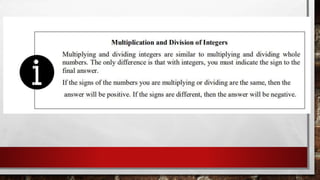
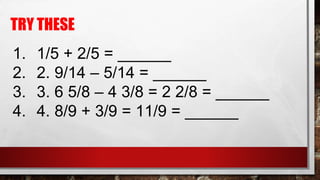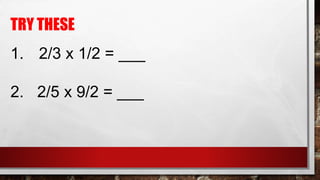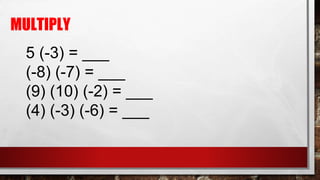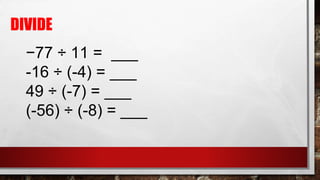The document is a lesson on fractions and decimals that explains various types of fractions, such as proper, improper, unit, and mixed fractions, including their definitions and examples. It also covers converting fractions to decimals and percentages, operations with fractions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, and provides sample problems for practice. The lesson emphasizes finding common denominators for unlike fractions and outlines methods for each mathematical operation.