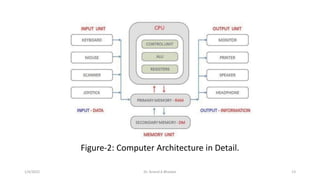
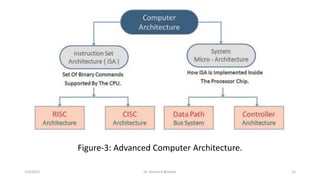
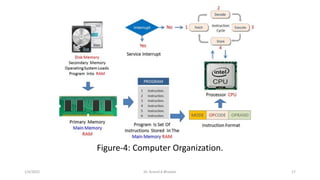
This document outlines the course content for the course "EC-2262: Computer Organization and Architecture". The course is a 3 credit course offered in the 4th semester of the B.Tech program. It will cover the basic structure and operation of computers, including data representation, arithmetic algorithms, processor organization, control unit design, memory organization, I/O organization, and advanced processor principles. The goal is for students to understand computer architecture fundamentals and how digital computers are designed and function at a basic level.