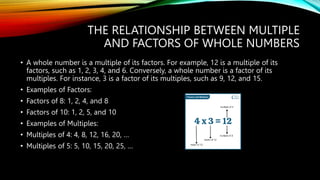
The document outlines the properties of whole numbers, including closure, commutative, associative, distributive, and identity properties, along with techniques for calculating using whole numbers through addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It explains methods for performing calculations, such as breaking down numbers by place value. Additionally, it covers the concepts of multiples and factors, demonstrating their relationships through examples.