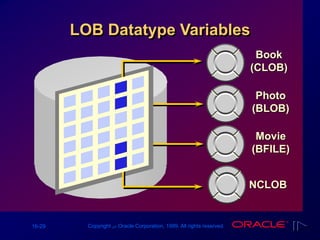
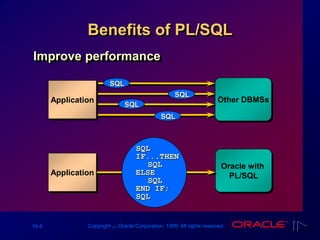
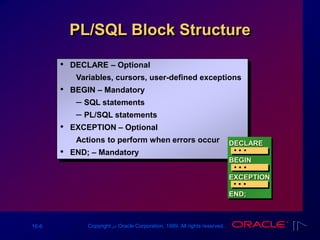
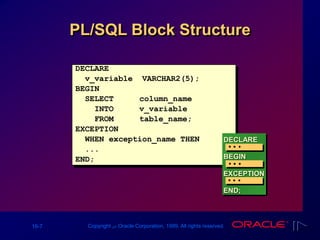
The document provides an overview of PL/SQL, emphasizing its structure and benefits as an extension of SQL, including variable declaration and usage. It covers the components of PL/SQL blocks, types of variables, and guidelines for declaration. Additionally, it discusses the handling of different data types, including scalar and LOB variables, and concludes with summaries of identifiers and practical exercises.



![16-8 Copyright س Oracle Corporation, 1999. All rights reserved.
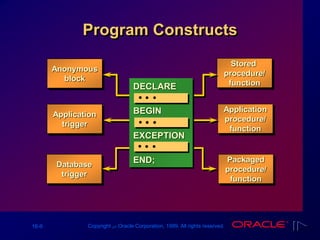
Block Types
Anonymous Procedure Function
[DECLARE]
BEGIN
--statements
[EXCEPTION]
END;
PROCEDURE name
IS
BEGIN
--statements
[EXCEPTION]
END;
FUNCTION name
RETURN datatype
IS
BEGIN
--statements
RETURN value;
[EXCEPTION]
END;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les161-220214161043/85/Les16-1-Declaring-Variables-8-320.jpg)



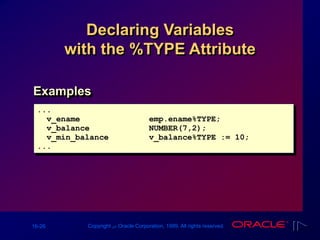
![16-16 Copyright س Oracle Corporation, 1999. All rights reserved.
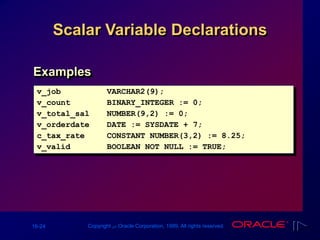
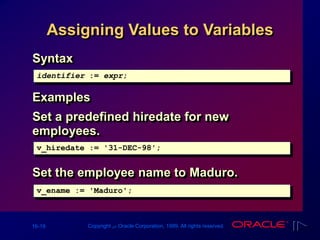
Declaring PL/SQL Variables
Syntax
Examples
identifier [CONSTANT] datatype [NOT NULL]
[:= | DEFAULT expr];
Declare
v_hiredate DATE;
v_deptno NUMBER(2) NOT NULL := 10;
v_location VARCHAR2(13) := 'Atlanta';
c_comm CONSTANT NUMBER := 1400;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les161-220214161043/85/Les16-1-Declaring-Variables-14-320.jpg)



![16-22 Copyright س Oracle Corporation, 1999. All rights reserved.
Base Scalar Datatypes
• VARCHAR2 (maximum_length)
• NUMBER [(precision, scale)]
• DATE
• CHAR [(maximum_length)]
• LONG
• LONG RAW
• BOOLEAN
• BINARY_INTEGER
• PLS_INTEGER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les161-220214161043/85/Les16-1-Declaring-Variables-20-320.jpg)