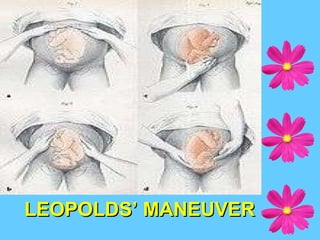
Leopold's maneuver is a systematic method to determine the position of a fetus in the uterus. It involves gently palpating the abdomen with both hands to feel the different fetal parts. The head feels hard and round while the buttocks feel softer. By assessing where the back, limbs, and head are located, the presentation and position of the fetus can be determined. Nursing considerations include ensuring privacy, a comfortable position, and explaining the procedure to the patient.