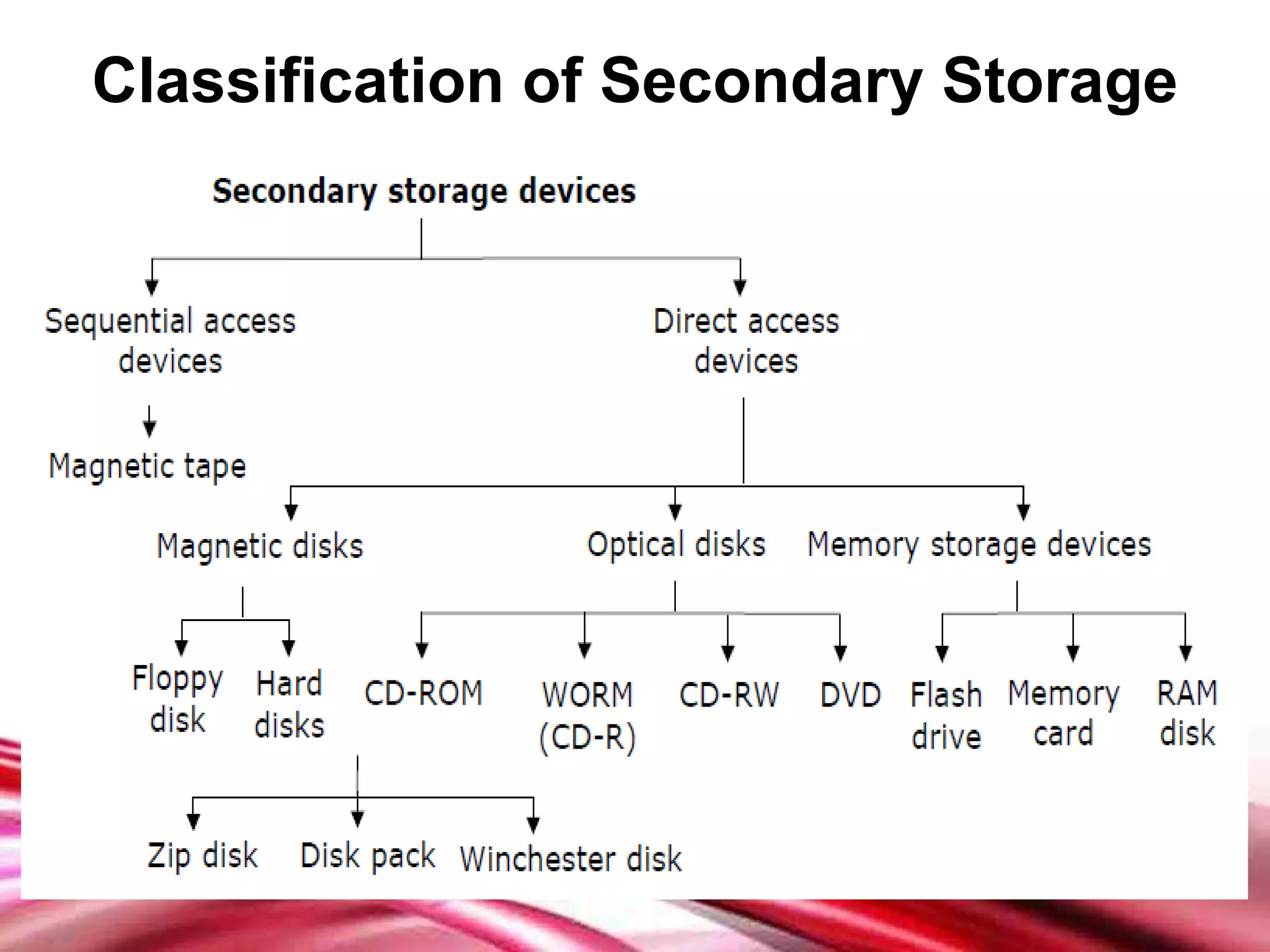
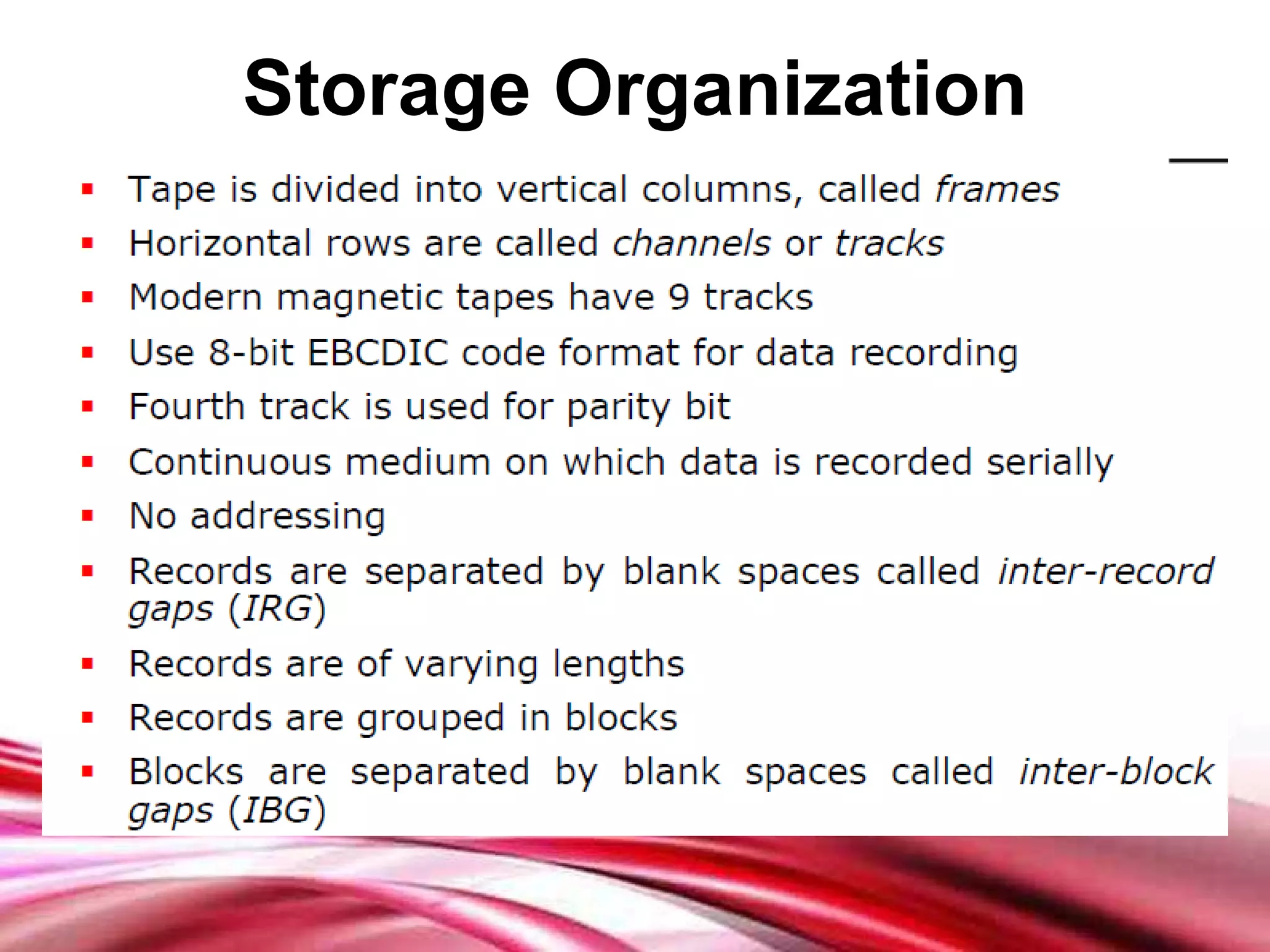
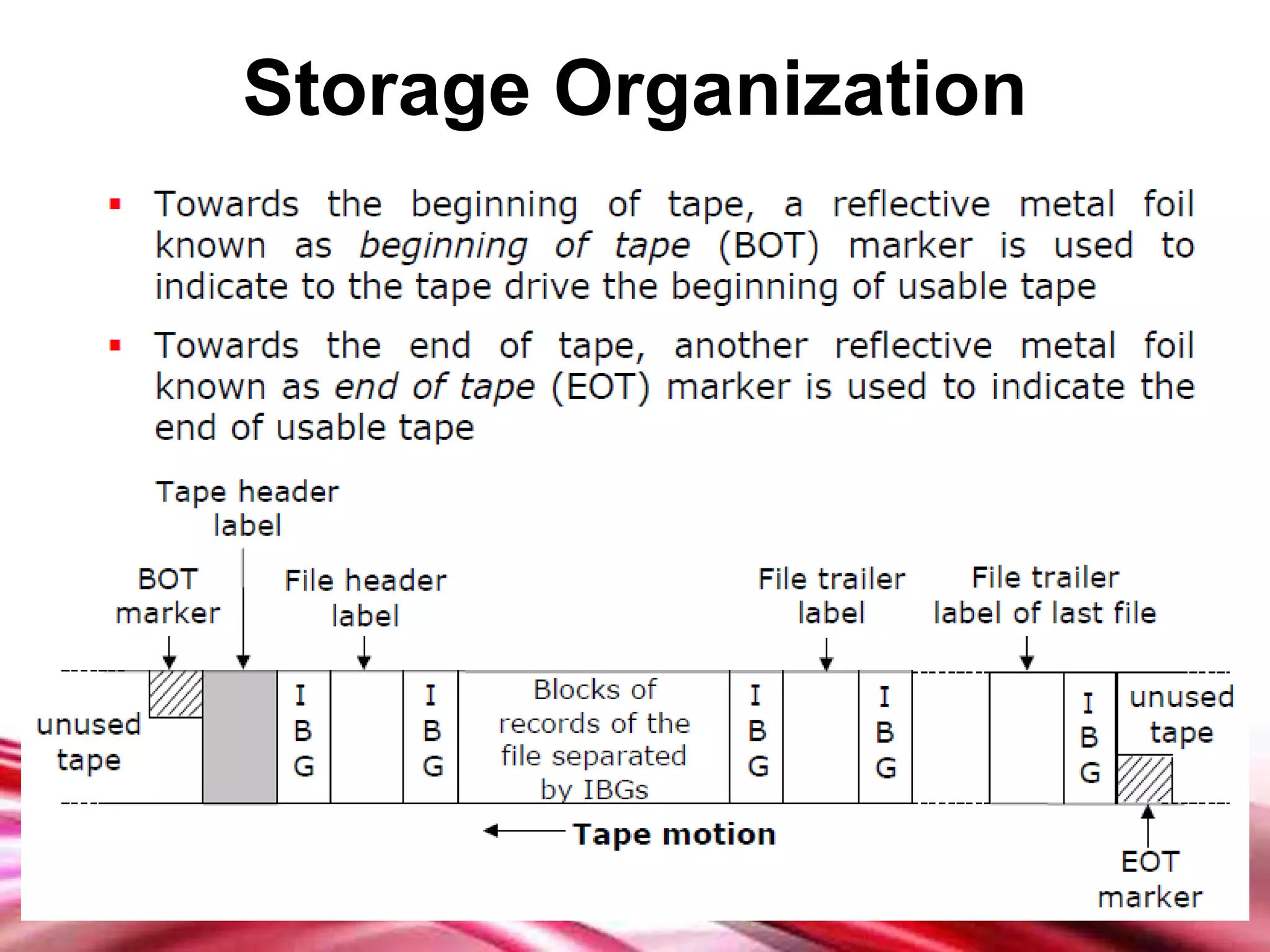
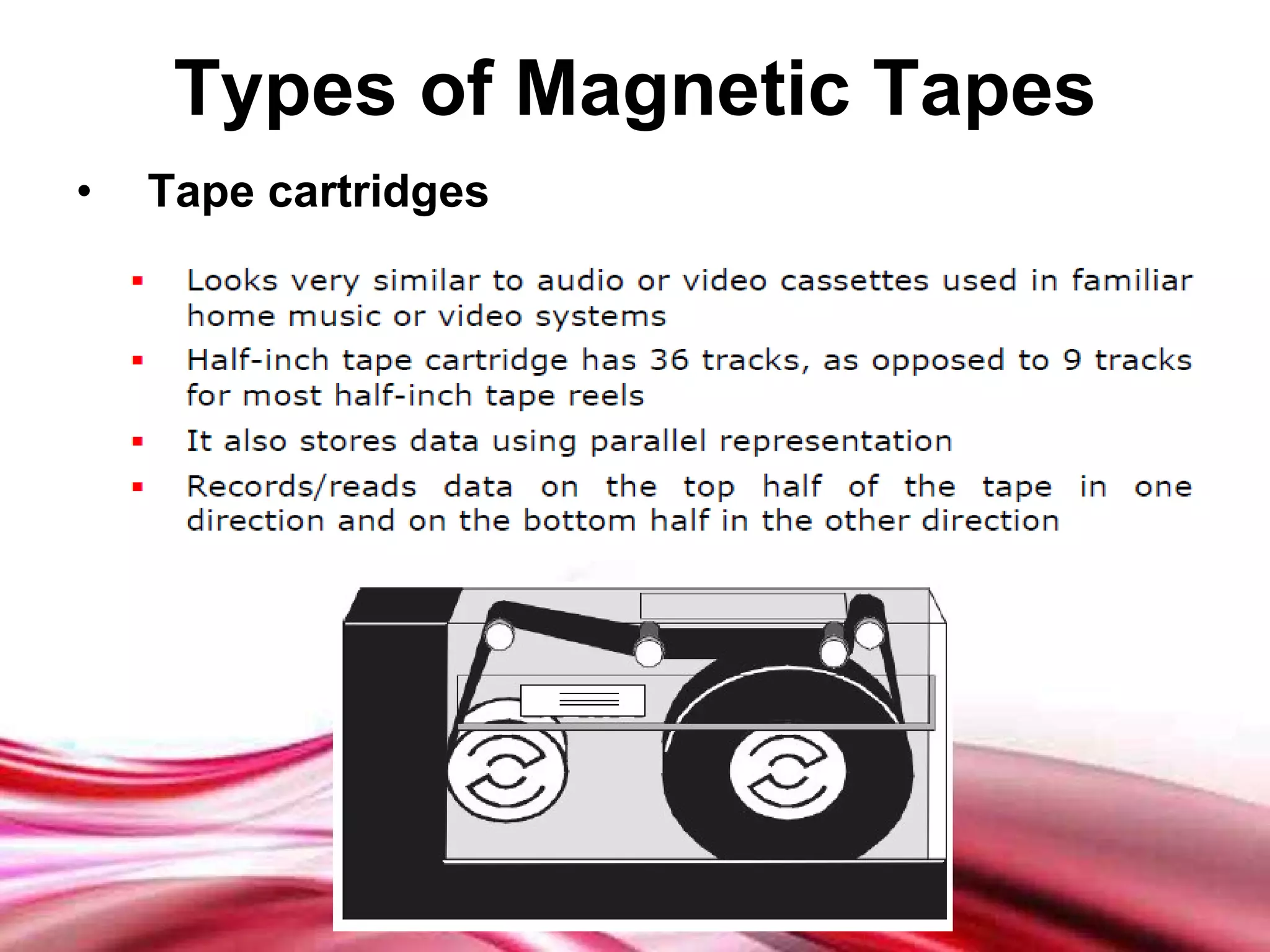
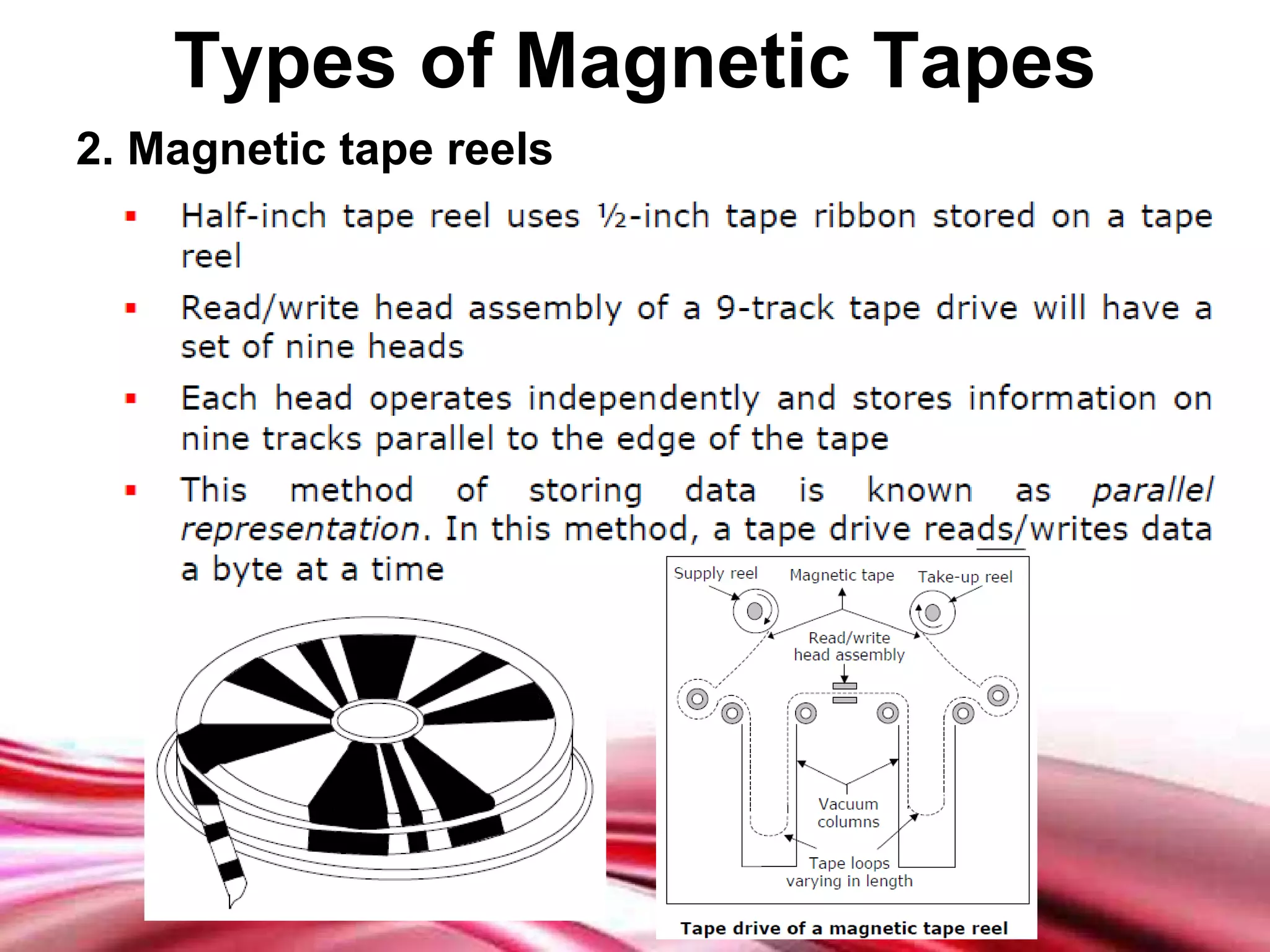
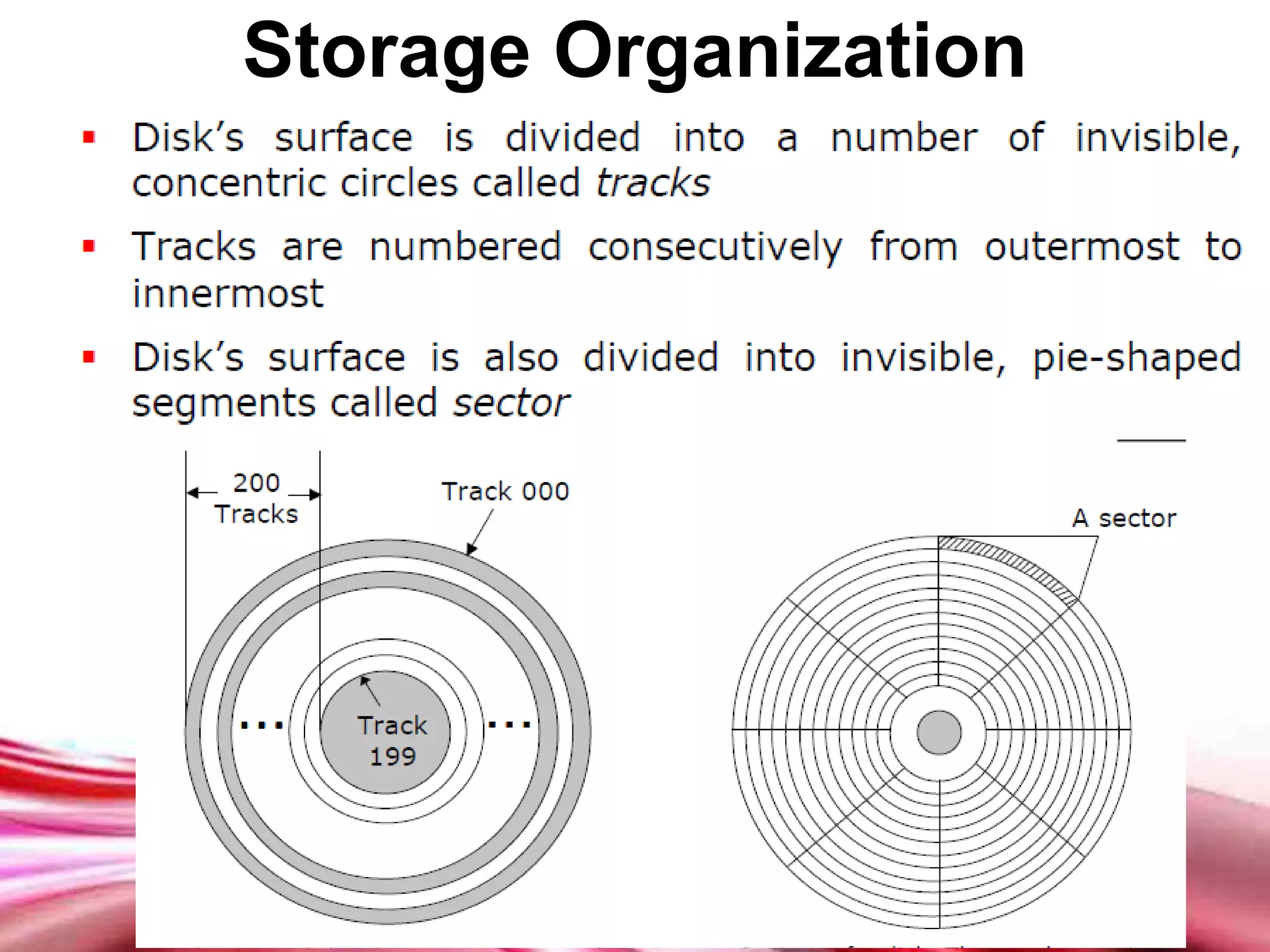
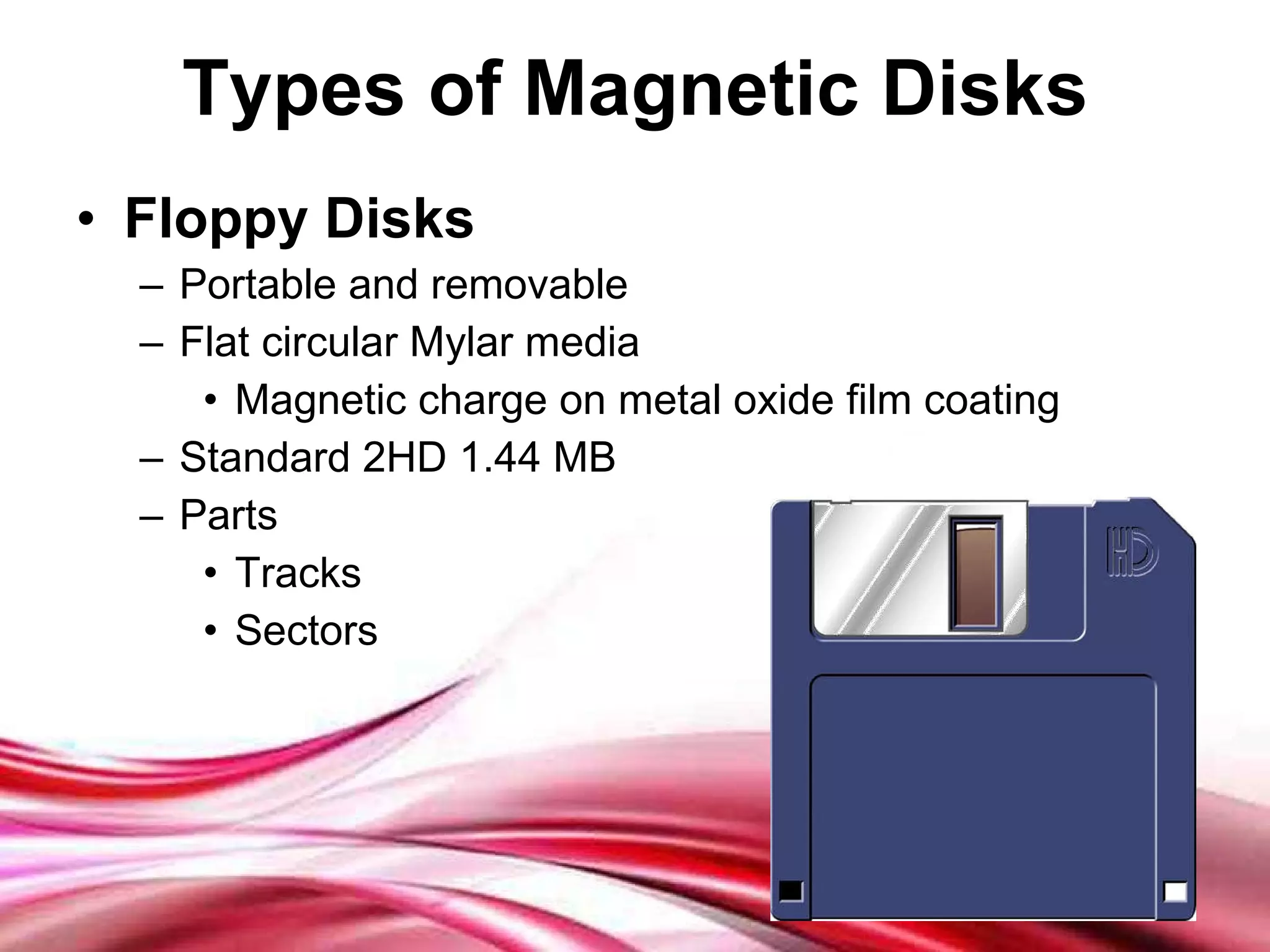
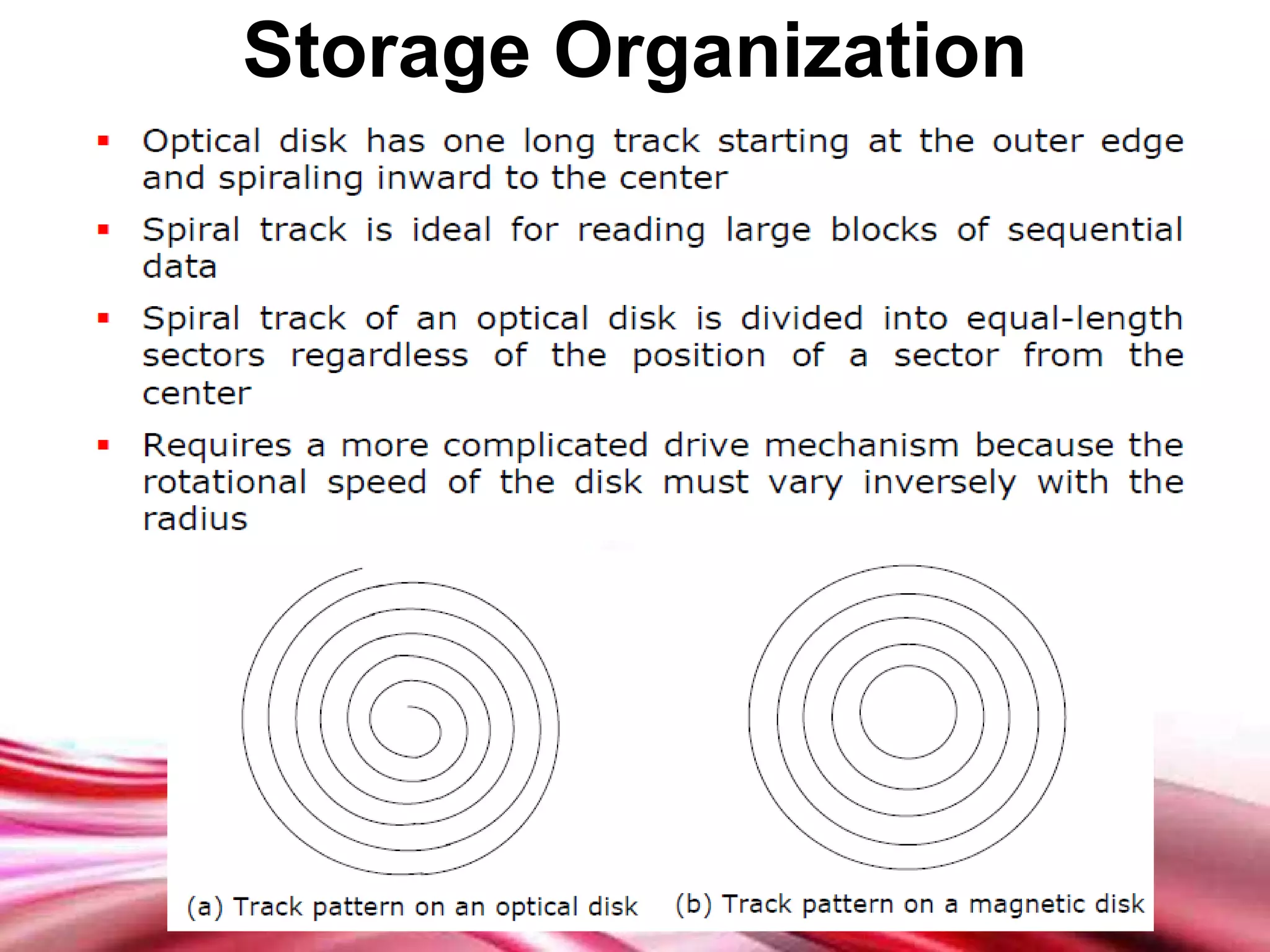
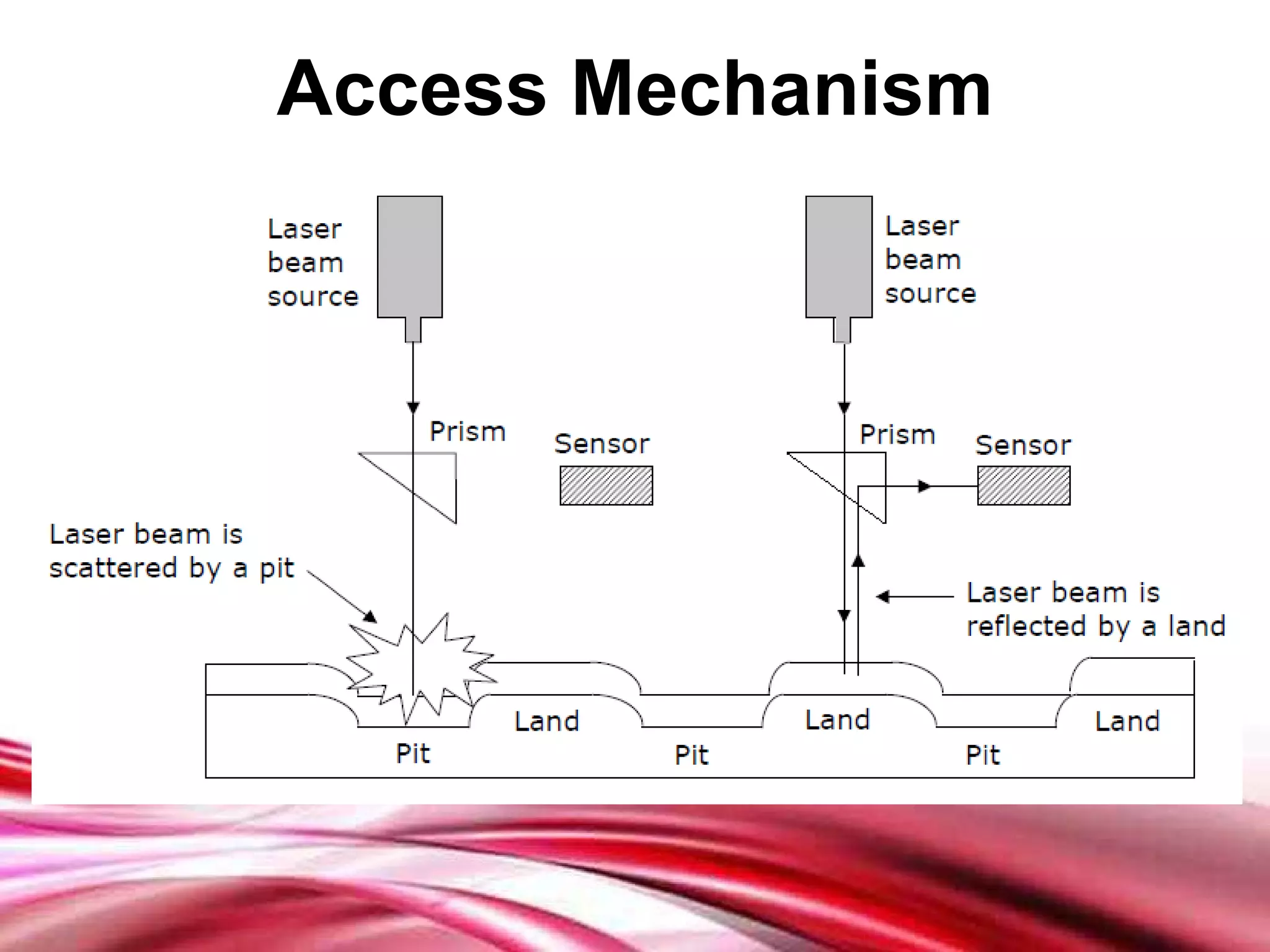
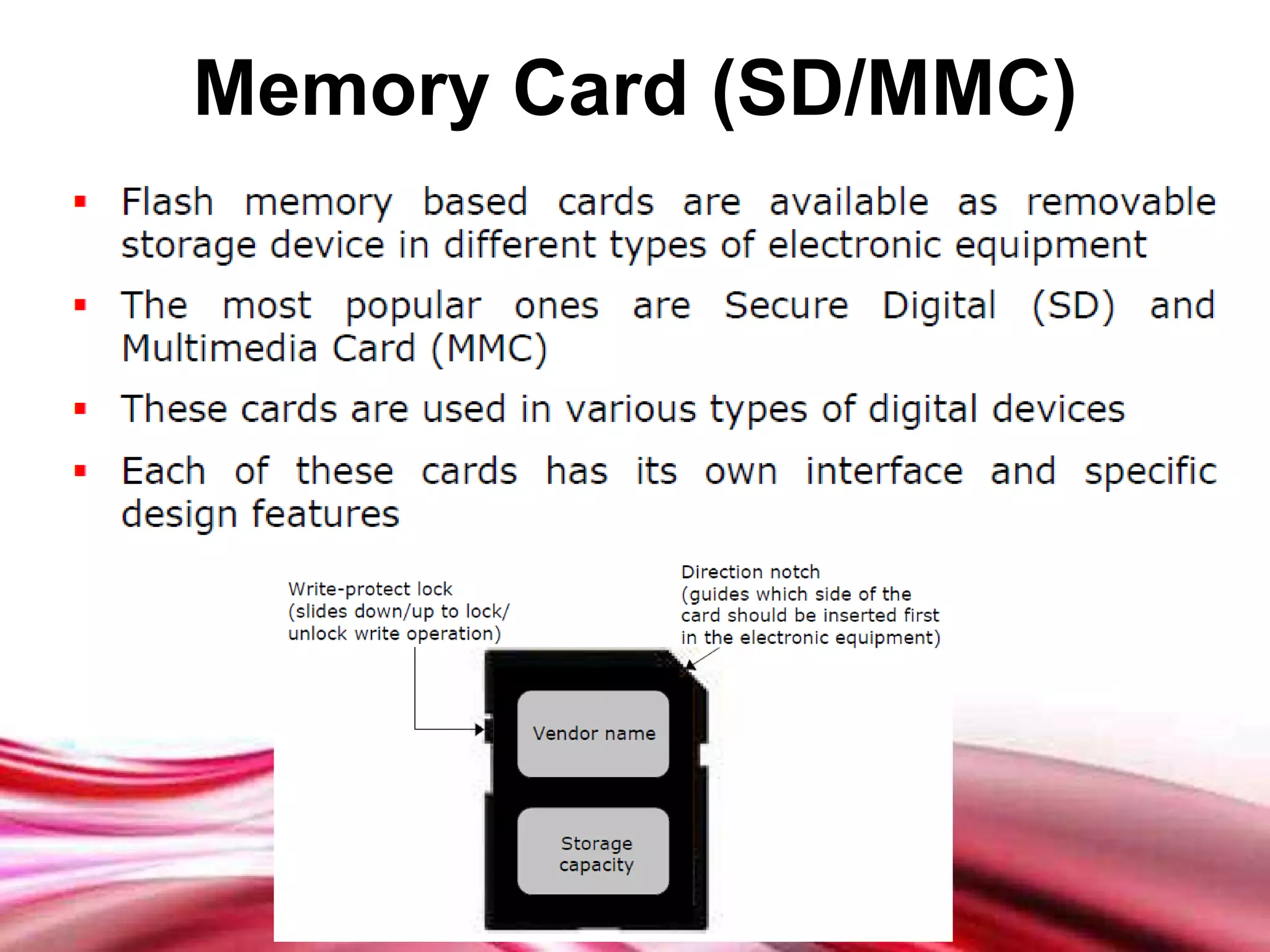
This document discusses different types of secondary storage devices including magnetic tape, magnetic disks, and optical disks. It describes the key characteristics and components of each type of storage device. Specifically, it covers how magnetic tape provides sequential access and large storage capacities. It also explains how magnetic disks can provide both direct and sequential access and compares floppy disks and hard disks. Finally, it outlines common optical disk formats like CDs, DVDs, and their read-only, write-once, and rewritable variants.