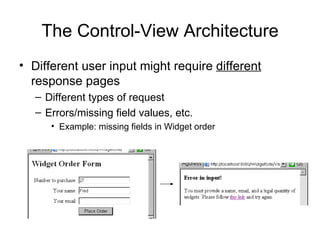
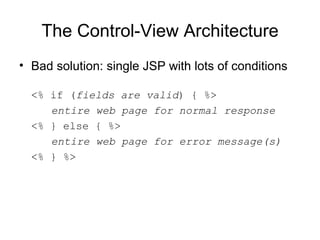
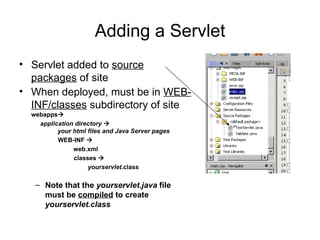
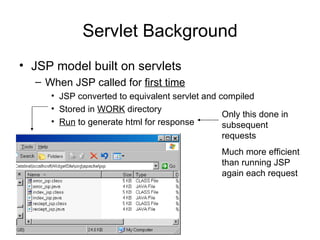
The document discusses the control-view architecture pattern for server-side web programming. Servlets act as controllers that categorize requests and decide which JSP view to forward the request to. Information can be passed from the servlet to the JSP using request attributes. Servlets are classes that contain methods executed by the server in response to requests, rather than generating web pages directly.