The document provides details of a lesson plan for a class on resources and their types for students aged 7-8 years old. The lesson plan aims to teach students to differentiate between capital, human, and natural resources and describe their role in society. It includes an explanation of the topic, objectives, prior knowledge, teaching aids, and presentations on the different types of resources including definitions and examples of natural resources, human resources, and capital resources.
![Allama Iqbal Open University
Submitted to: Sir Zulfiqar
Submitted by: AQSA MUBEEN
Course Code: 6554
Assignment title: Lesson Plans [primary level to O level]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplansfor6554-220826172702-3431283f/75/Lesson-Plans-for-6554-docx-1-2048.jpg)

![1 Heading Explanation
2 General
objectives
What do you mean by Resources?
How Resources use for a live a happy life?
3 Specific
Objectives
Students will be able to differentiate between capital, human, and natural
resources.
Students will be able to describe the role of capital, human and natural resources
in a healthy society
4 Previous
knowledge
Prior knowledge is the information and educational context a learner already has
before they learn new information. A learner's understanding of educational material
can be improved by taking advantage of their prior knowledge before dealing with the
new material.
5 A.V aids textbook, charts, pictures, board maker, White board etc.
6 Announcement
of the topic
Resources and Its Types
7 Presentations Resources:
A resource is something that can be used for making profits or benefits, whether that
be a source, supply, or support. Resource refers to all the materials available in our
environment which help us to satisfy our needs and wants.
Resources are usually classified into three types, viz. natural, human made and
human resources. [ ل سائ و وہ یز چ ےہ سے ج ع ناف م ا ی د وائ ف ے ک یے ل عمالت س ا
یا ک جا تا ک س ےہ ، ےچاہ وہ عہ ذری وہ ، ی الئپ س وہ ا ی پورٹ س و۔ہ ل سائ و سے مراد وہ
مام ت مواد ےہ جو ہمارے ماحول یں م یاب ت س د یں ہ جو ہماری ات ضروری اور شاتخو اہ و ک
ورا پ ے رن ک یں م ہماری مدد ے رت ک یں۔ ہ
ل سائ و و ک عام طور ر پ ین ت سام اق یں م یم س ق ت یا ک ا جات ے۔ہ ی درت ق ، ی سان ان ساخت
اور ی سان ان ل سائ ]و
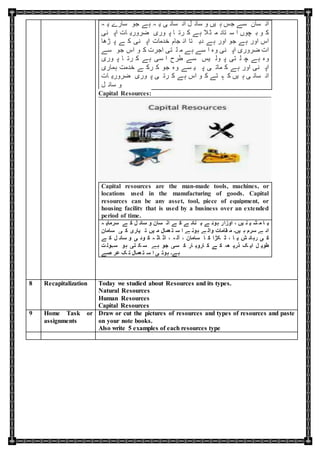
Types Of Resources:
Natural Resources [ی درت ق ل سائ ]و
Human resources [ی سان ان ل سائ ]و
Capital resources [ے سرمائ ے ک ل سائ ]و
Natural Resources:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplansfor6554-220826172702-3431283f/85/Lesson-Plans-for-6554-docx-3-320.jpg)