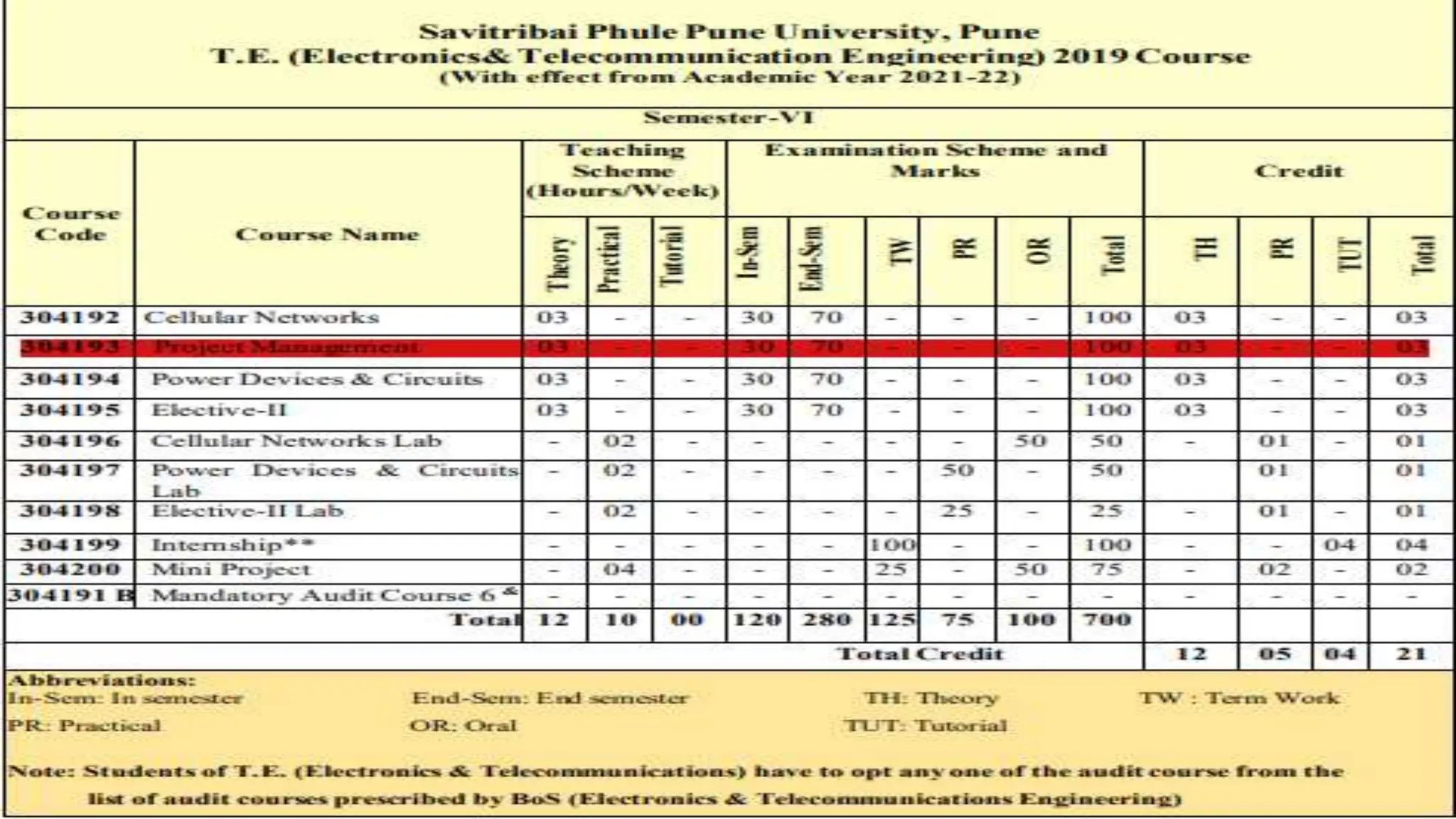
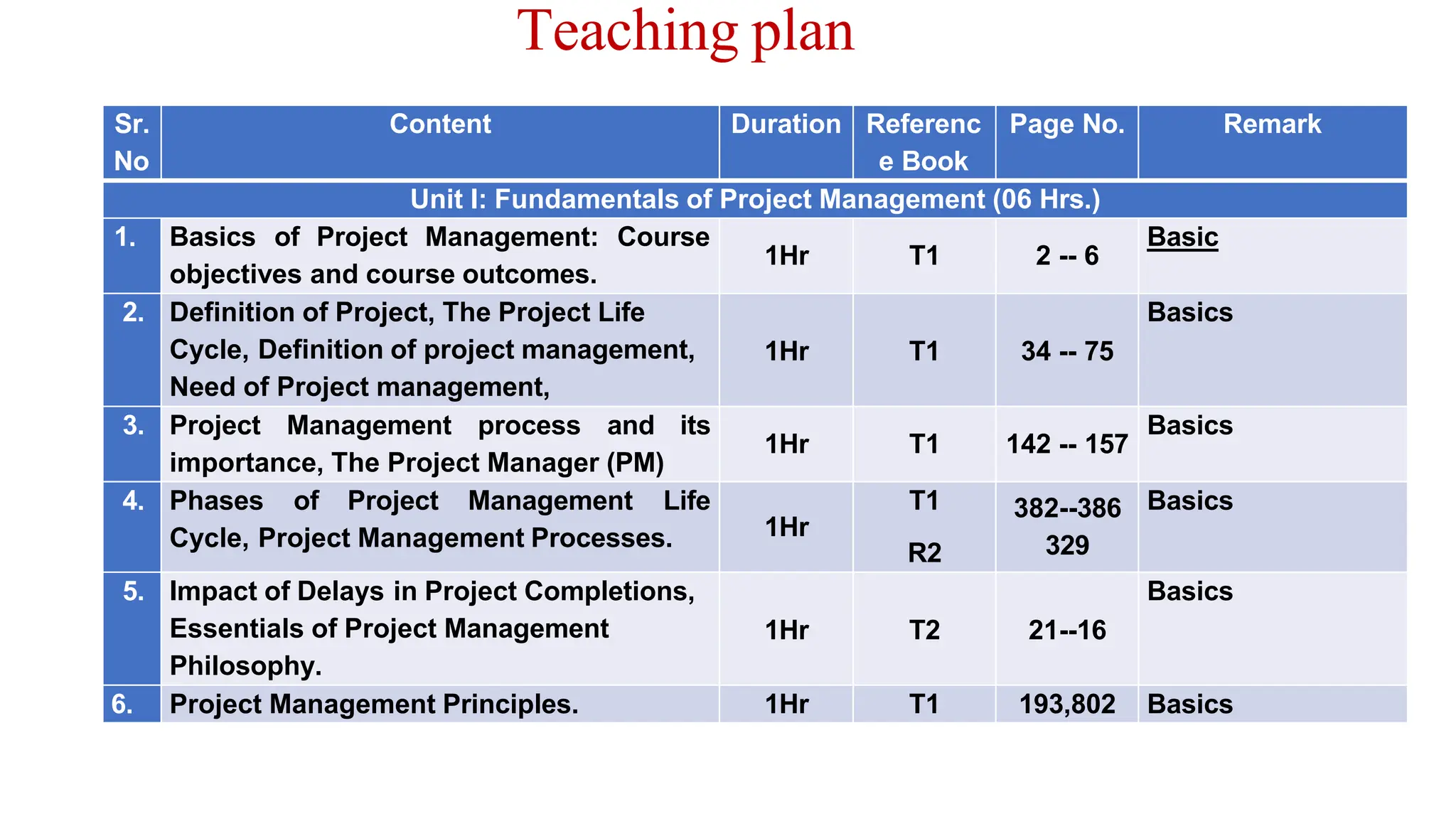
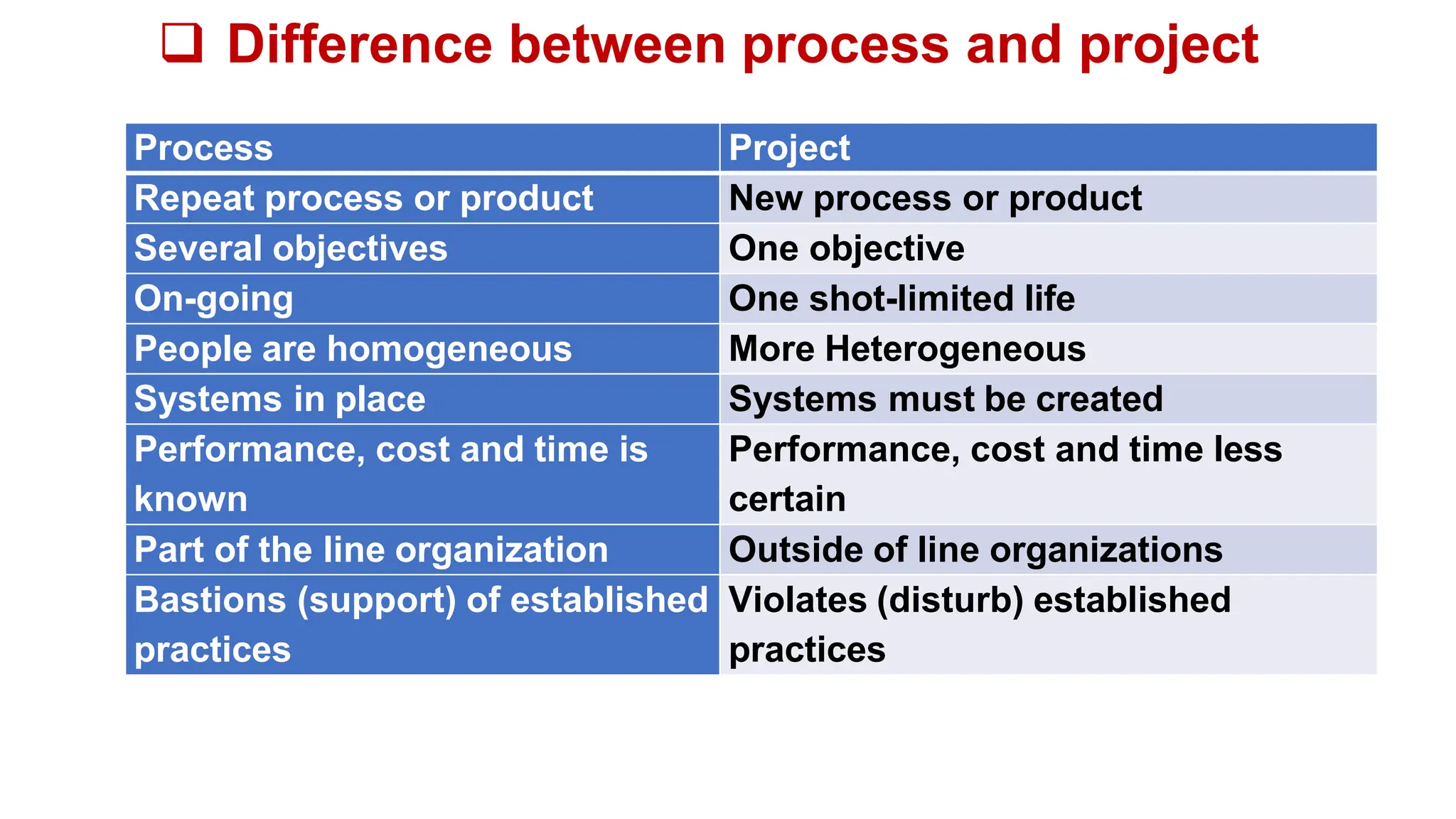
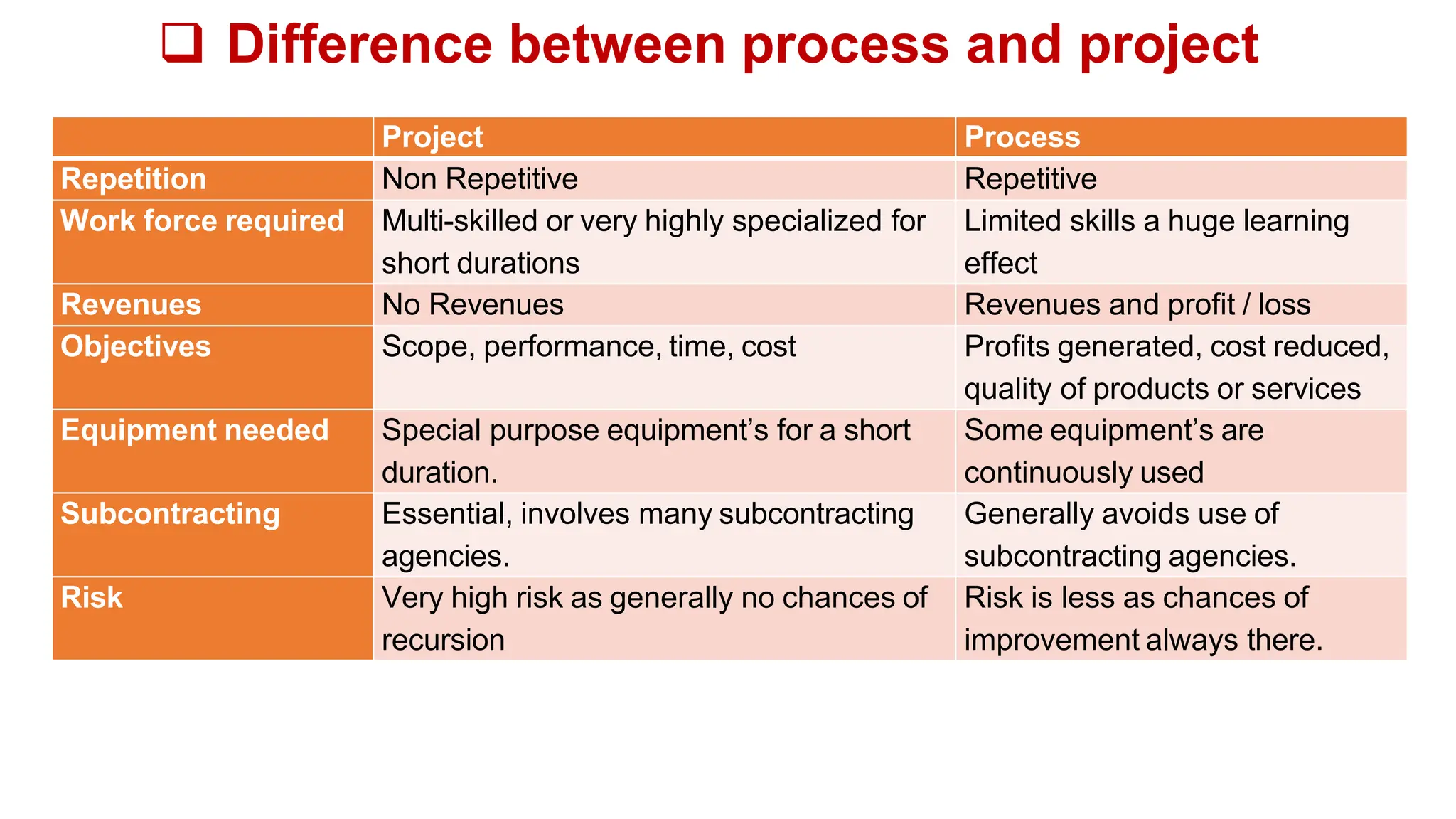
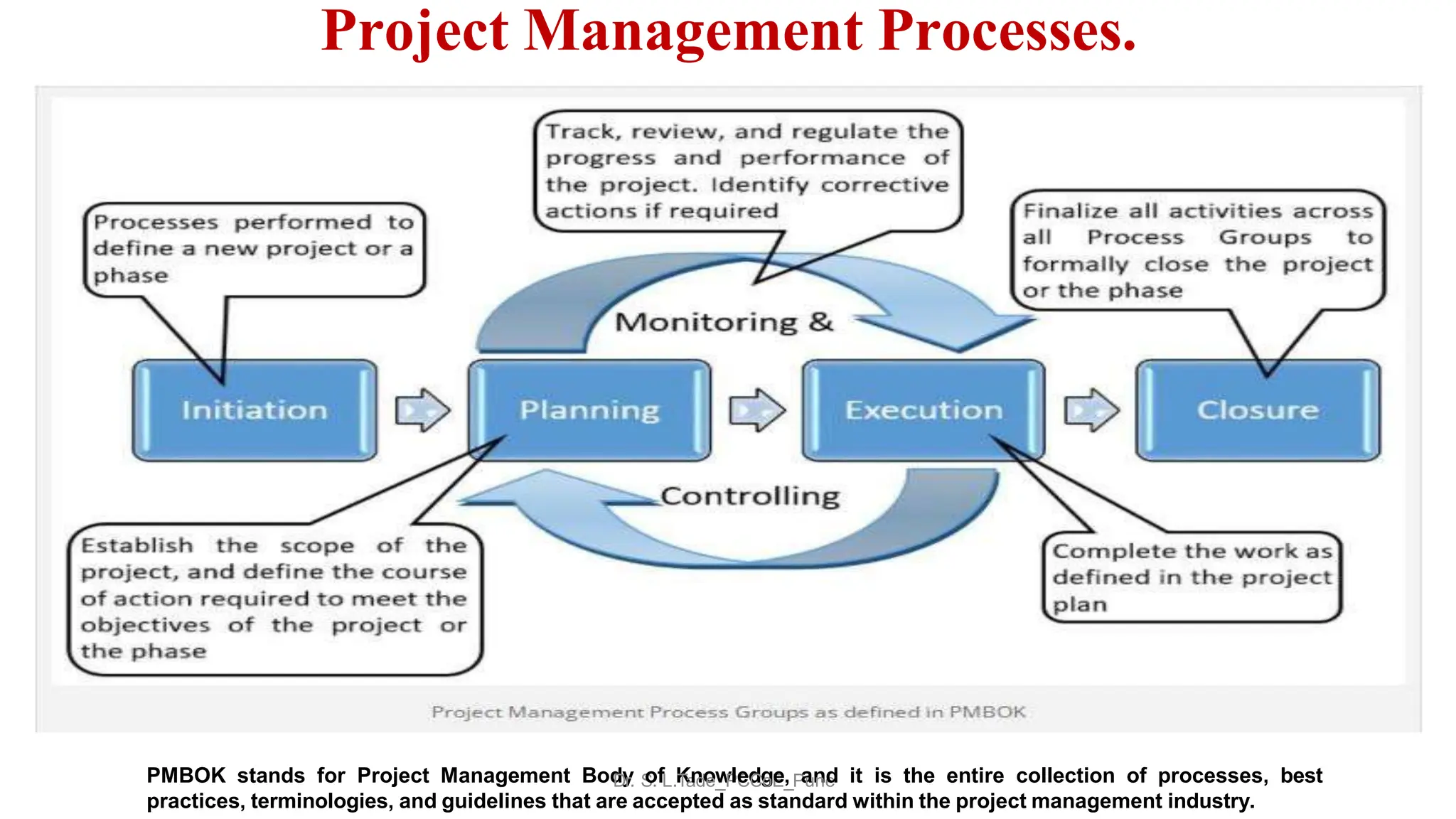
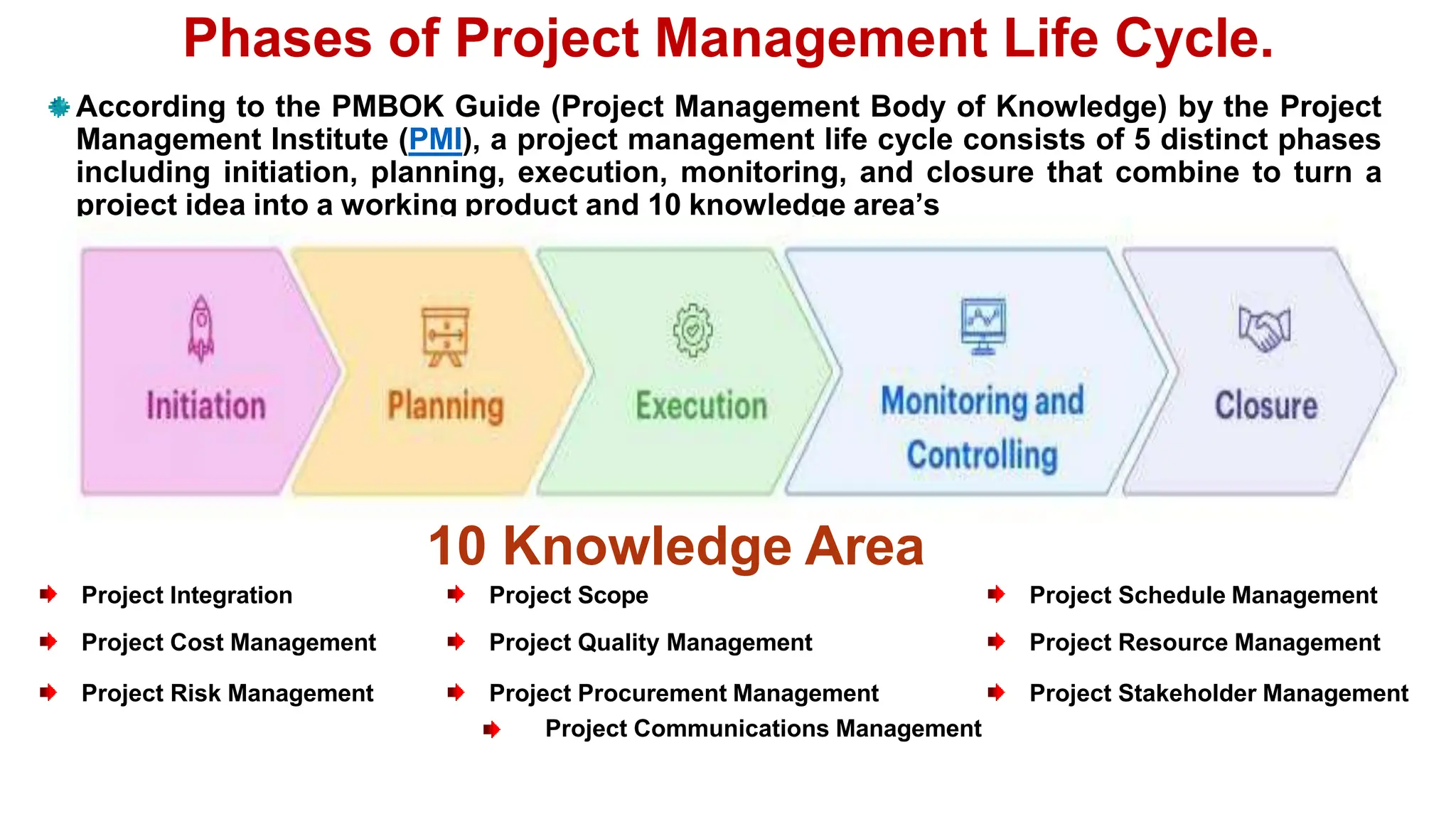
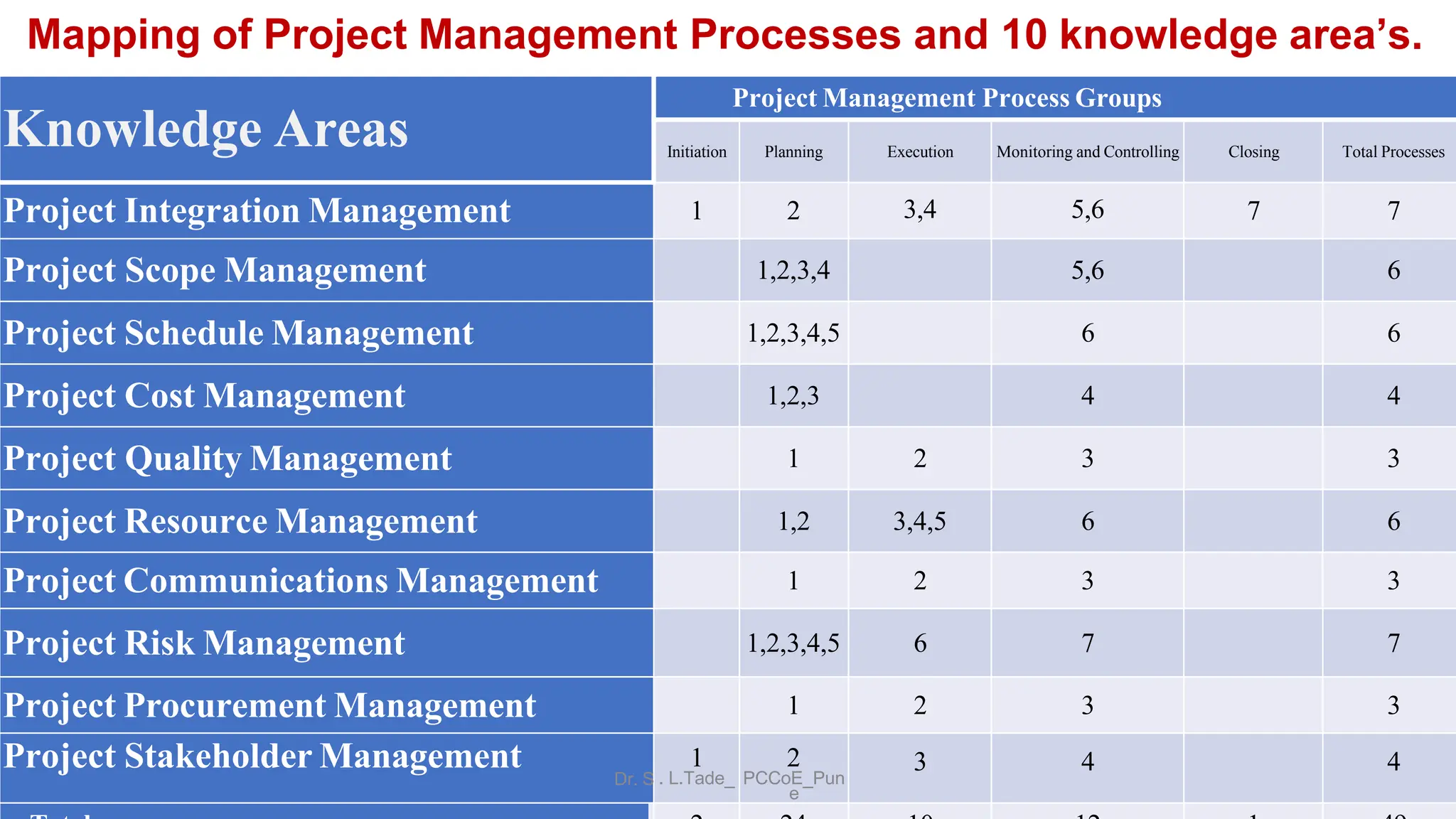
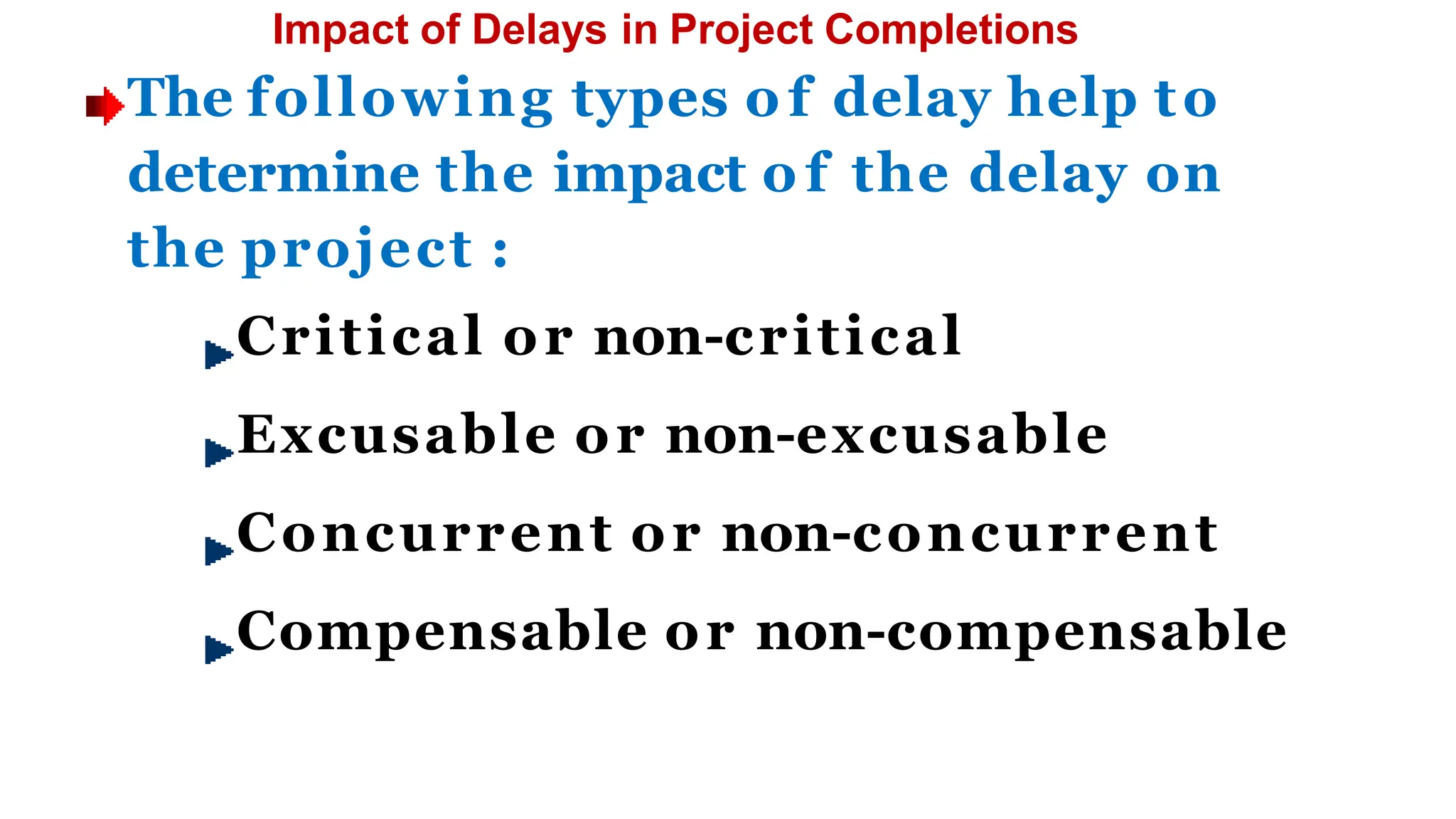
The document outlines the course objectives, teaching scheme, examination scheme, prerequisites, companion courses, course outcomes, elective courses, and teaching plan for the Project Management course offered at Savitribai Phule Pune University. It provides details on the 6 units that will be covered in the course, mapping the course outcomes to the units, and lists the topics, duration and references for each unit.