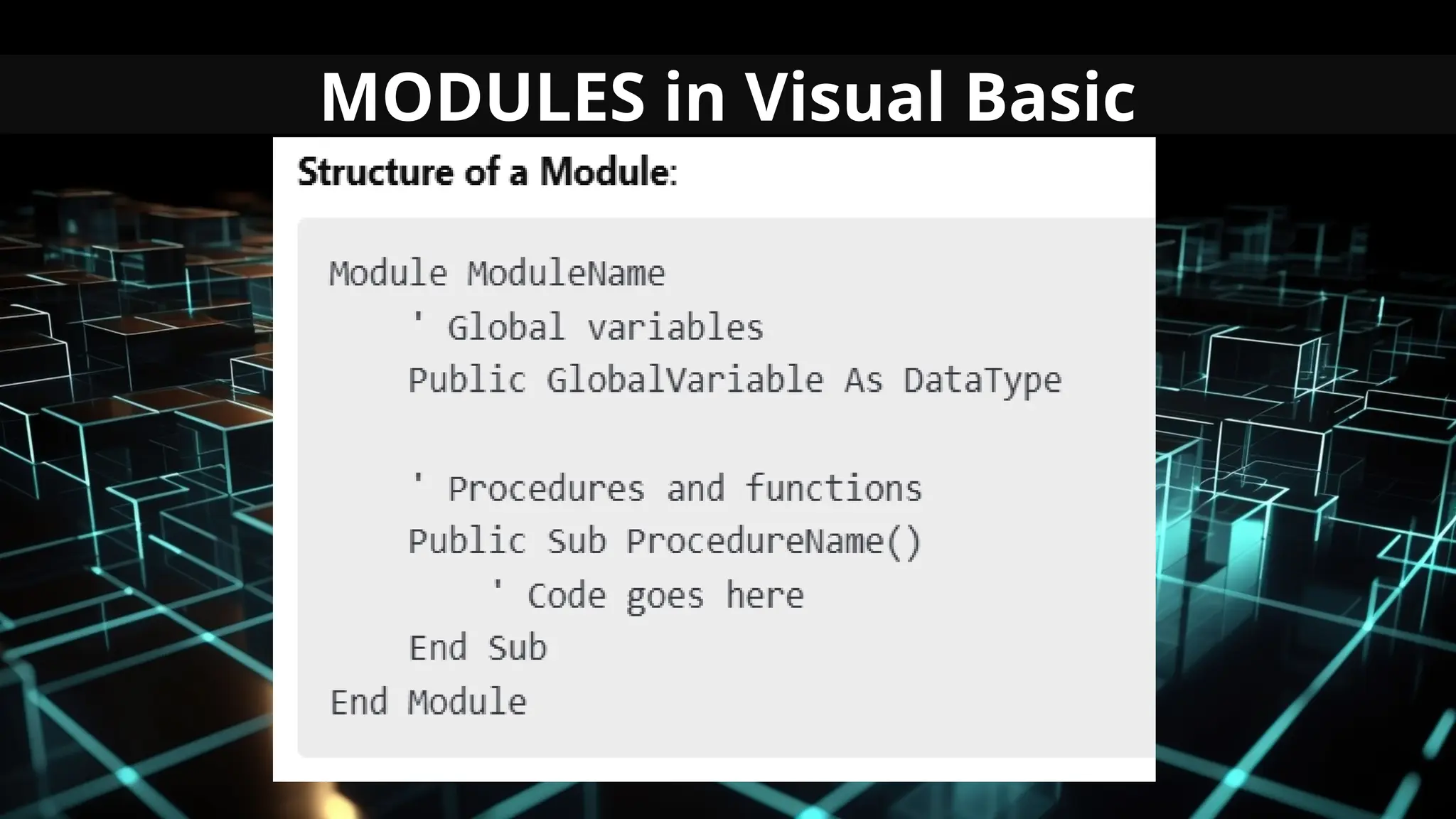
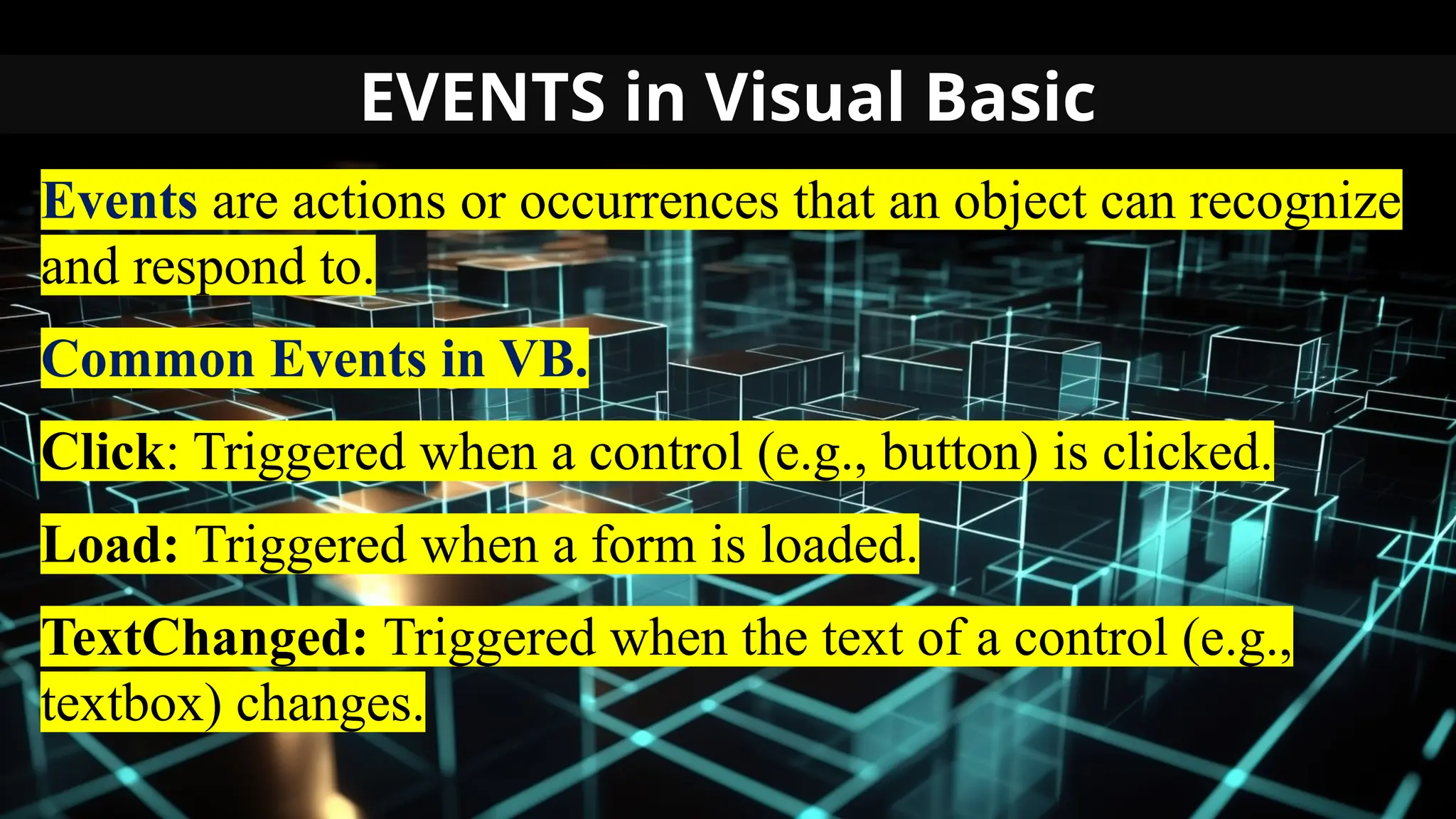
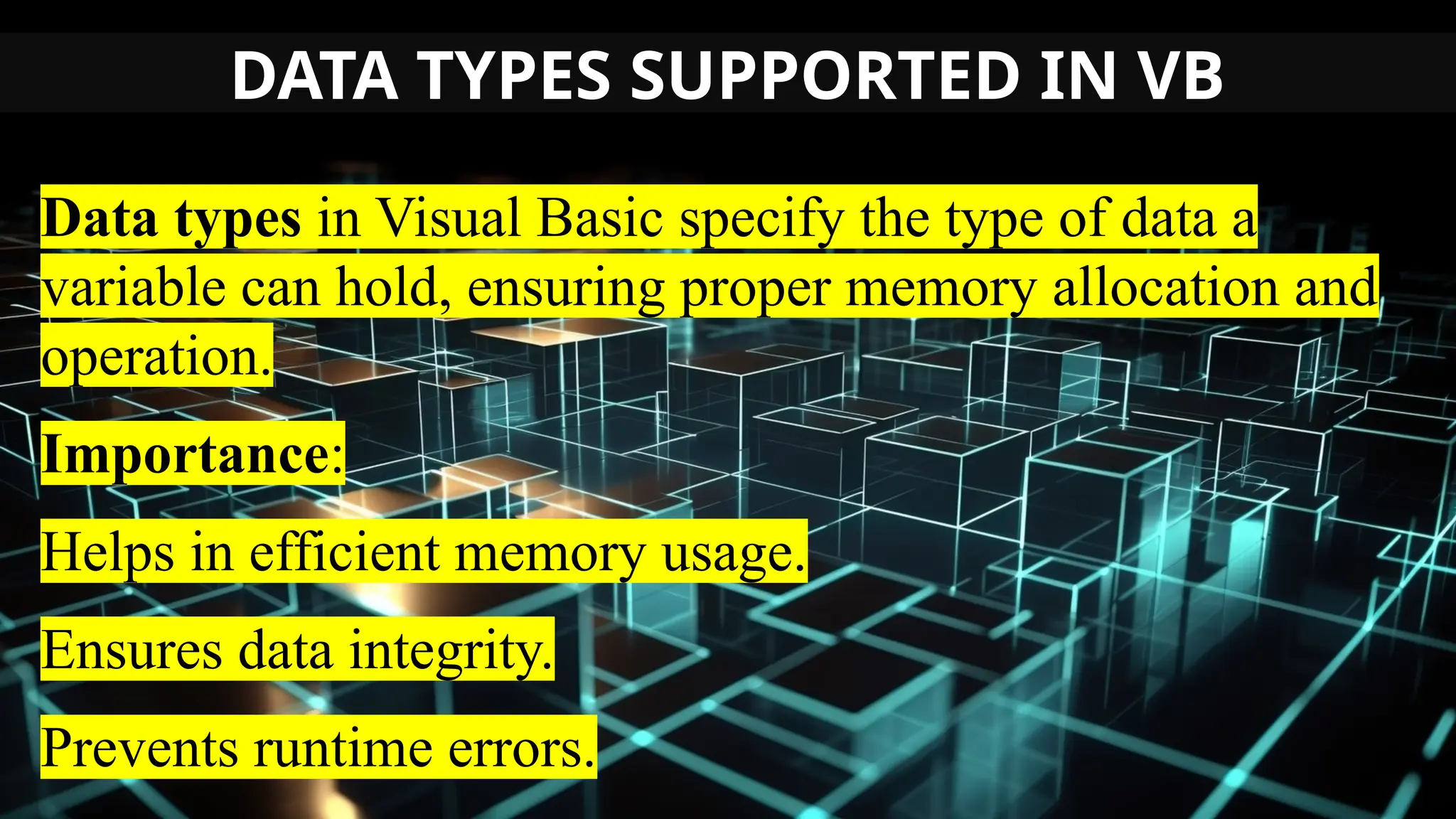
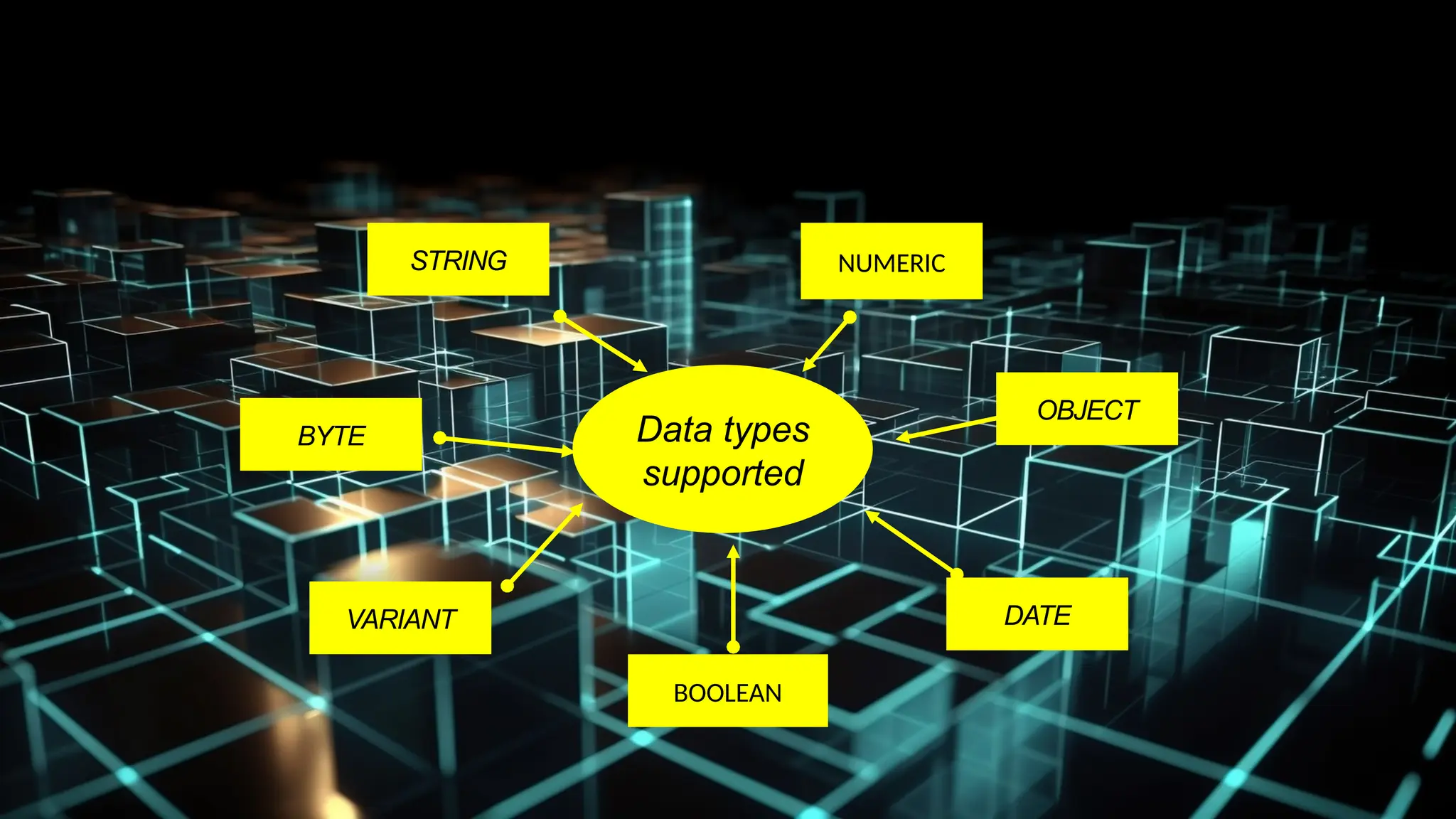
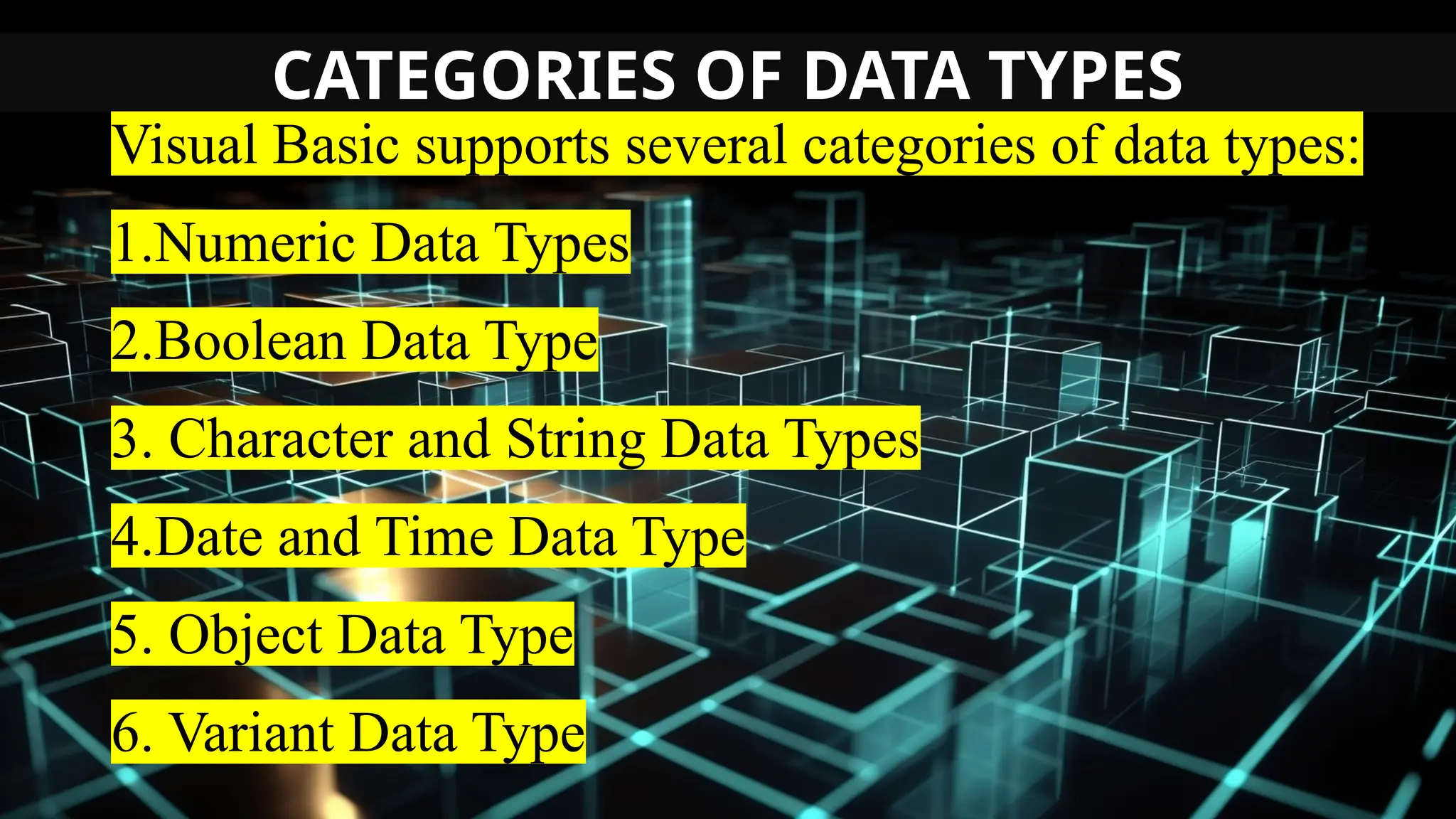
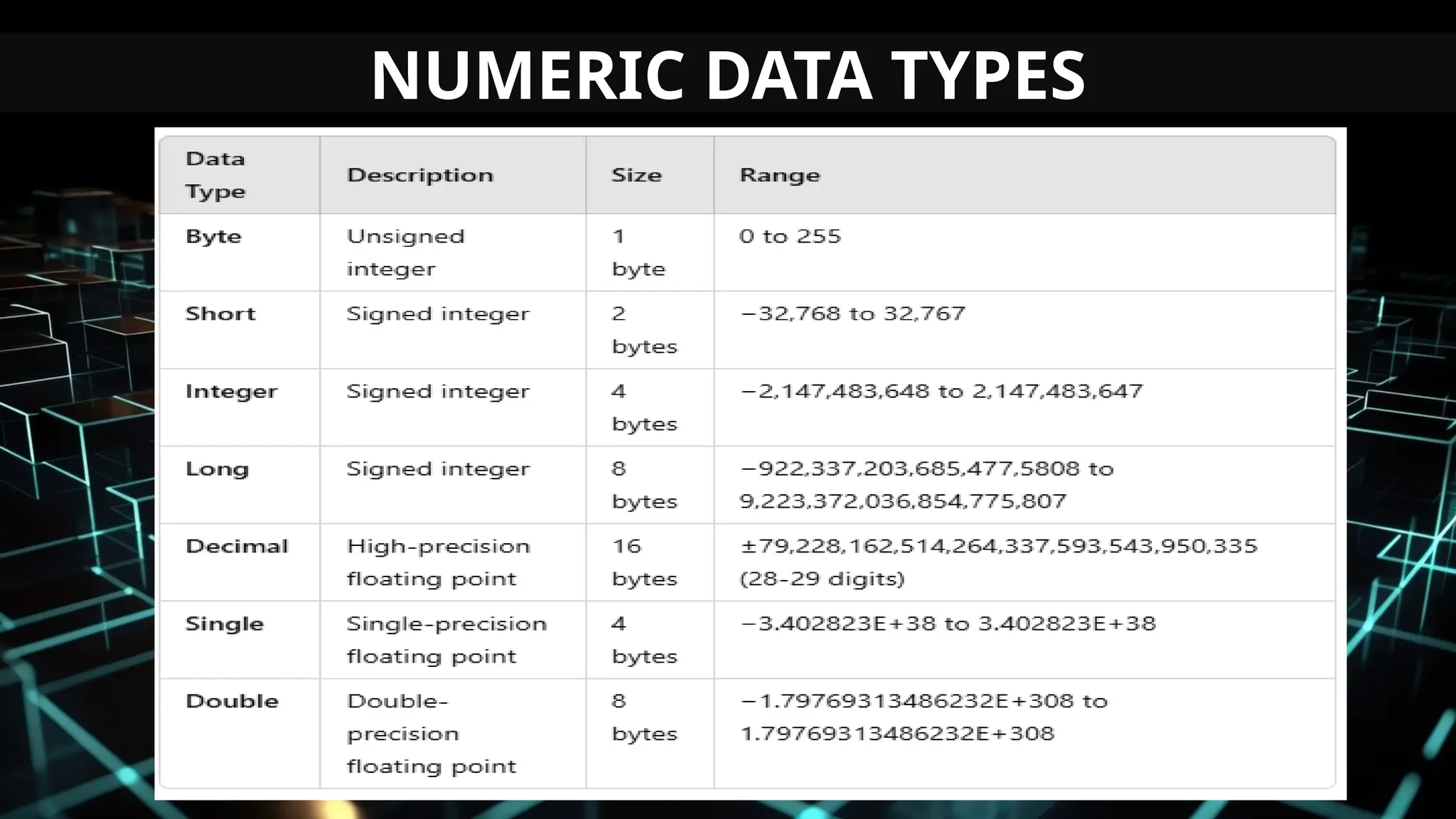
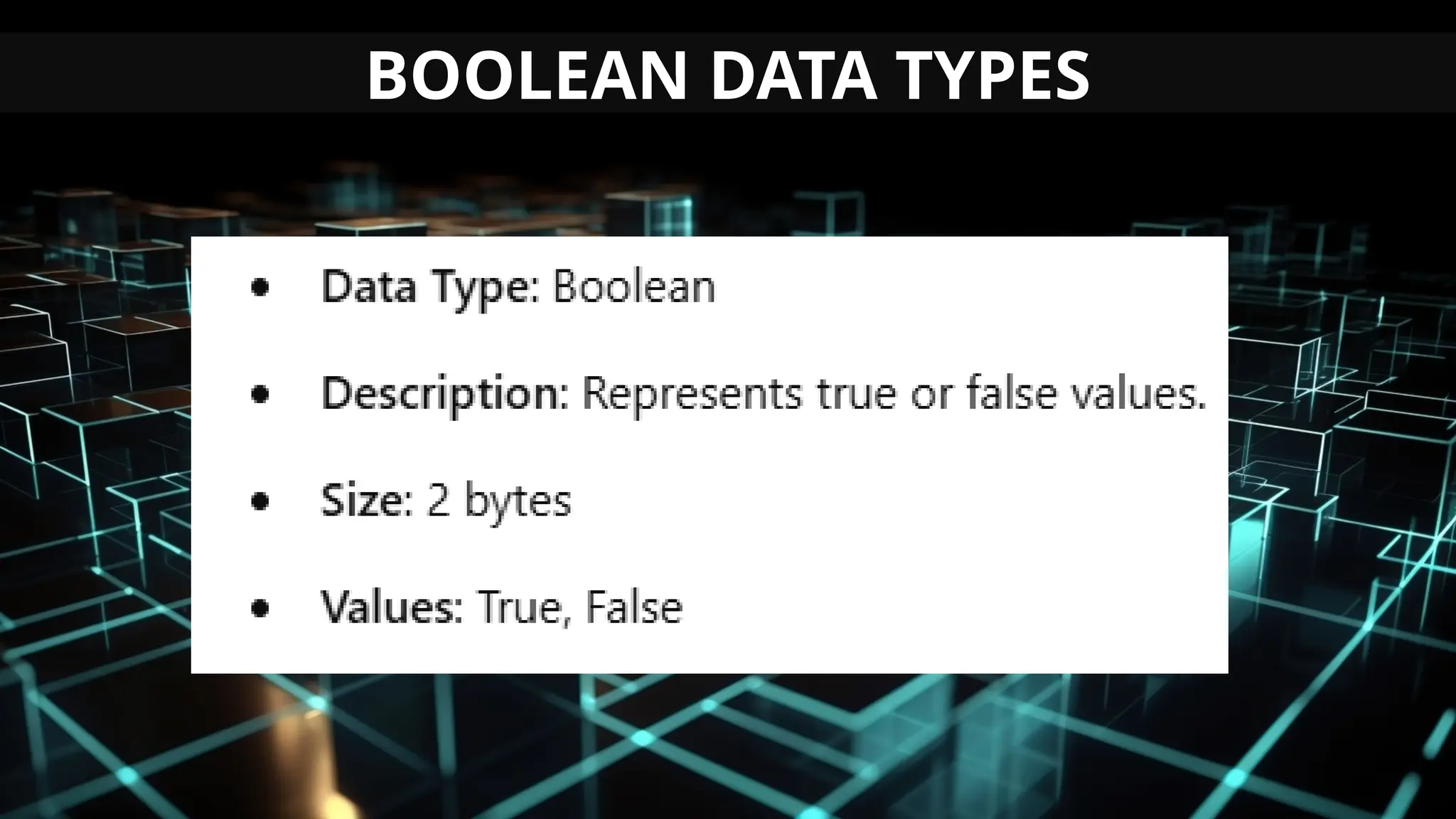
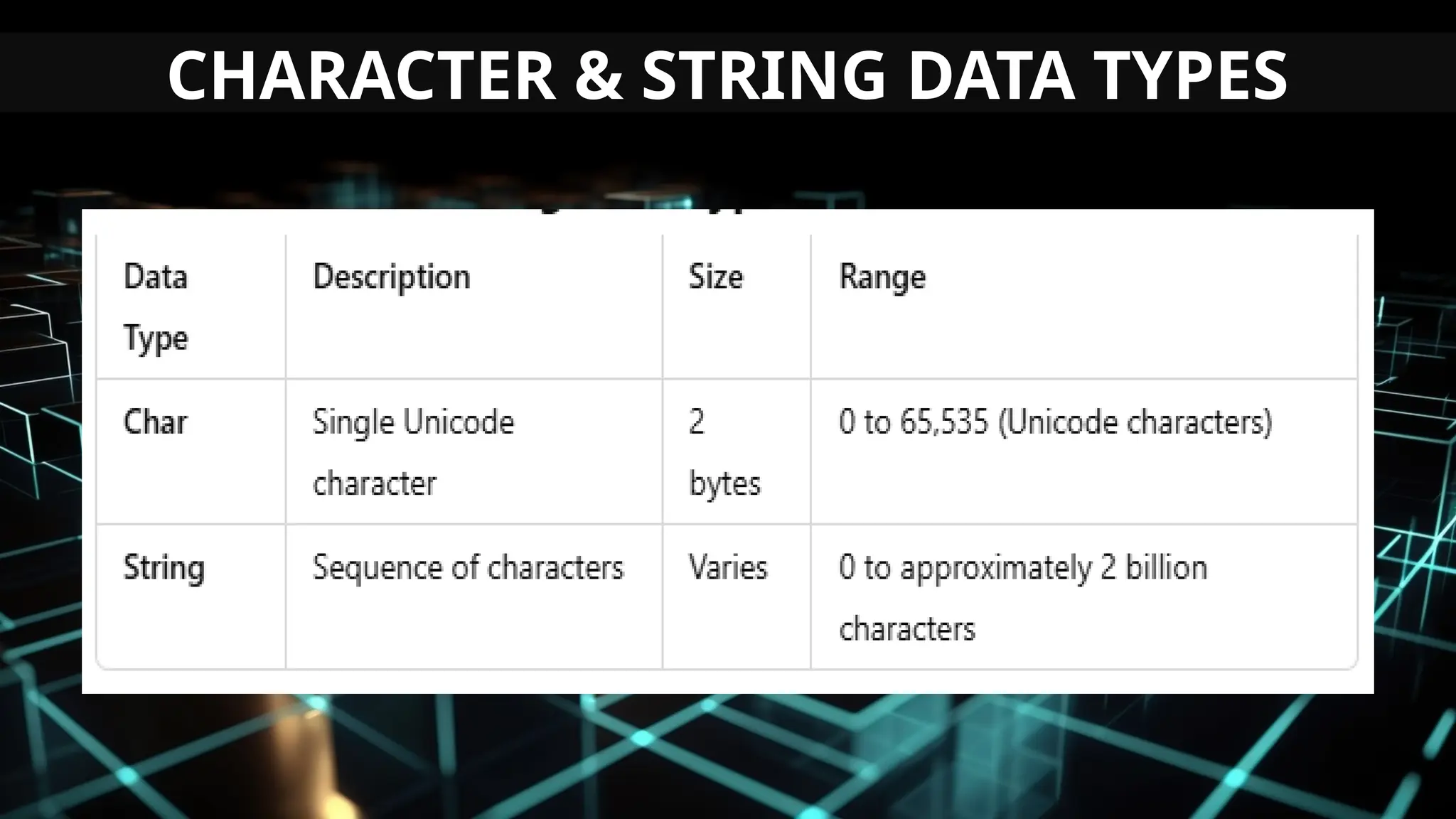
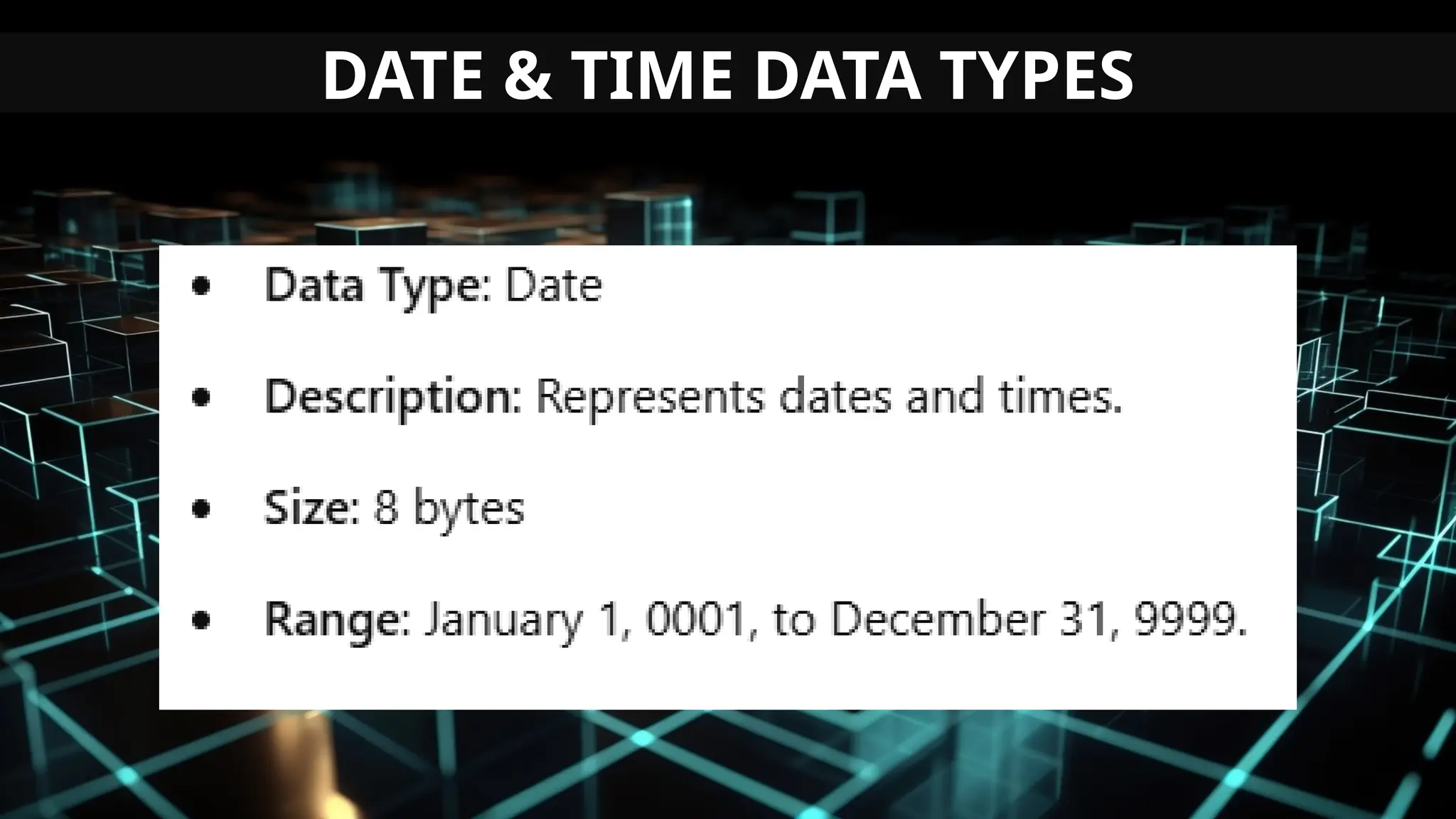
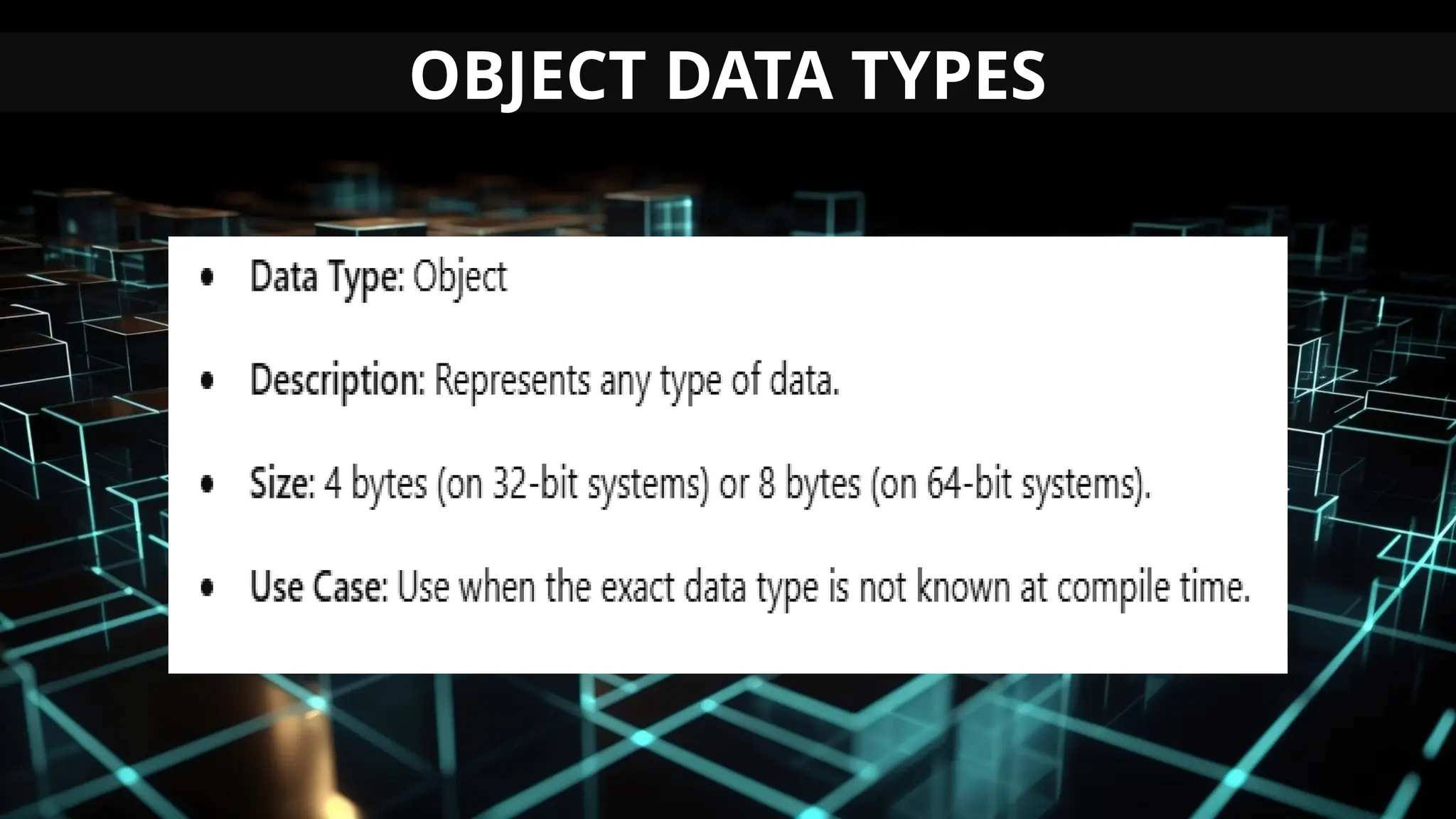
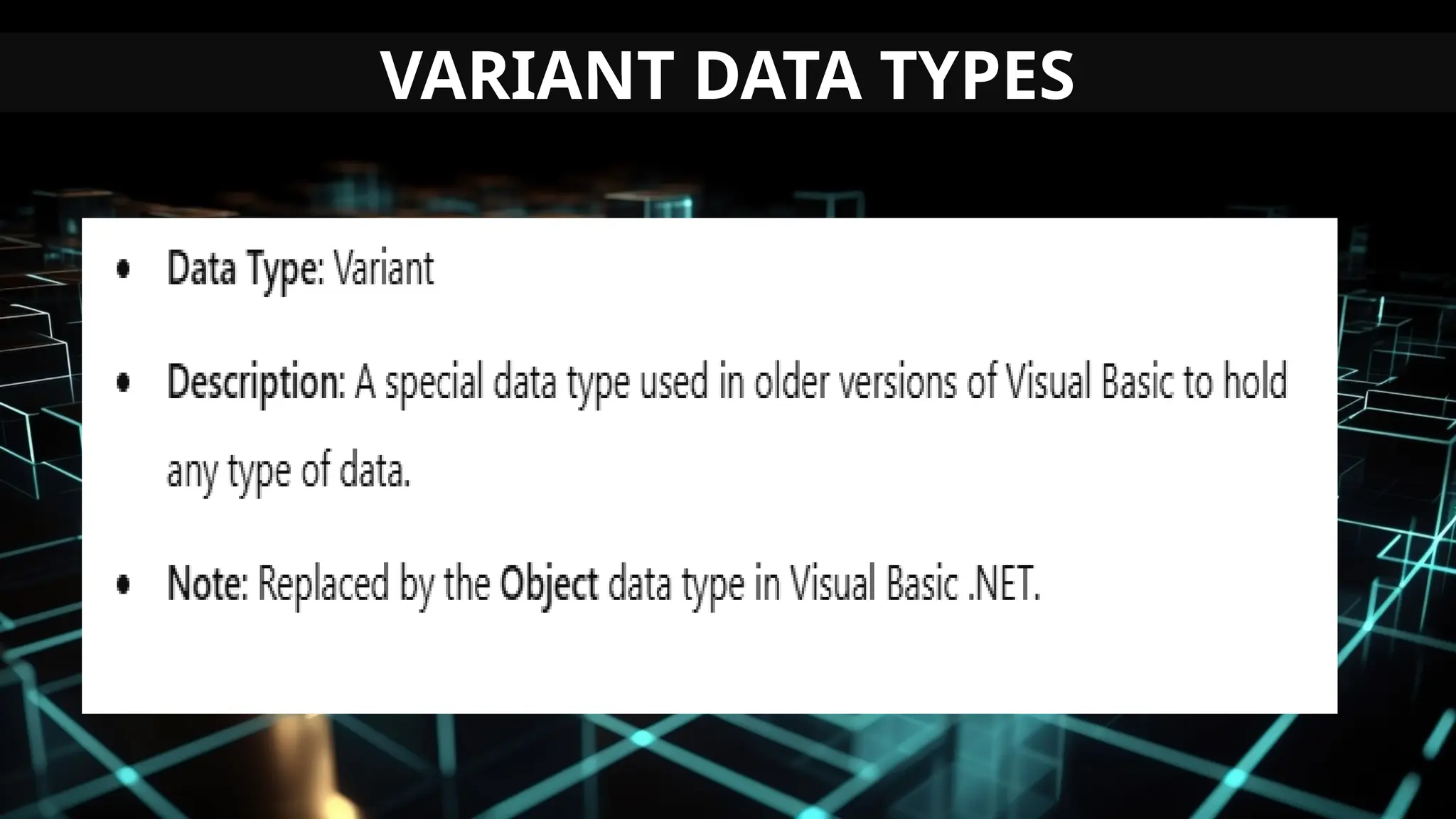
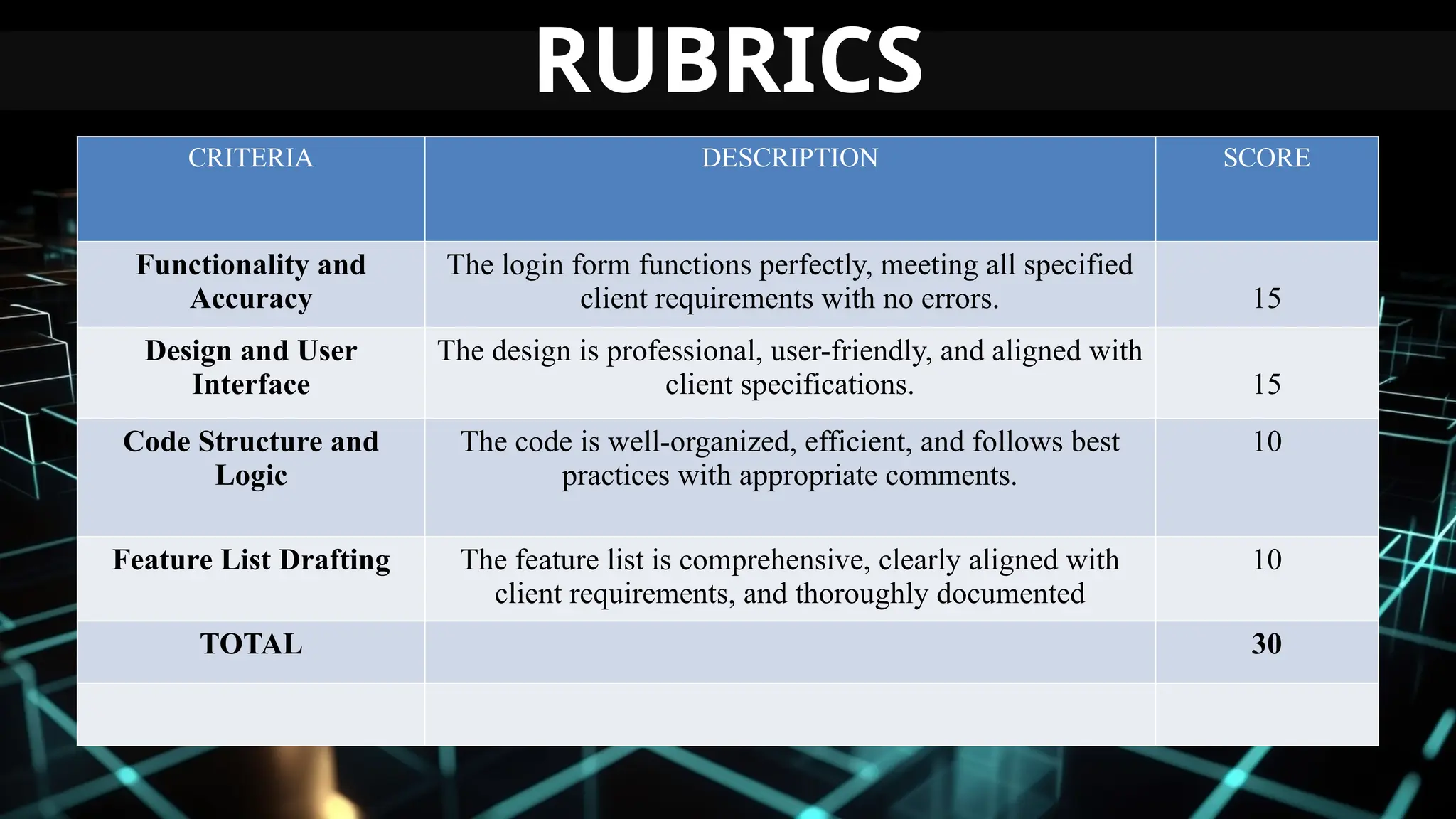
This document serves as an introduction to Visual Basic programming, outlining learning competencies for creating feature lists and release plans based on client requirements. It covers the history, features, and advantages of Visual Basic, along with its integrated development environment (IDE), object-oriented programming concepts, and supported data types. Additionally, it provides tasks for drafting a login form and associated features in line with specified criteria.

![LEARNING COMPETENCIES
Prepare feature list in line with client
requirements. [TLE_ICTP.NET11-12DAMWAIc-h-35]
Prepare release plan and agree with clients based
on dependencies and business values.
[TLE_ICTP.NET11-12DAMWAIc-h-35]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1-intro-to-visualbasic-1-250204004943-35dfcf40/75/LESSON1-INTRODUCTION-TO-VISUALBASIC-1-pptx-2-2048.jpg)