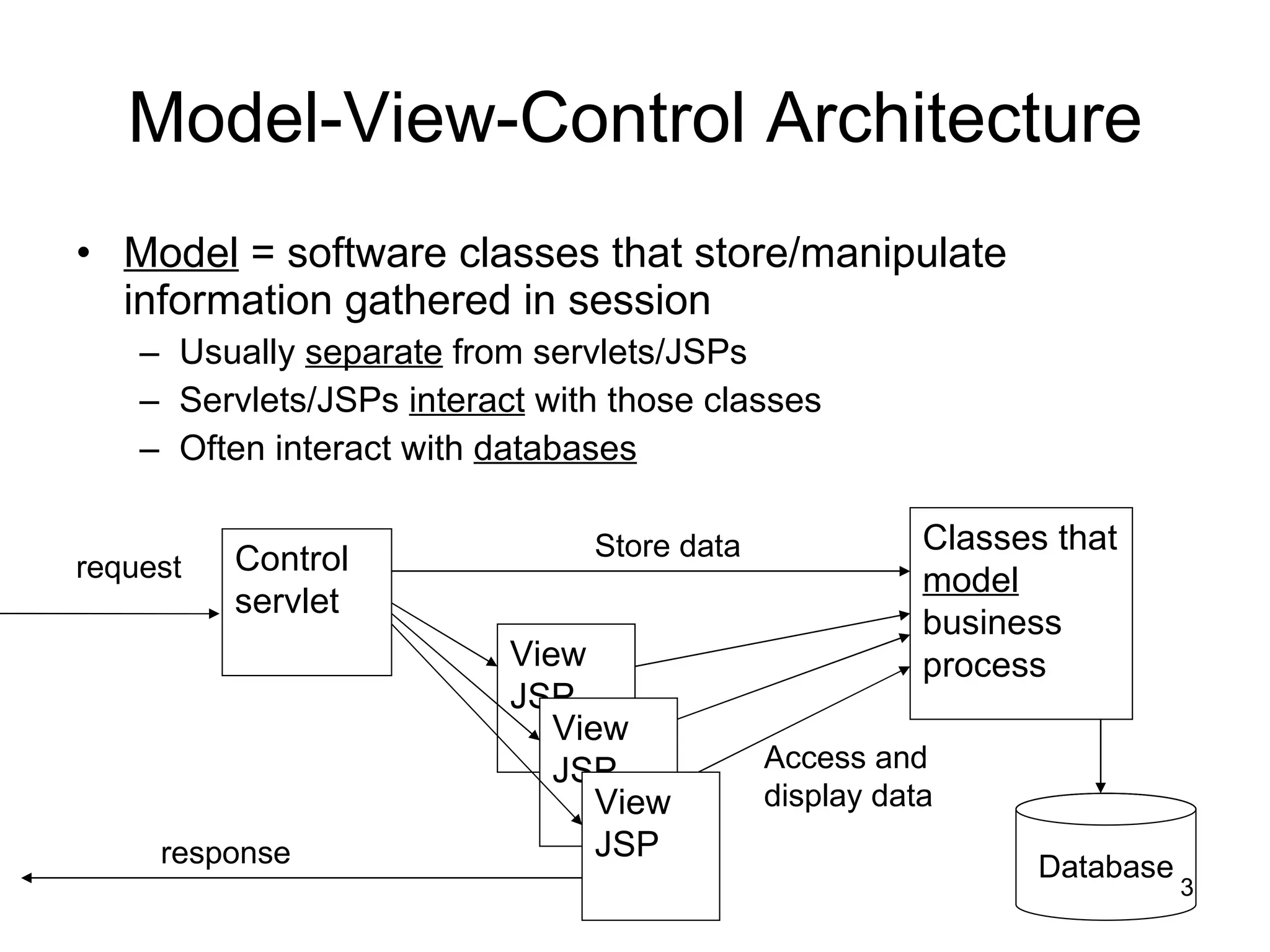
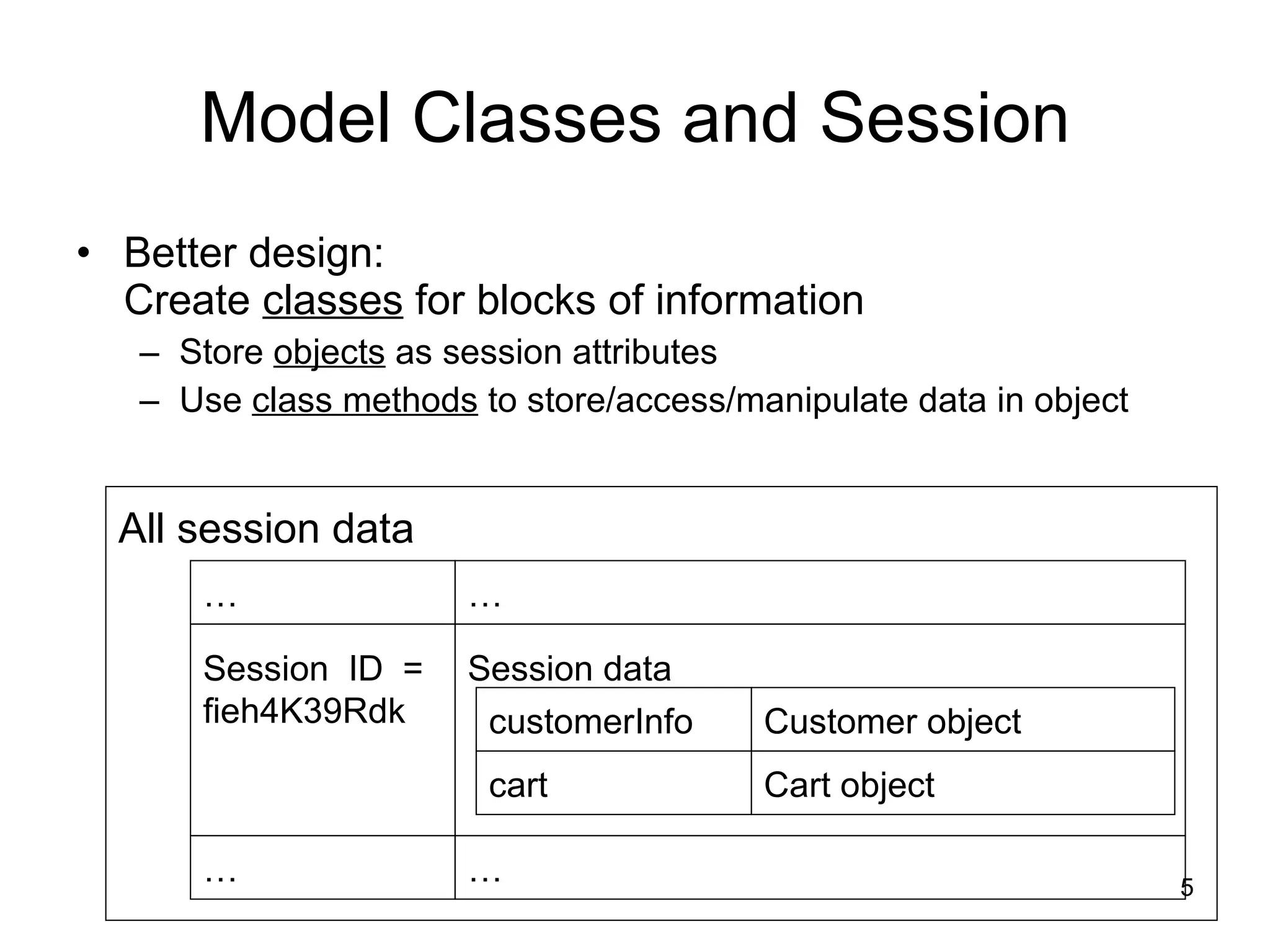
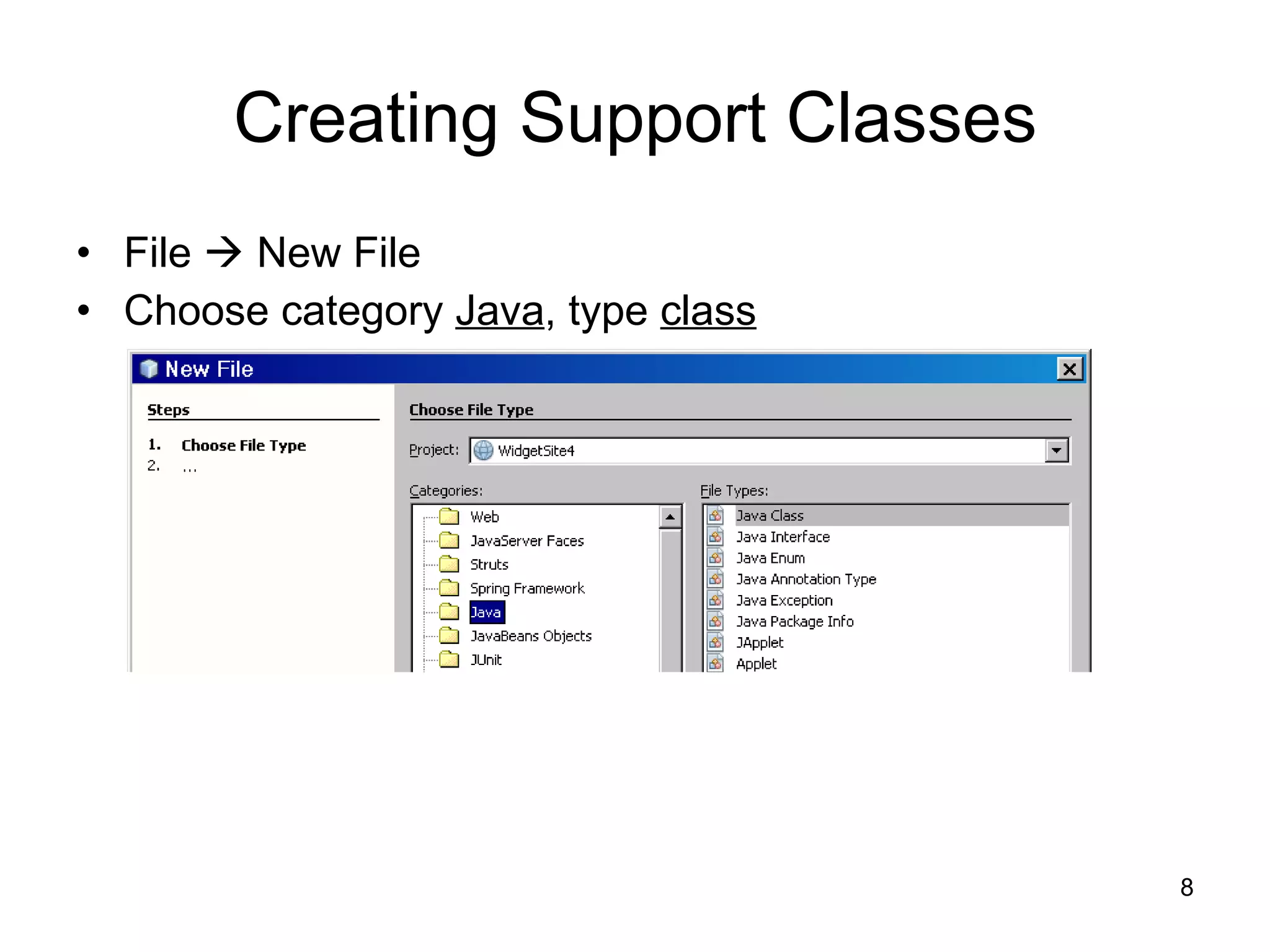
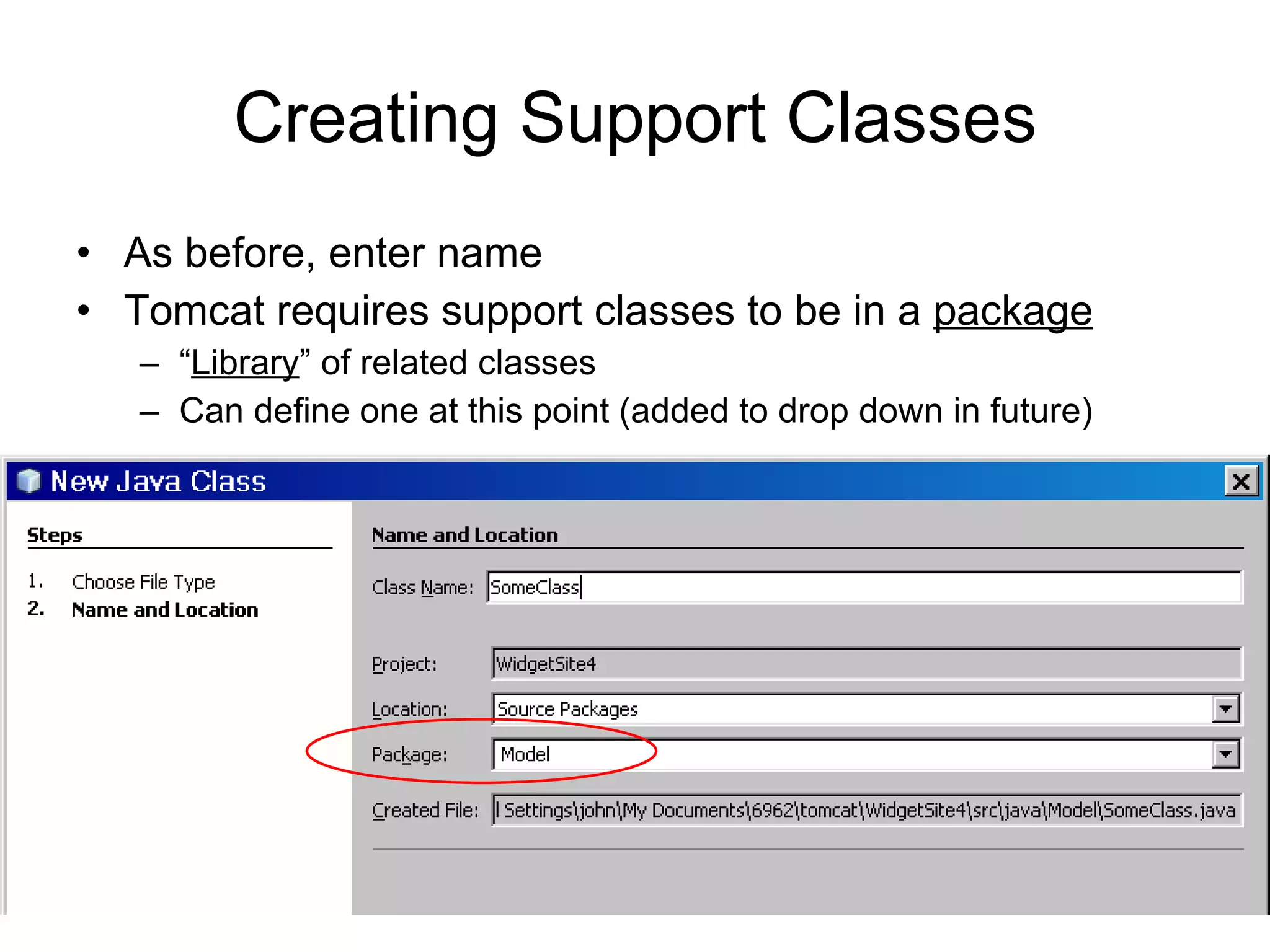
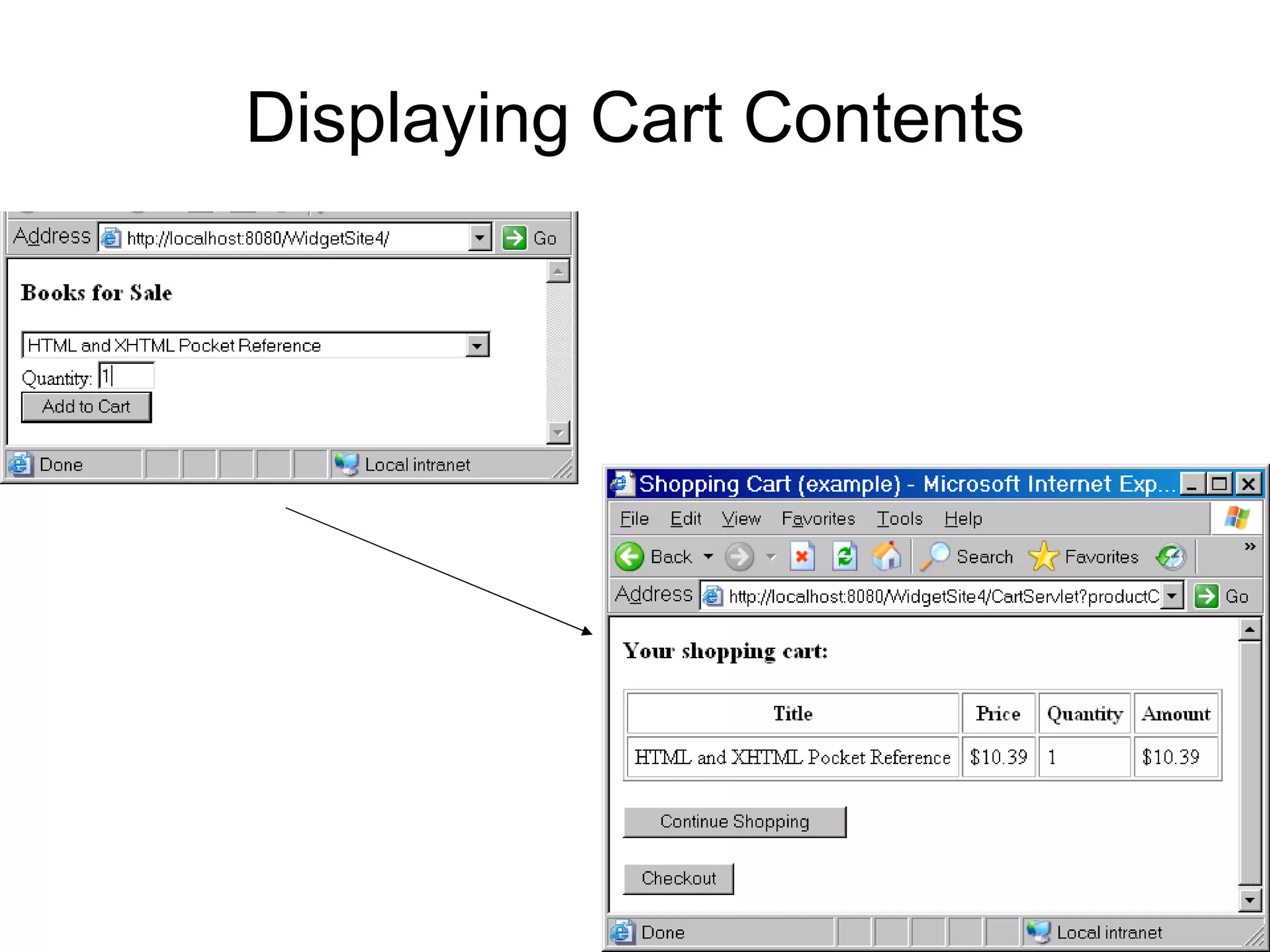
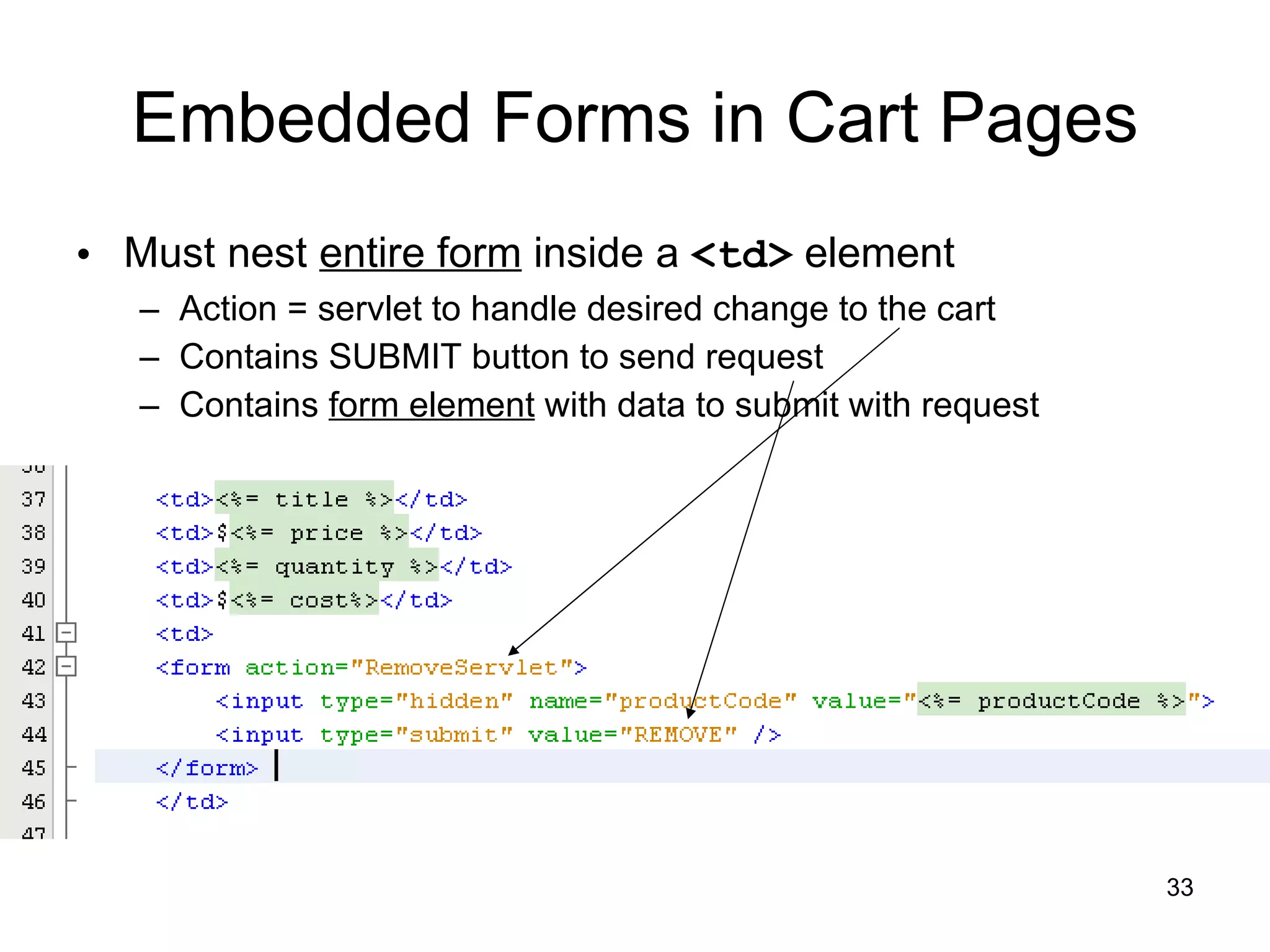
The document discusses model-view-controller (MVC) architecture as it relates to server-side web programming and shopping cart applications. It describes using model classes to store and manipulate session data rather than storing all data as session attributes. Model classes encapsulate related data and business logic. Servlets interact with model classes to store and retrieve data, while JSPs display data by accessing model class getter methods. The document provides examples of model classes for a customer and shopping cart item, and how they would be used by servlets and JSPs to add items to a cart and display the cart contents.