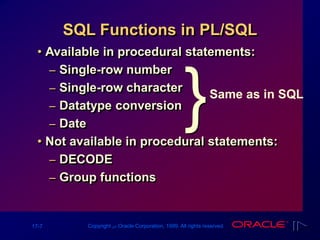
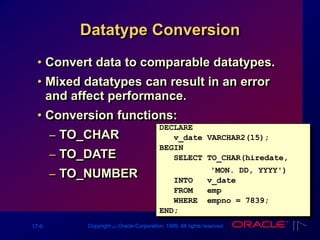
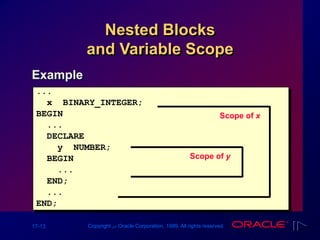
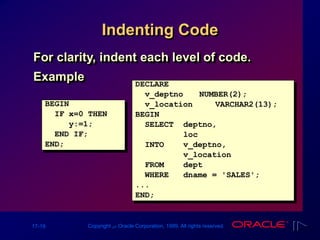
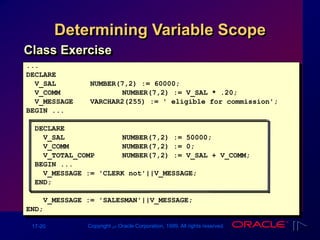
The document outlines PL/SQL block structure, including executable statements, syntax rules, and coding conventions. Key topics include variable scope, nested blocks, datatype conversions, and the use of operators. It provides guidelines for writing and testing PL/SQL blocks to ensure code clarity and maintainability.