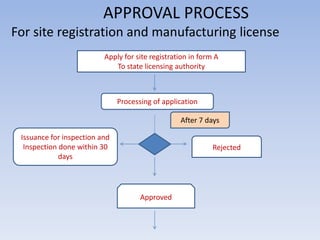
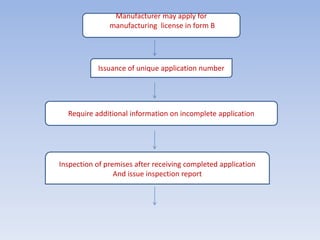
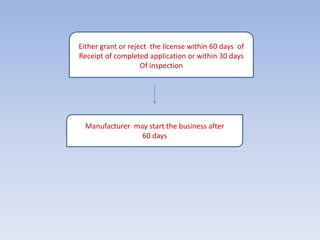
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) was established under the Food Safety and Standards Act of 2006. FSSAI is responsible for framing regulations and standards for food safety and enforcing food standards. It oversees a food licensing and registration system where food businesses must obtain a license or registration from FSSAI or state authorities depending on their annual turnover. The document outlines FSSAI's roles and responsibilities, food categories, license application processes, required documents, offences and penalties under the Act.