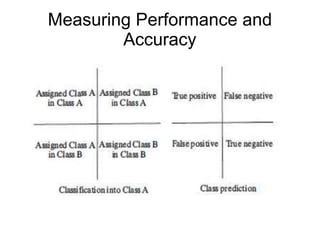
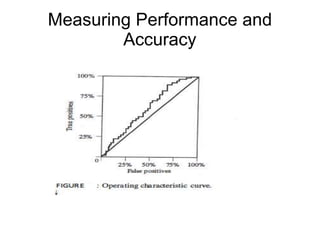
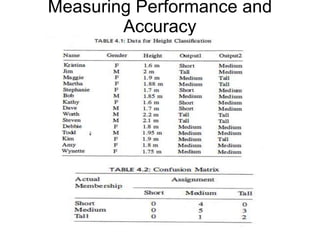
This document discusses classification algorithms. It introduces statistical, distance-based, tree-based, rule-based, neural network-based, and combining classification techniques. It defines classification as mapping input data to classes. The problem is solved in two phases: creating a model from training data and applying the model to classify new data. Issues like missing data and performance measurement are also covered. Performance is measured by calculating classification accuracy as a percentage of correctly classified instances using a confusion matrix of true positives, false positives, true negatives and false negatives.