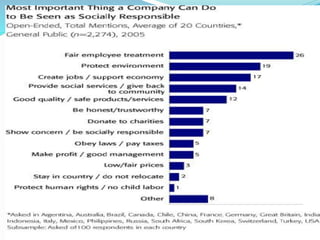
Corporate social responsibility refers to businesses having an obligation to work for social betterment beyond just increasing profits. While traditionally the view was that businesses only responsibility was to shareholders, the contemporary view is that as influential members of society, businesses are responsible for helping maintain and improve overall welfare. Businesses have accountability to key stakeholders like shareholders, employees, customers, creditors/suppliers, society, and government. Strategies for social responsibility range from proactive initiatives to meet all responsibilities to defensive approaches that do just the legal minimum.