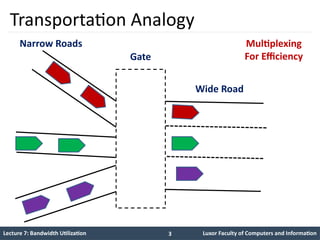
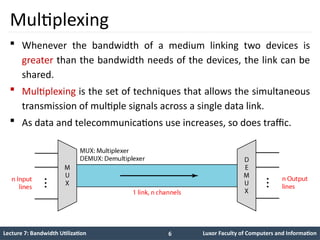
The document is a lecture on bandwidth utilization in data communications, covering topics such as multiplexing techniques (FM, WDM, TDM), efficient bandwidth use, and spread spectrum methods for privacy and security. It details analog and digital multiplexing techniques, including frequency-division and time-division methods, and explores concepts like synchronous TDM and spread spectrum techniques like FHSS and DSSS. The lecture includes various examples and calculations relevant to bandwidth requirements and multiplexing processes.