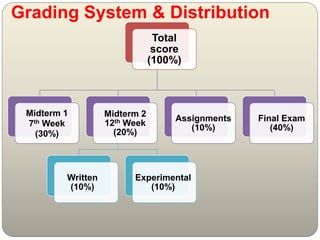
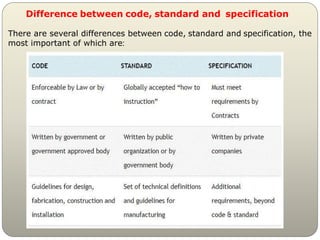
This document outlines the contents and structure of a lecture on differences among codes, standards, and specifications for electro-mechanical systems. The lecture will cover international standards like IEC, firefighting codes from NFPA, HVAC standards, and international building codes. It will be graded based on midterms, assignments, experiments, and a final exam. References will include Egyptian codes, IEC, NFPA, ASHRAE, and IEEE standards. Definitions provided clarify that standards describe how to do something, codes are legally enforceable and reference standards, and specifications provide additional product or application requirements beyond codes and standards.