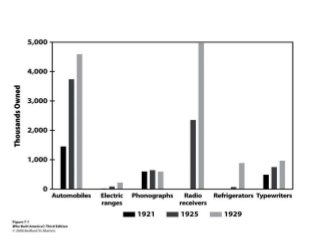
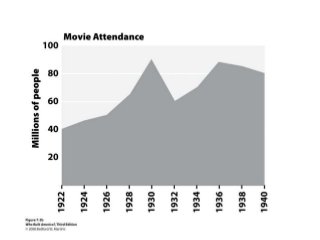
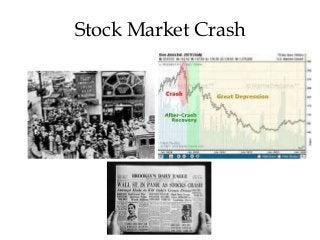
This document summarizes women's experiences in the United States from the 1920s to 1945. It discusses key events and movements such as women gaining the right to vote in 1920, the flapper culture of the 1920s, women's increasing participation in the workforce during this period, as well as their roles during the Great Depression and World War II when many took jobs in factories and the military. The document also mentions figures like Margaret Sanger who advocated for birth control, as well as Amelia Earhart and Eleanor Roosevelt, reflecting the expanding opportunities and activism of women during this transformative period in American history.