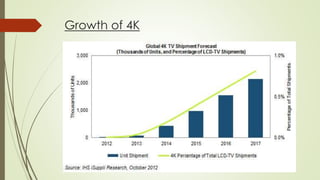
The document discusses 4k display technology, detailing its resolution, history, and the differences between 4k and 1080p formats. It covers technical specifications, advantages, and disadvantages of 4k, as well as mentions the emerging 8k technology. The conclusion suggests that while 4k offers better resolution, factors like contrast ratio and color quality are more important for overall picture quality.