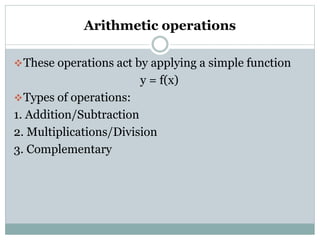
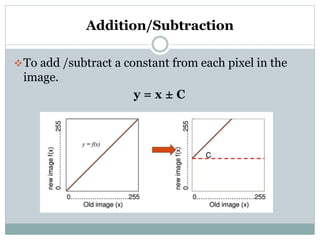
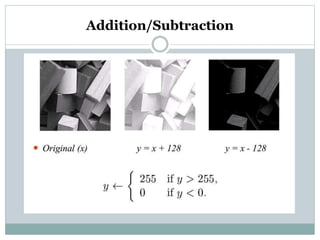
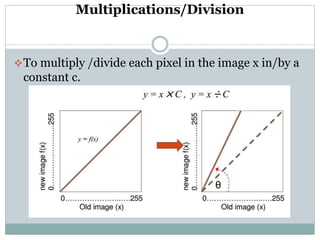
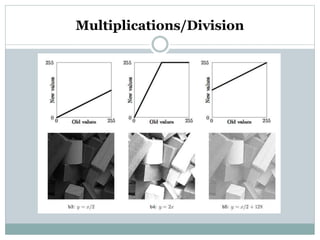
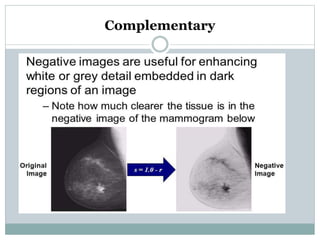
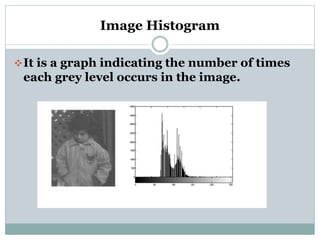
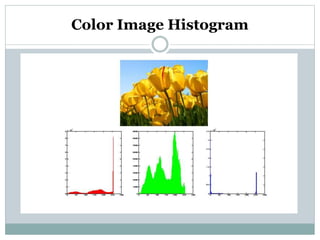
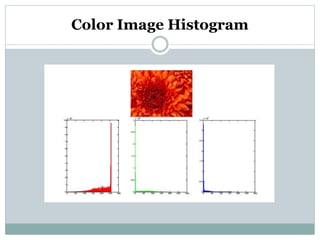
This document discusses various point operations that can be performed on digital images. Point operations modify pixel values without considering neighboring pixels. The key point operations covered are arithmetic operations like addition/subtraction and multiplication/division, color operations like changing lighting color and swapping/eliminating channels, multiple image operations like combining two images, and histograms which show pixel value distributions. Point operations are useful for image pre-processing tasks like contrast adjustment and color corrections.