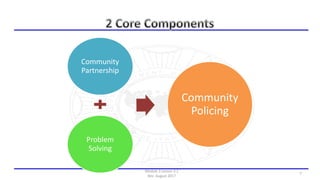
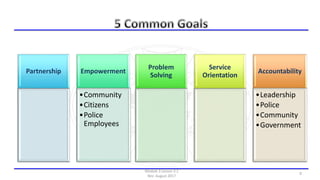
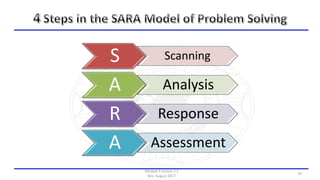
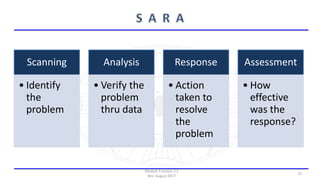
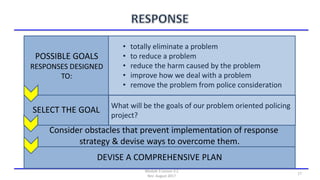
The document discusses community policing and the SARA problem-solving model. It defines community policing as a philosophy of full-service, personalized policing where officers partner with citizens to identify and solve problems. The goals of the lesson are to define key concepts of community policing, compare traditional and community policing approaches, and explain the SARA model's scanning, analysis, response, and assessment steps to solve problems.