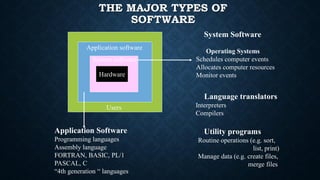
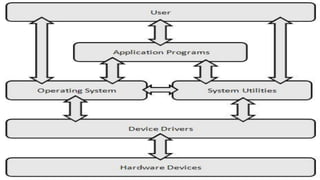
Computer software is essential for operating hardware, categorized into system software and application software. System software includes operating systems, utilities, and device drivers, while application software encompasses specialized programs like word processors, spreadsheets, and graphic software. Each type of software plays a critical role in executing tasks and managing resources within a computer system.