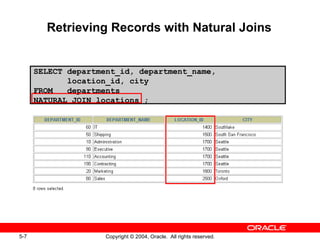
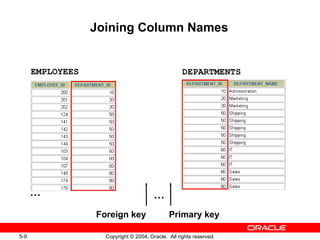
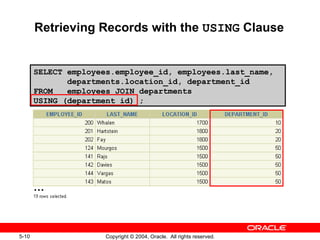
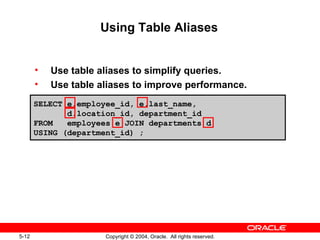
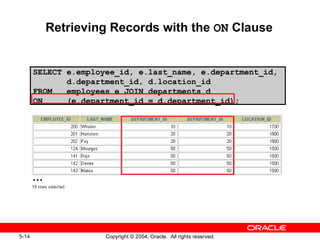
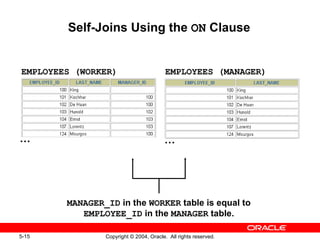
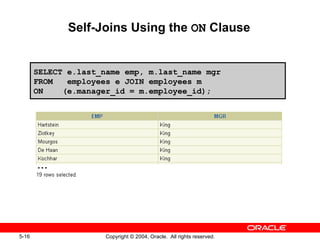
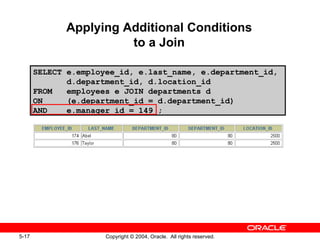
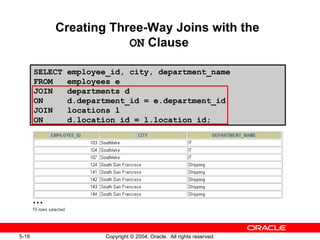
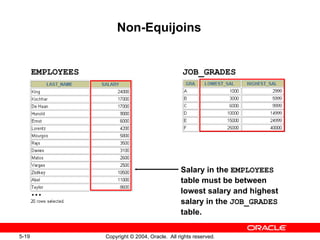
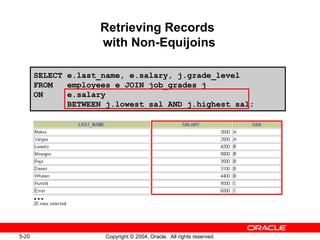
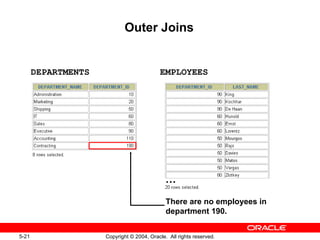
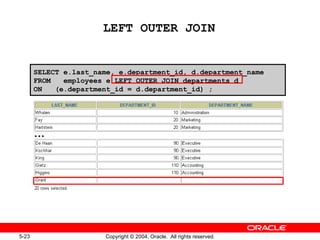
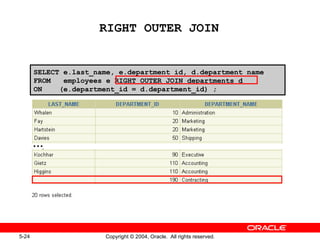
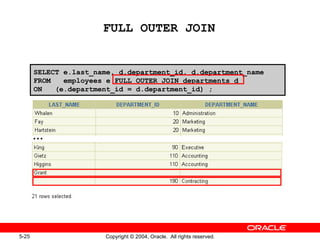
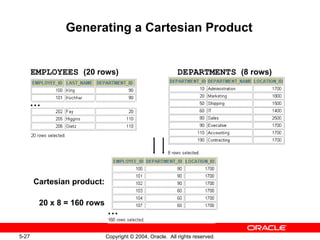
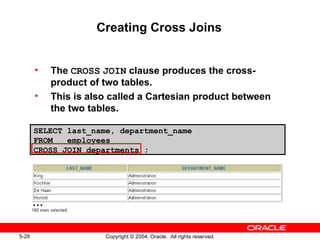
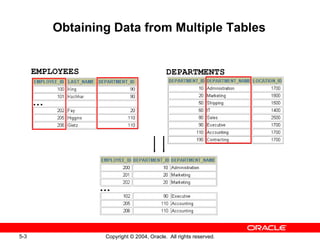
This document discusses different types of joins in SQL for combining data from multiple tables, including equijoins, non-equijoins, outer joins, self-joins, natural joins, and cross joins. It provides examples of SQL statements using various join types and explains how to qualify column names, use table aliases, apply conditions to joins, and avoid Cartesian products. The goal is for readers to learn how to write SELECT statements to retrieve and display data involving two or more tables.


![Joining Tables Using SQL:1999 Syntax Use a join to query data from more than one table: SELECT table1.column, table2.column FROM table1 [NATURAL JOIN table2 ] | [JOIN table2 USING ( column_name )] | [JOIN table2 ON ( table1.column_name = table2.column_name )]| [LEFT|RIGHT|FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON ( table1.column_name = table2.column_name )]| [CROSS JOIN table2 ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les05-100209113554-phpapp02/85/Les05-5-320.jpg)