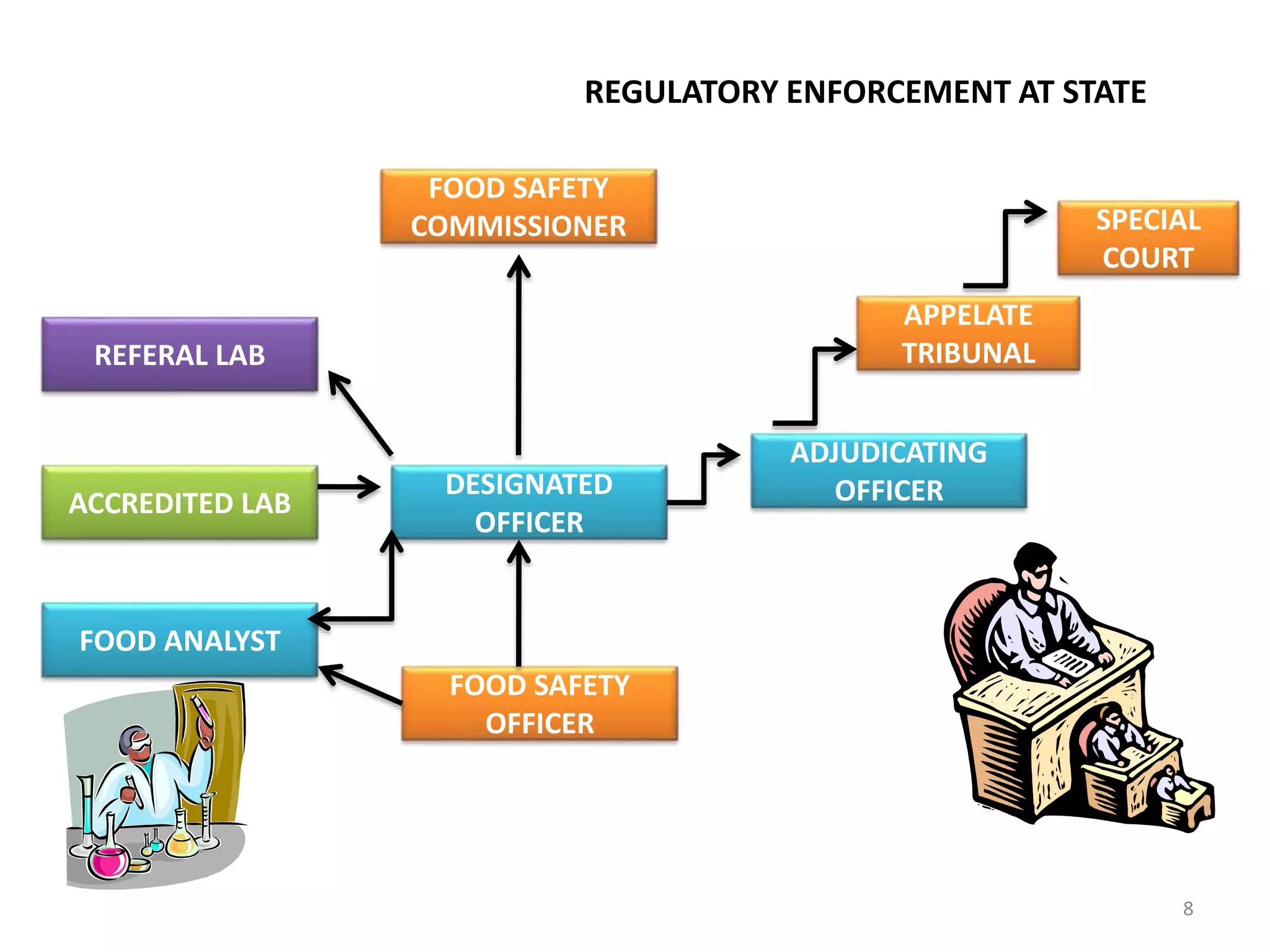
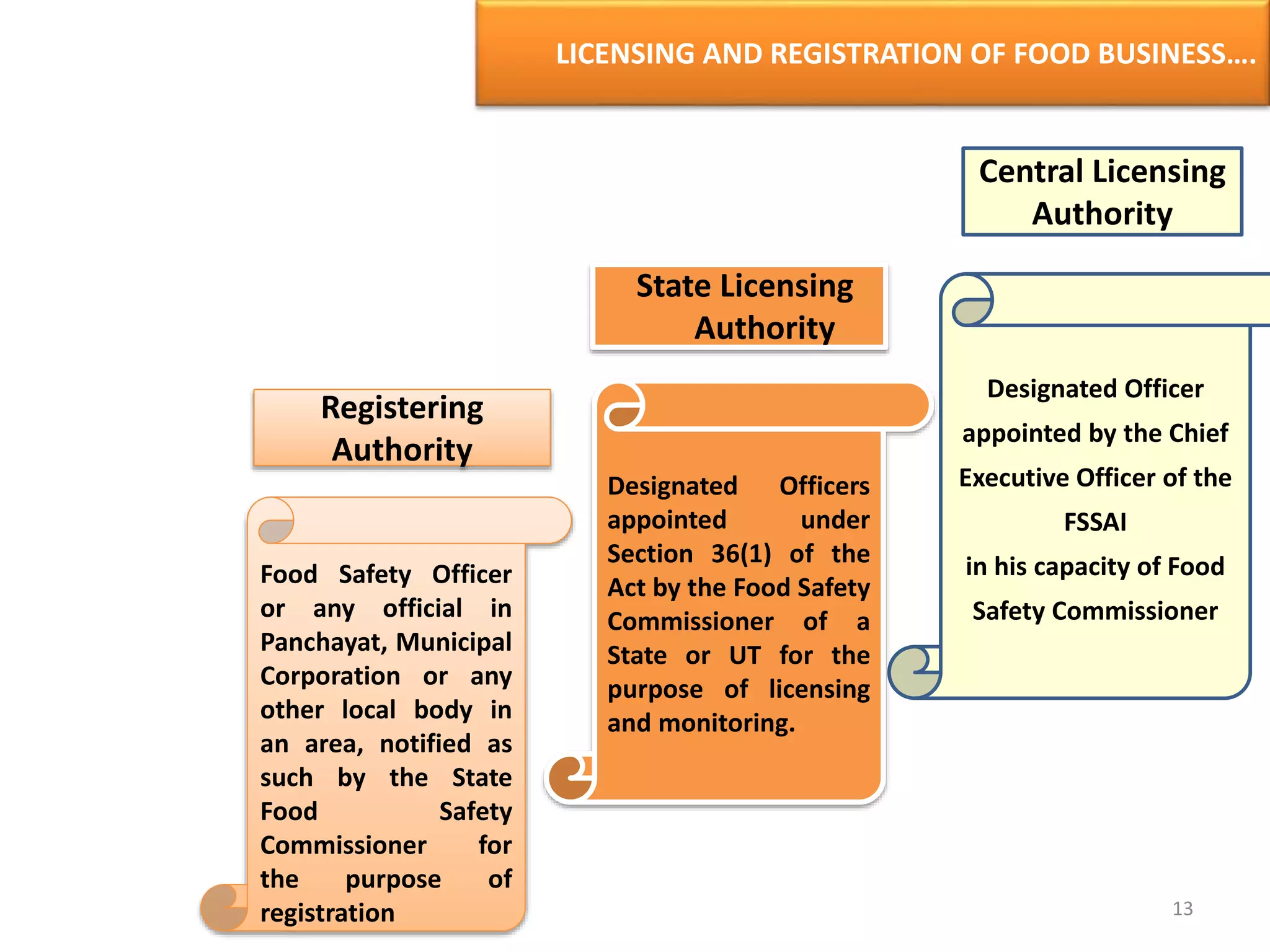
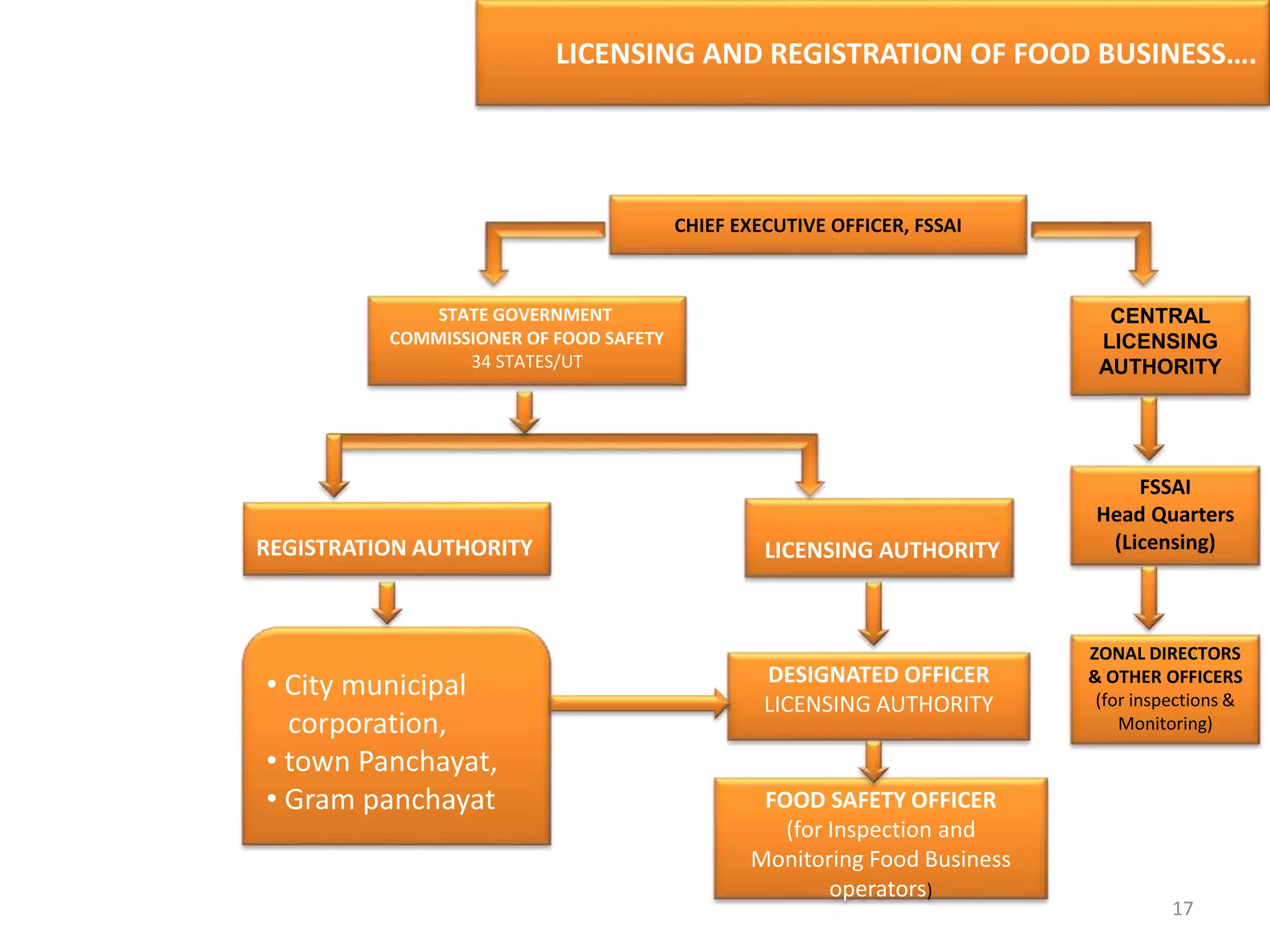
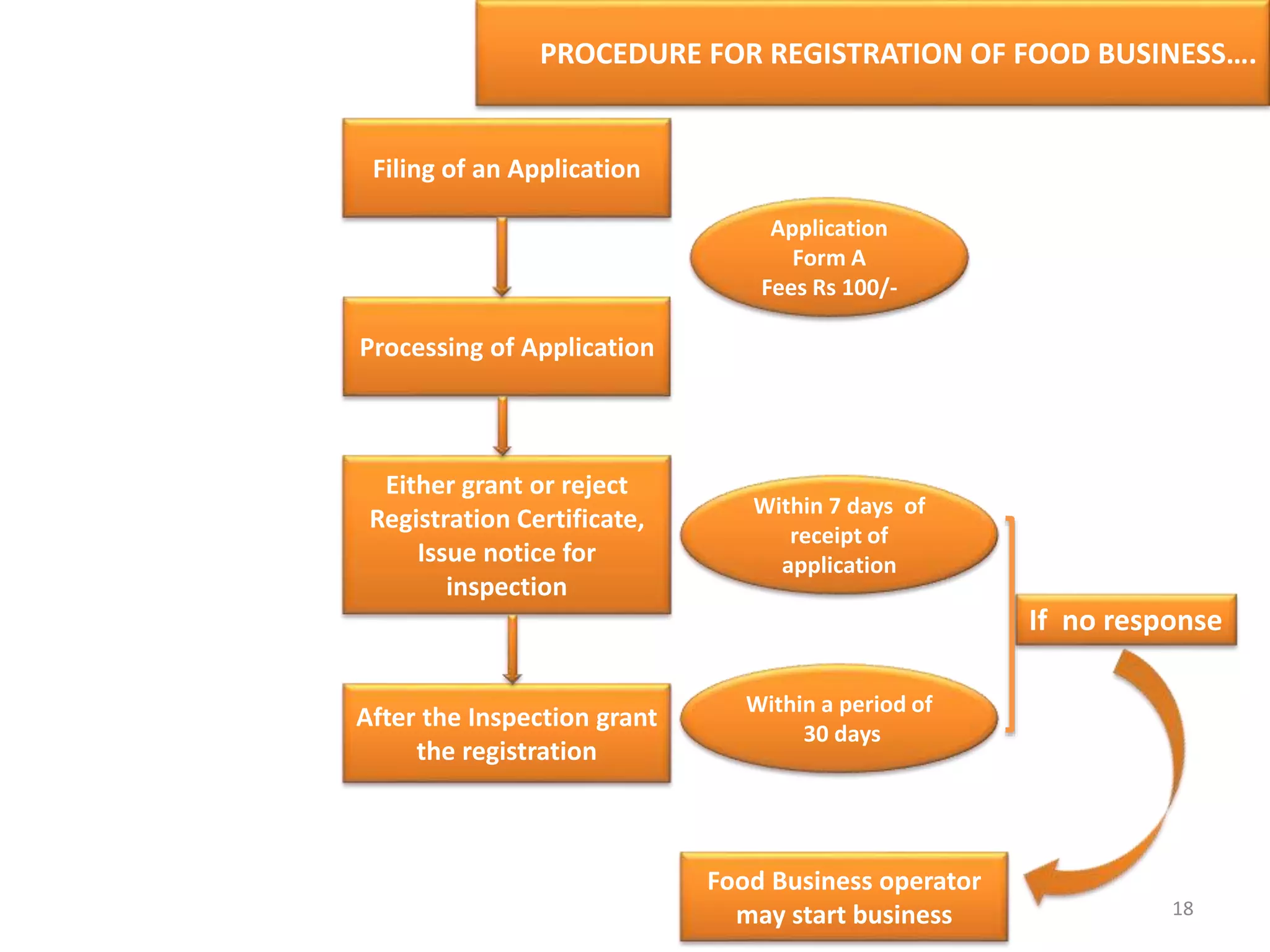
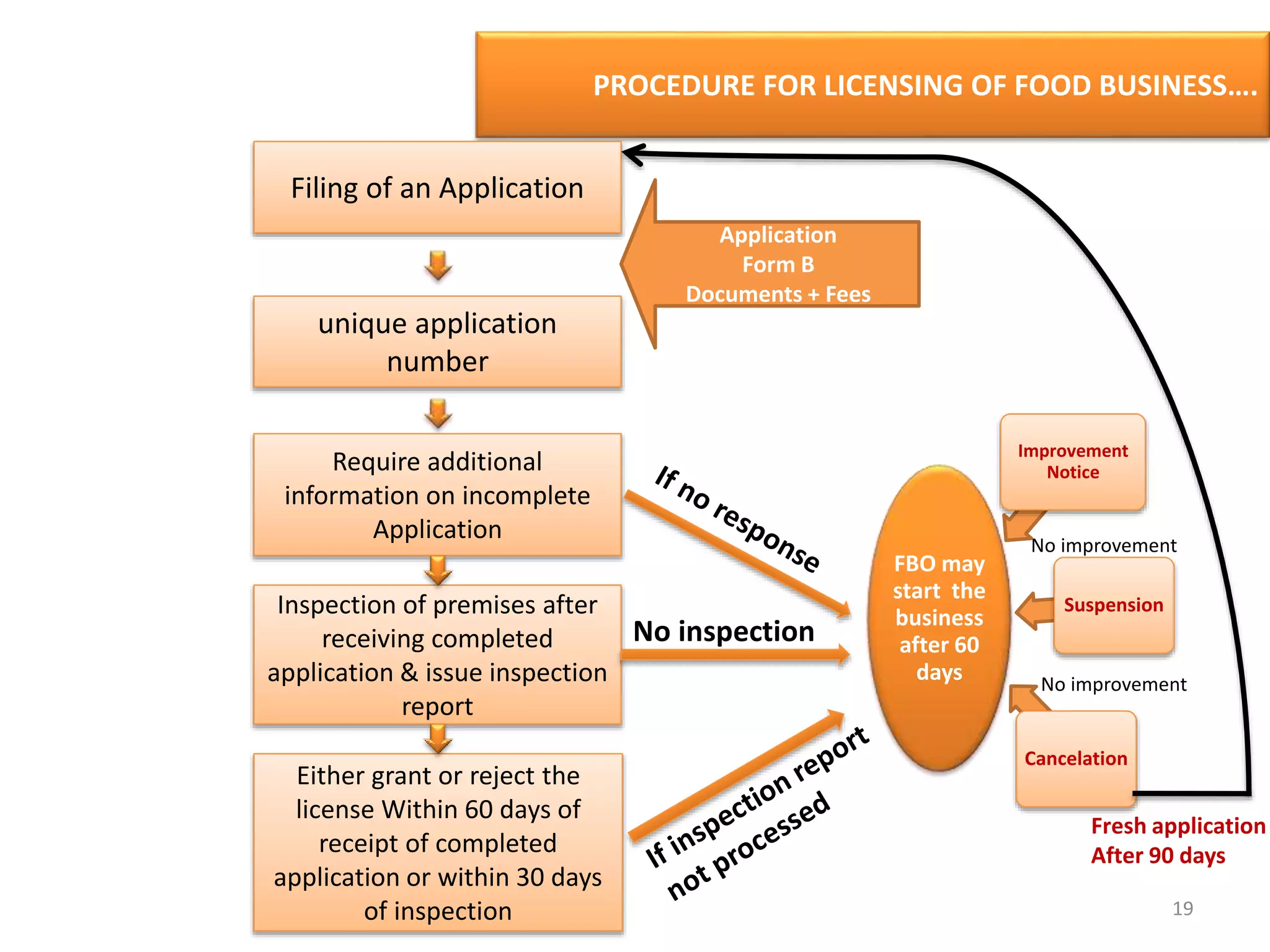
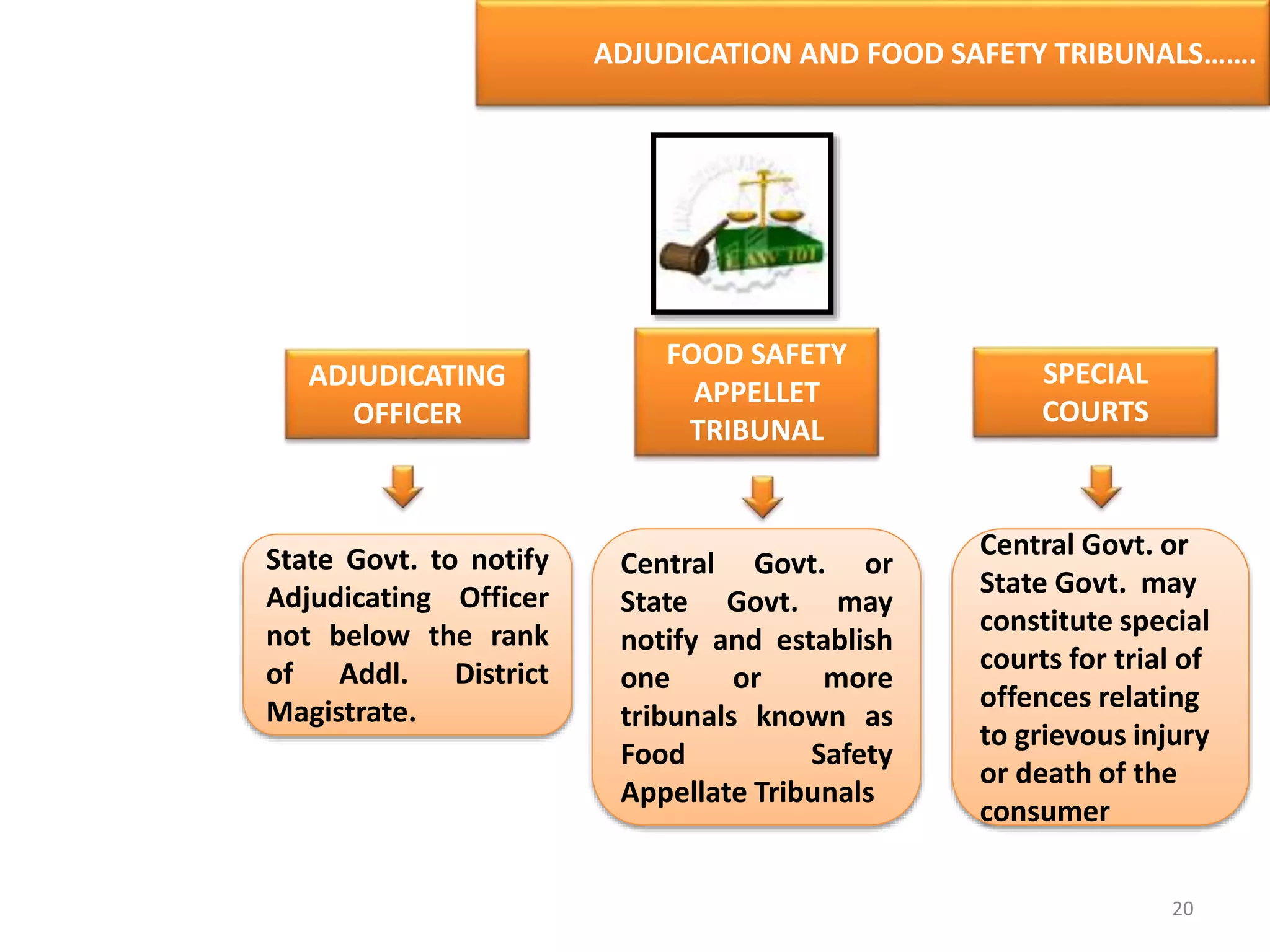
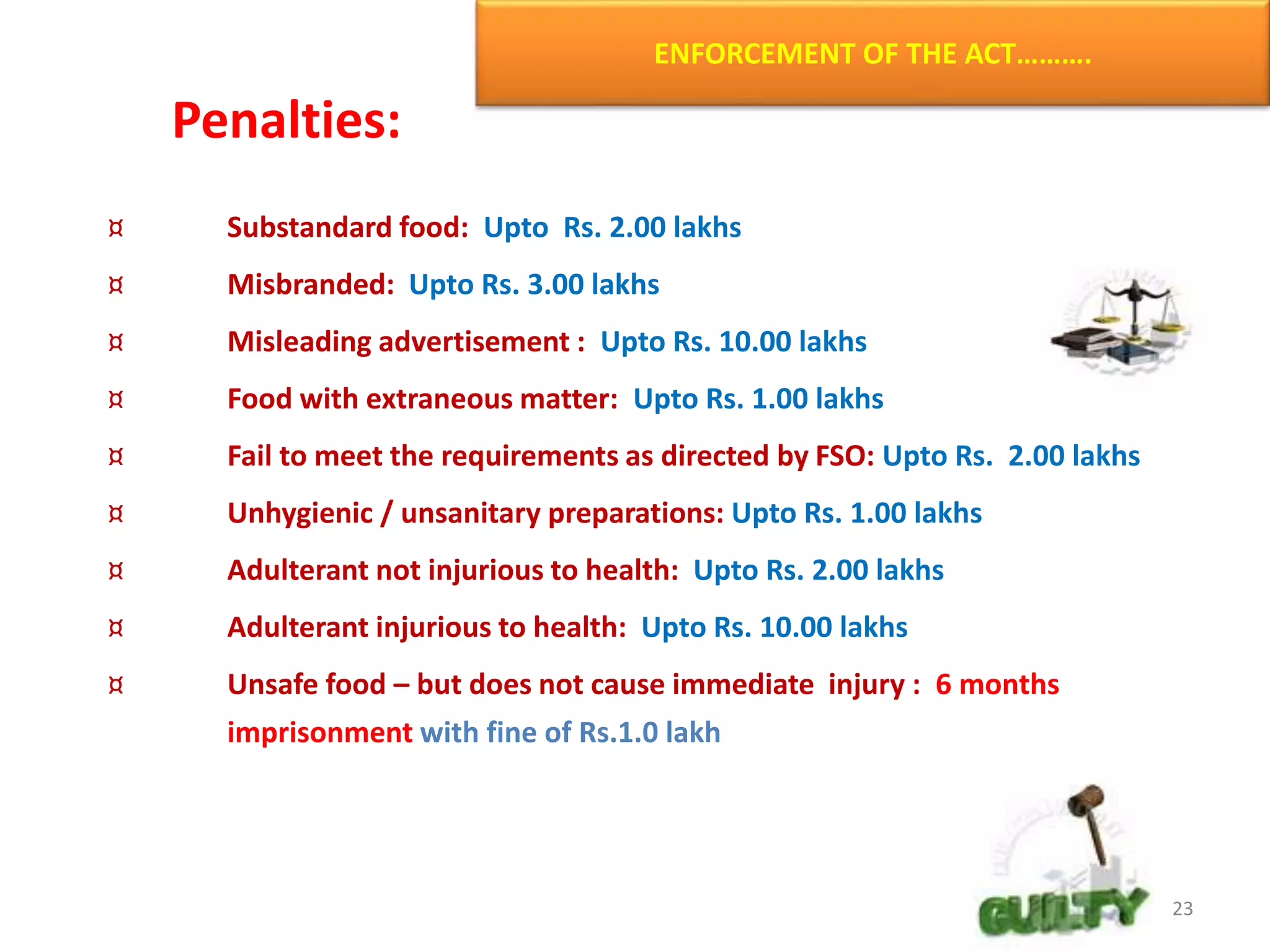
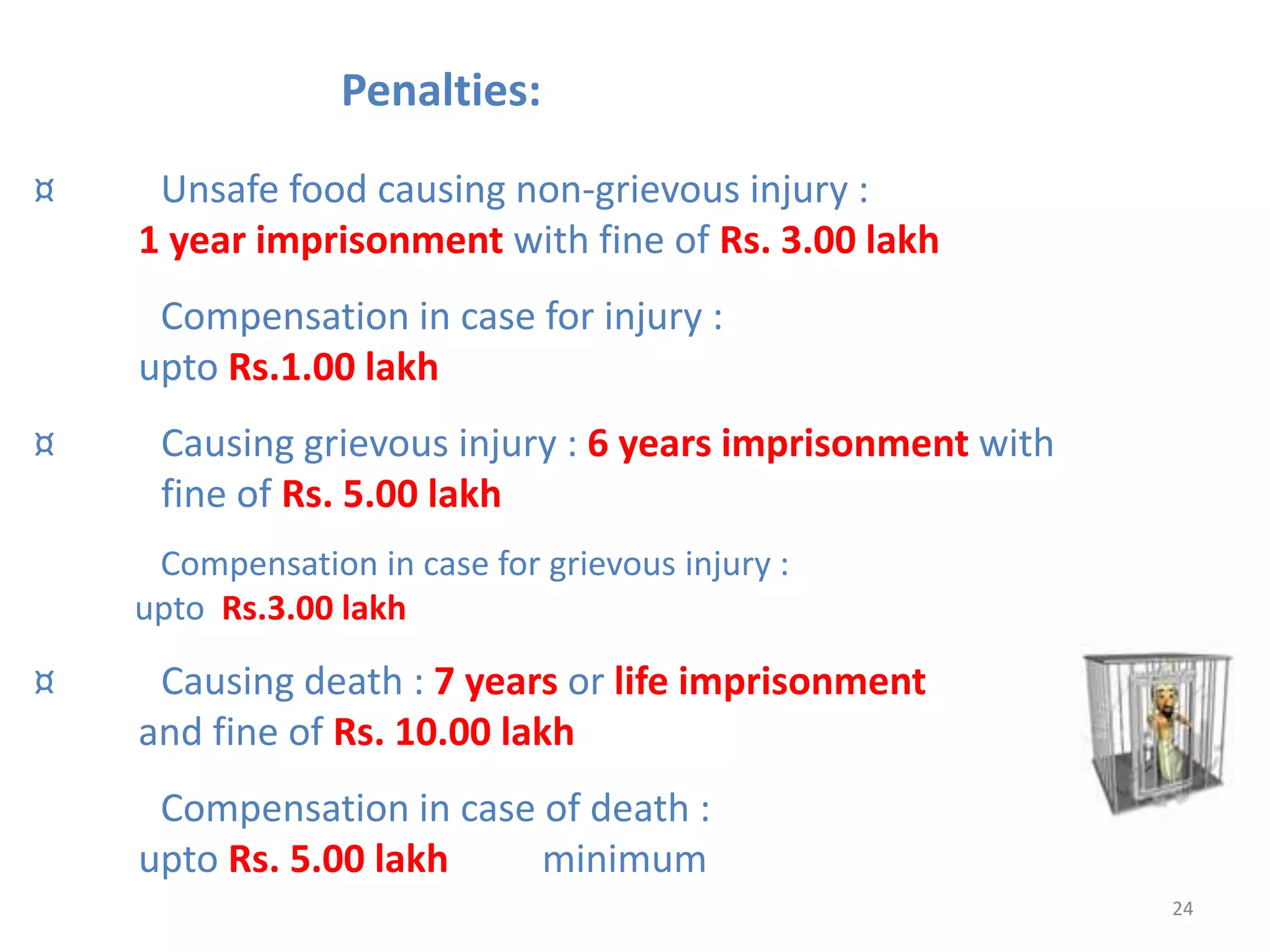
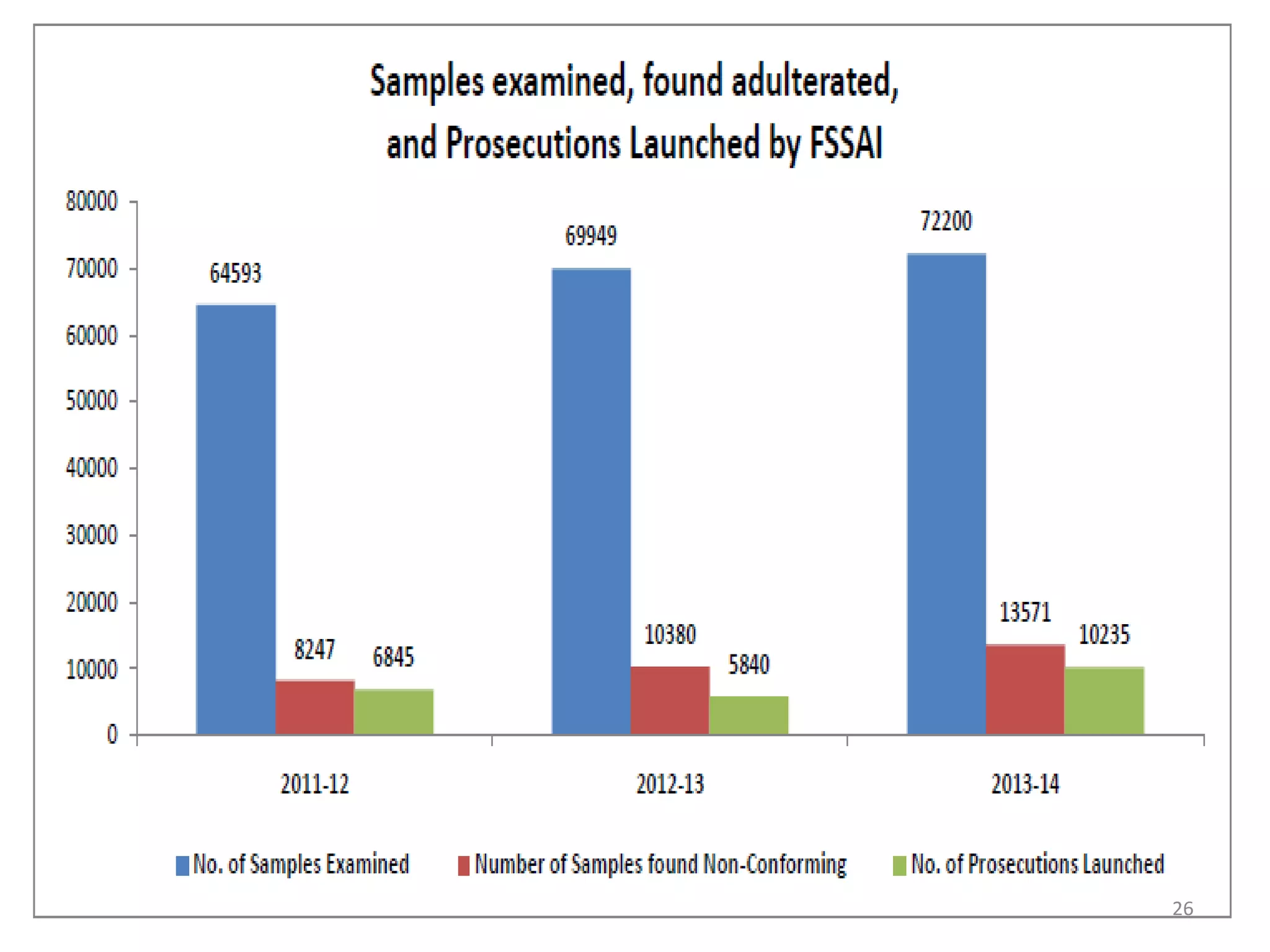
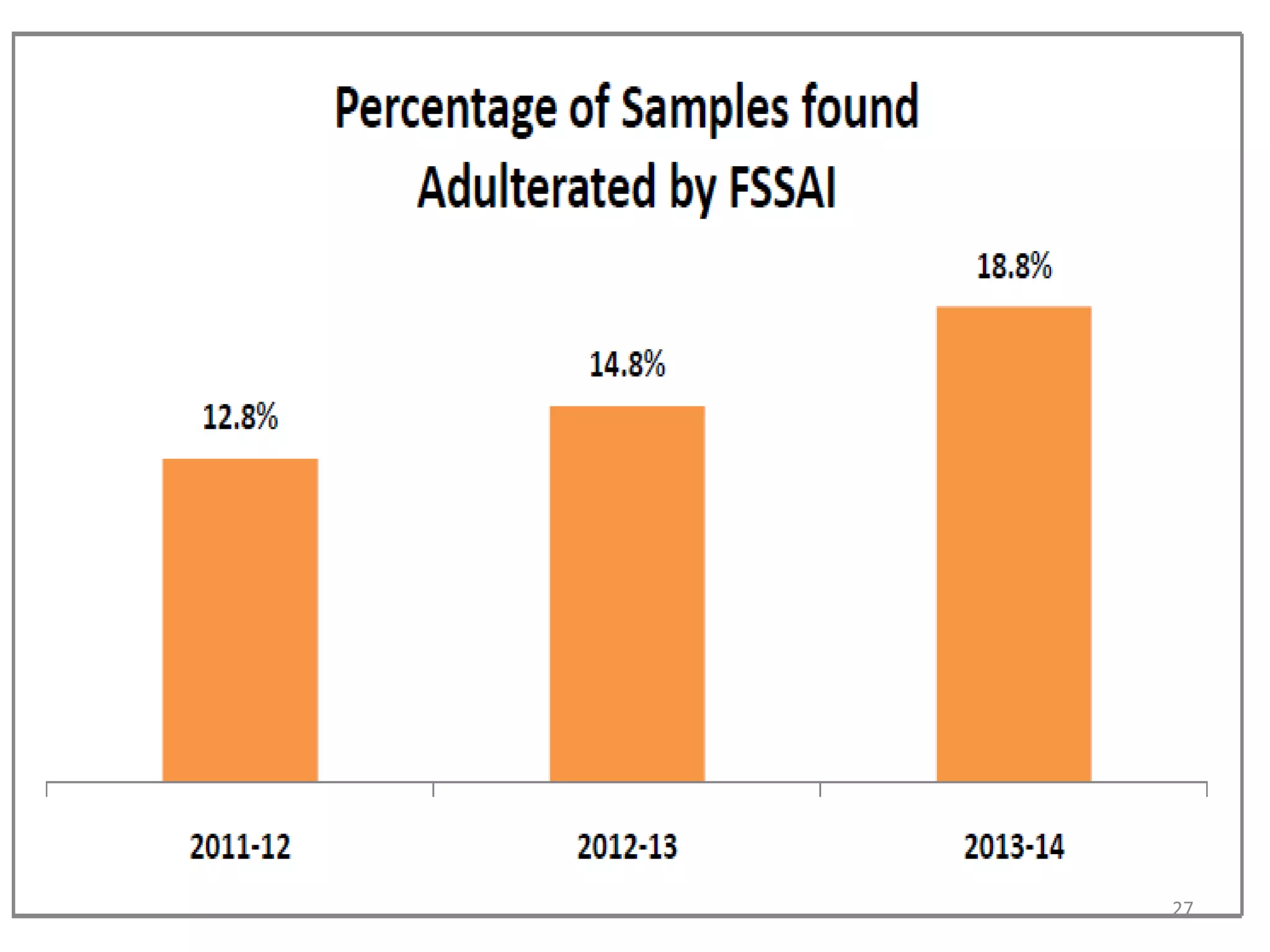
The document provides information about food safety legislation in India. It discusses the need for new consolidated food safety laws to replace existing fragmented laws governed by multiple ministries. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) was established in 2006 under the Food Safety and Standards Act to harmonize and consolidate food safety laws. The Act introduced science-based standards for food articles and established a single regulatory body for food safety. Key functions of FSSAI include setting food standards, accreditation, quality control of imports, and providing scientific advice to governments. Enforcement occurs at the state level through commissioners, officers, and other designated authorities.