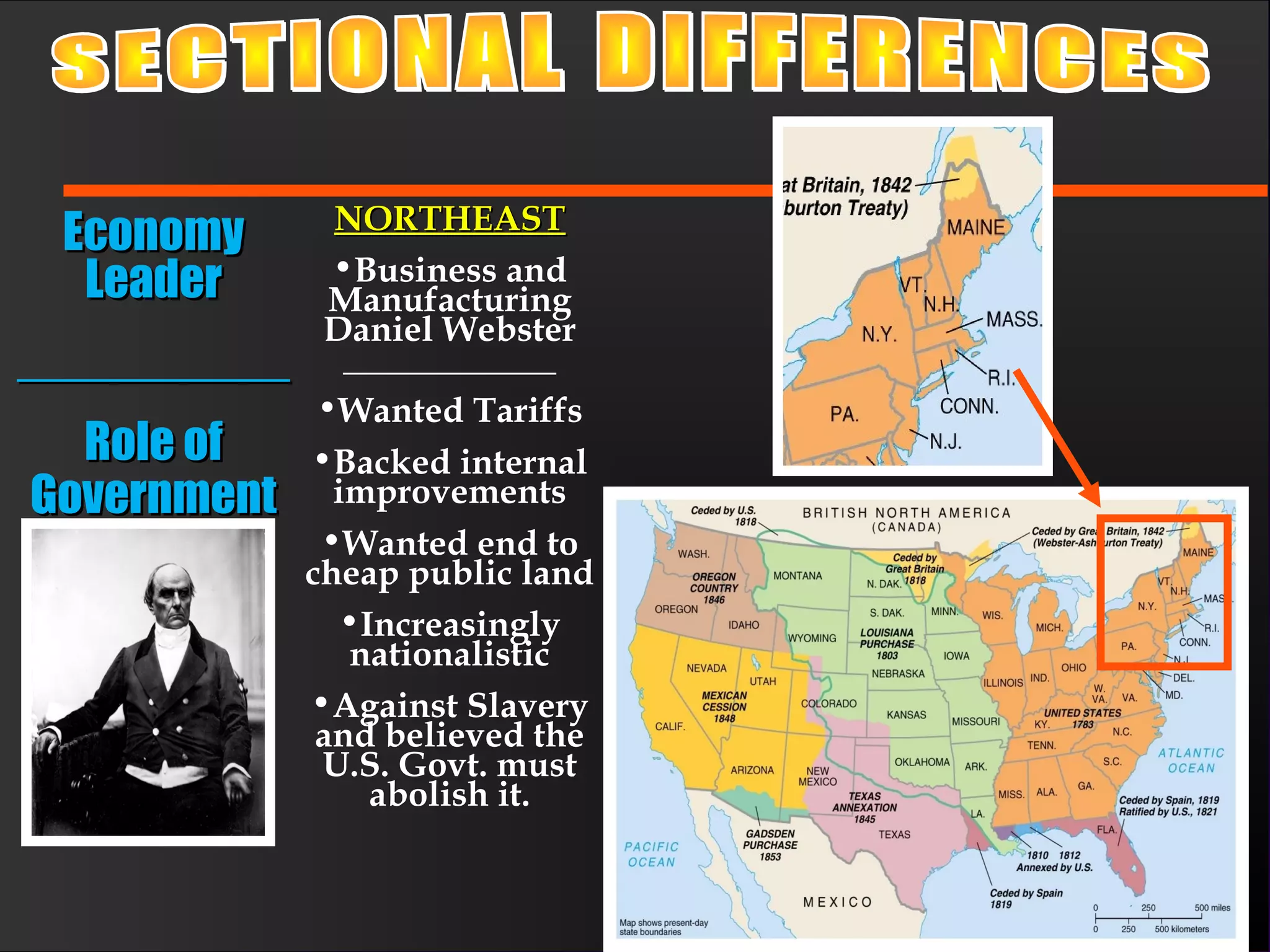
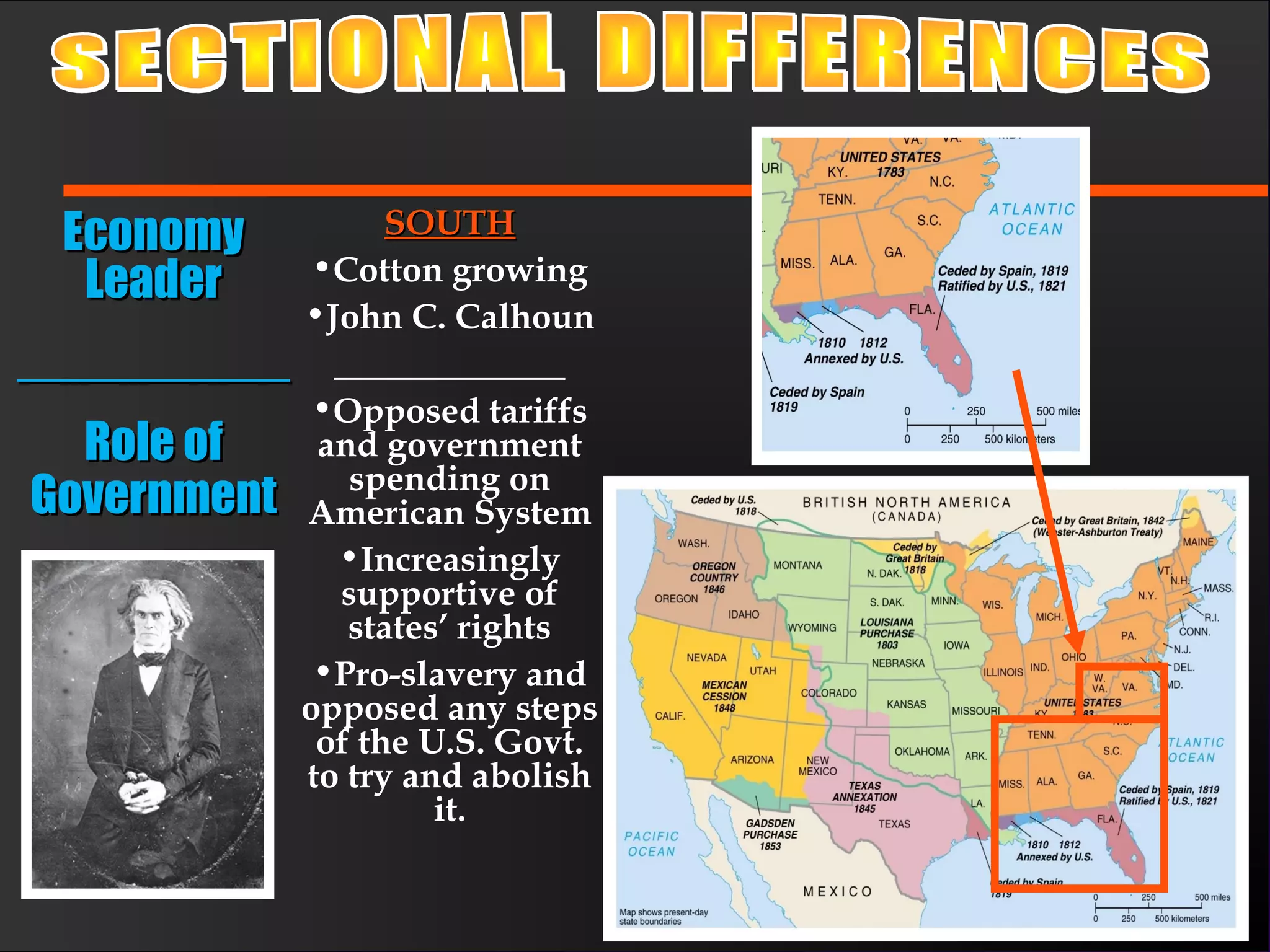
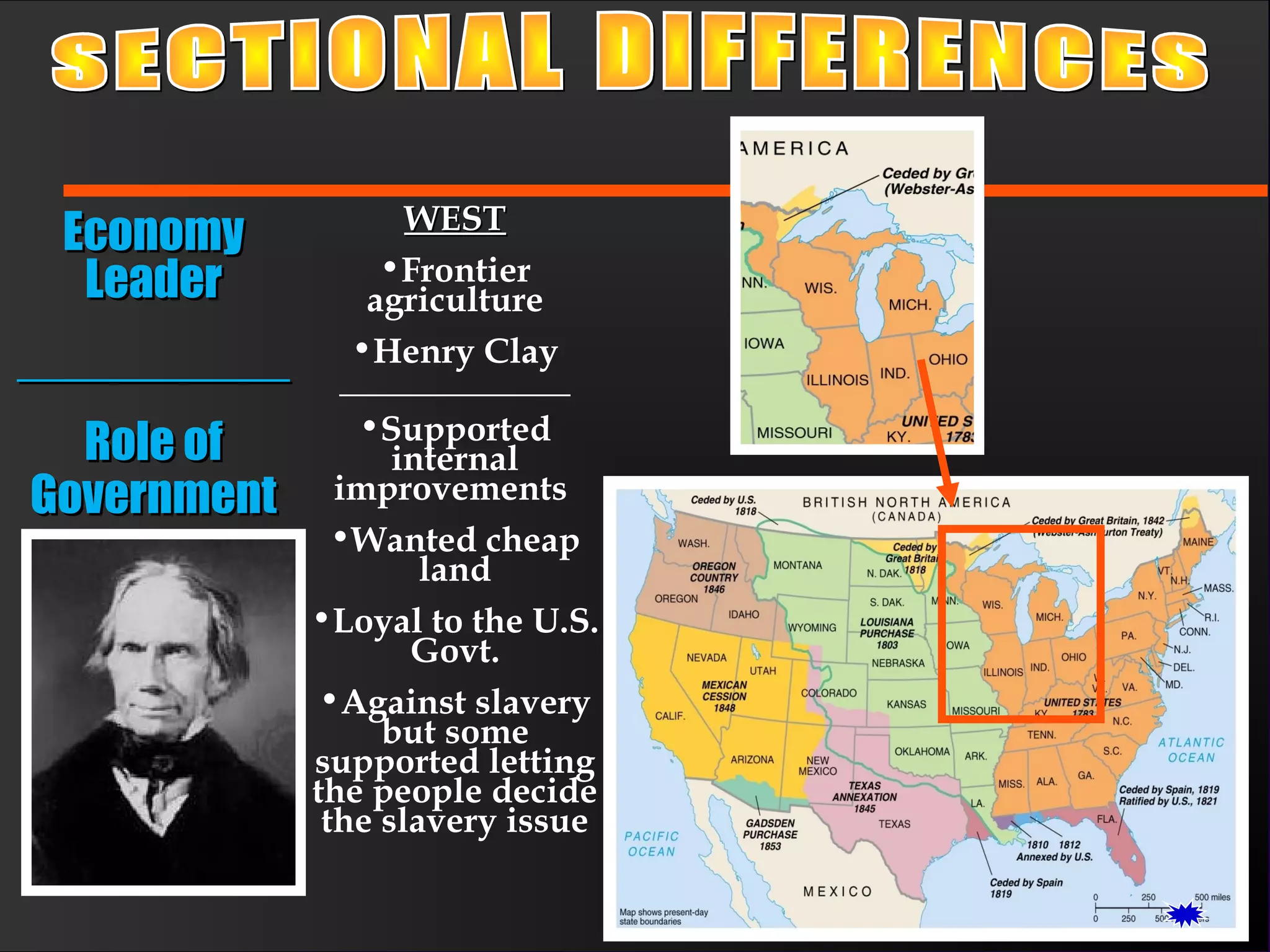
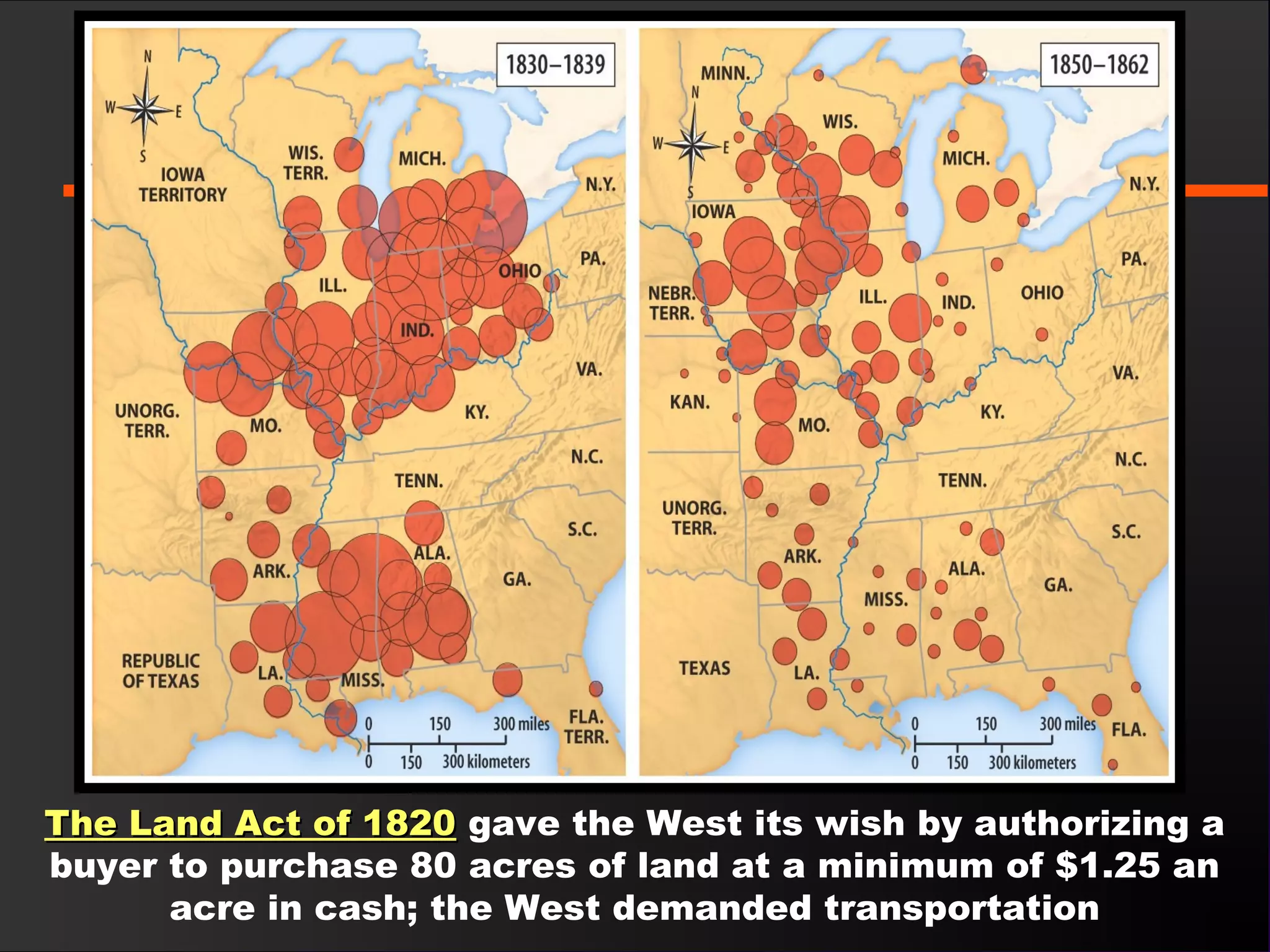
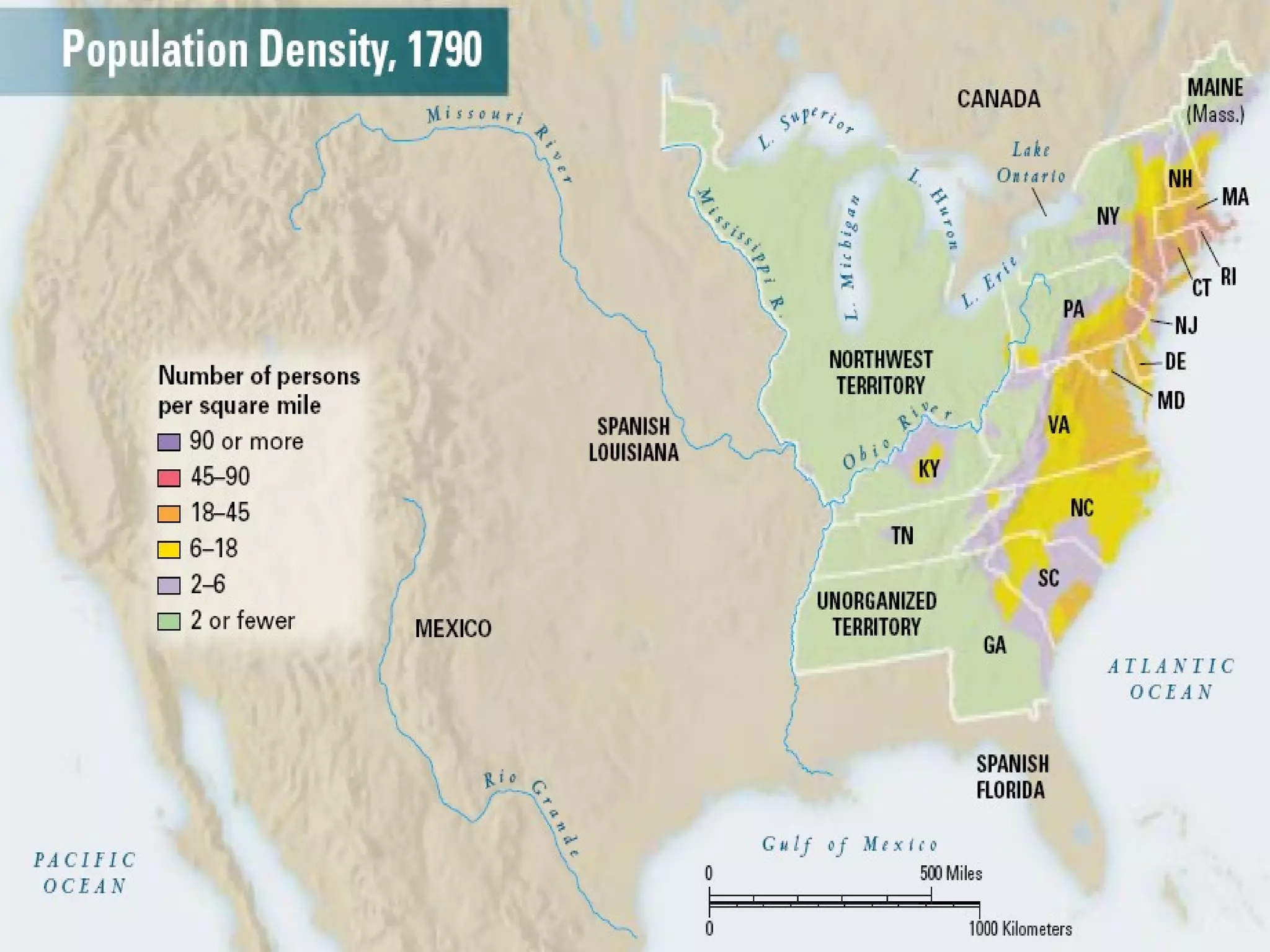
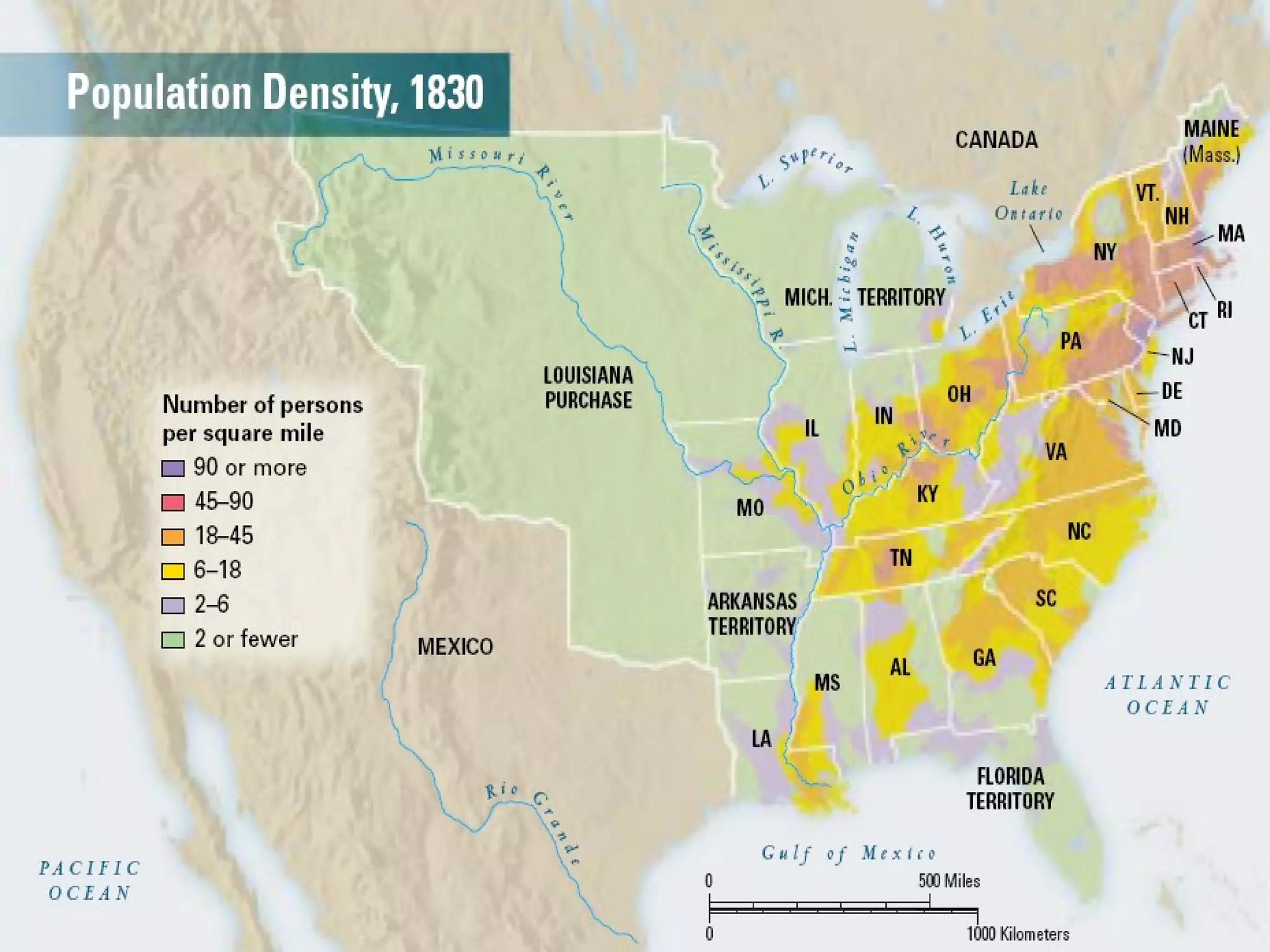
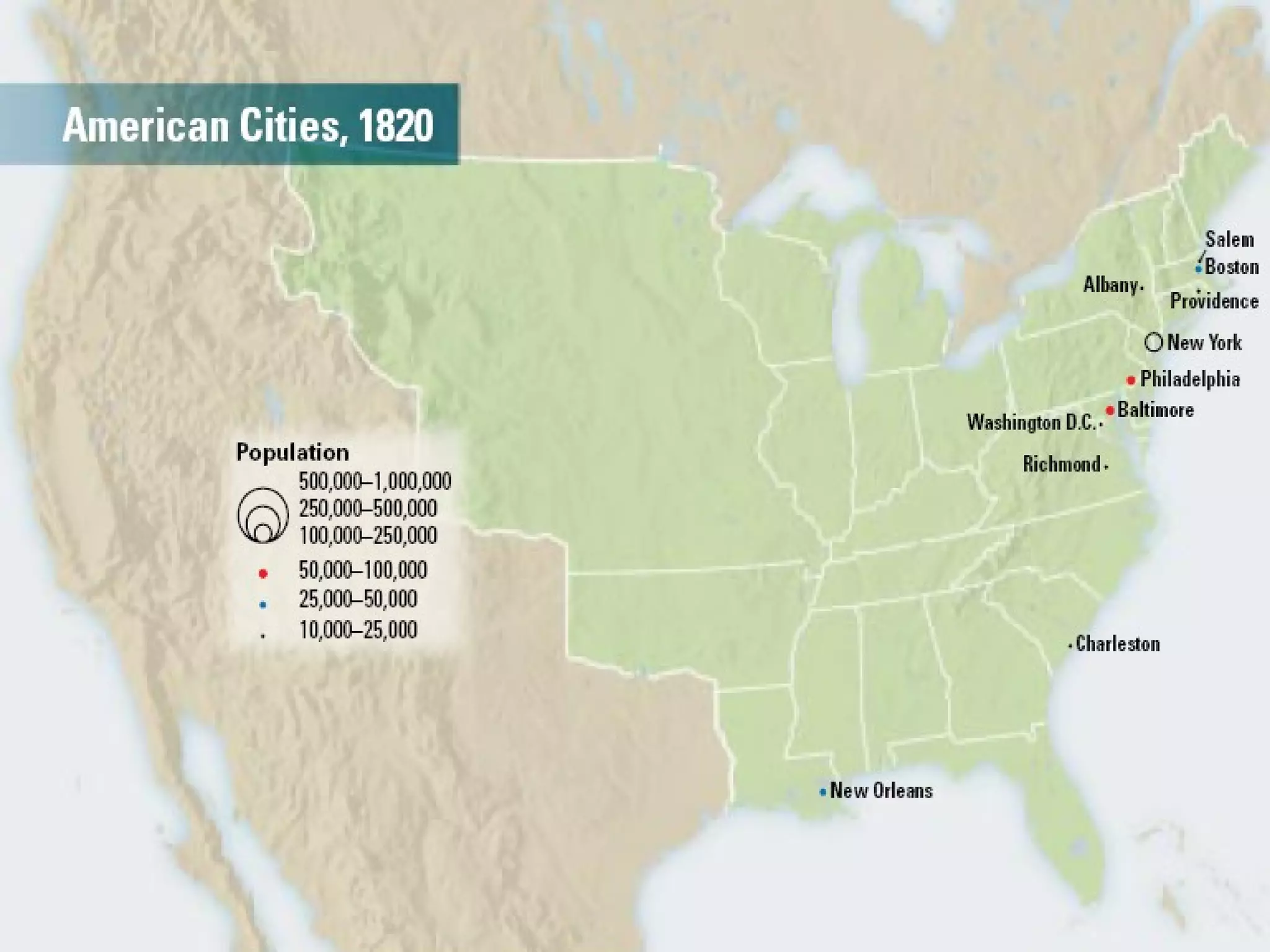
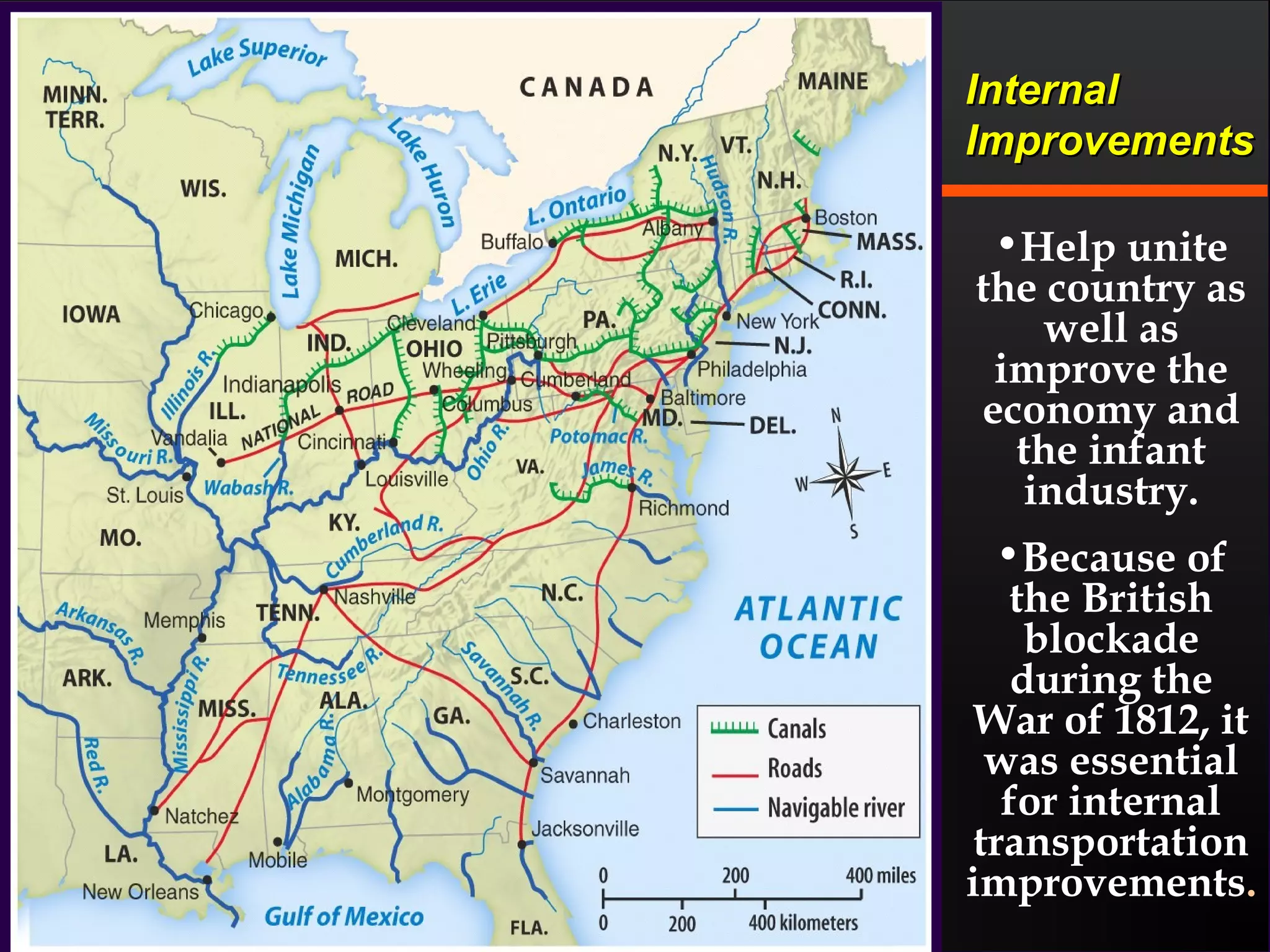
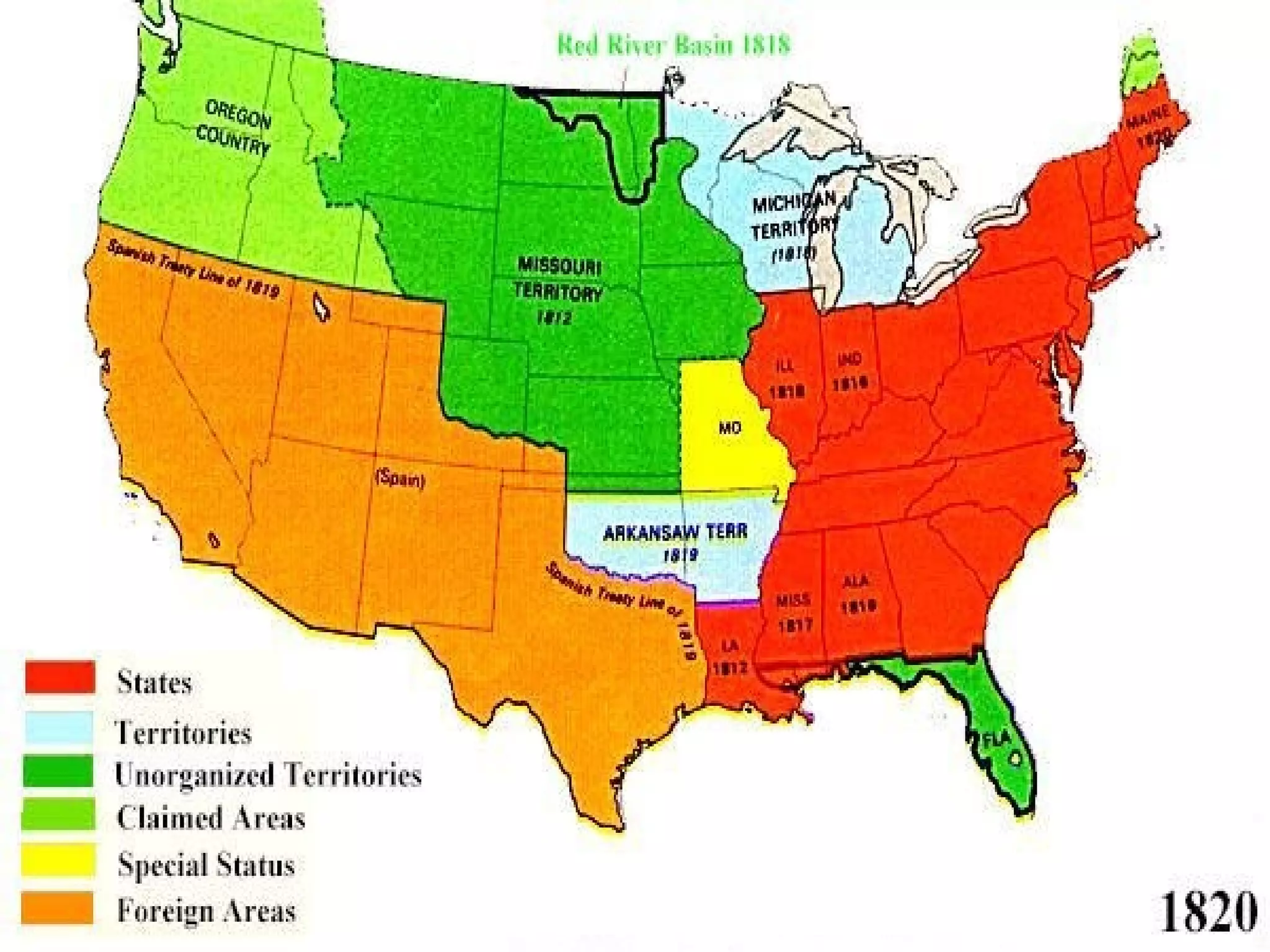
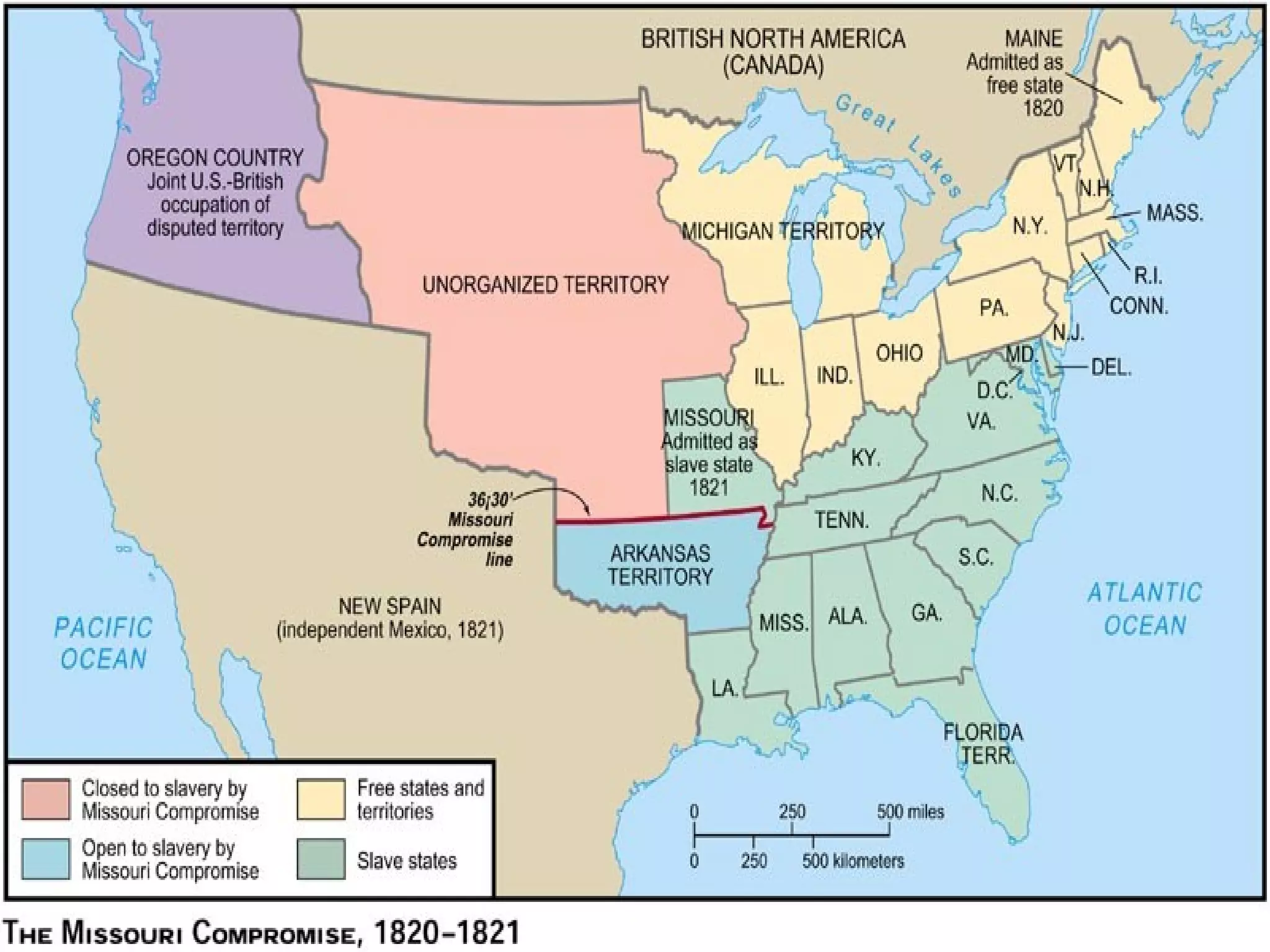
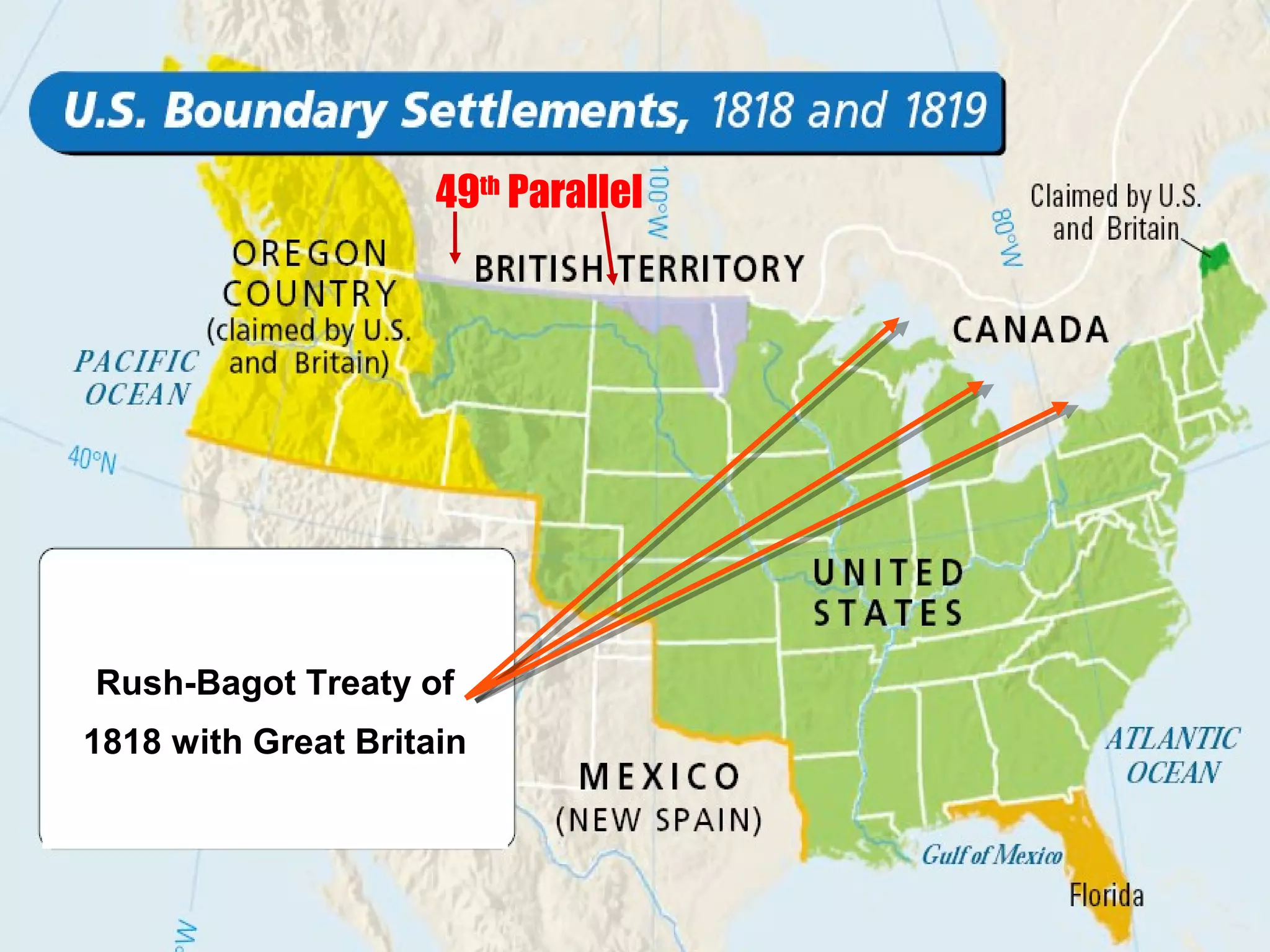
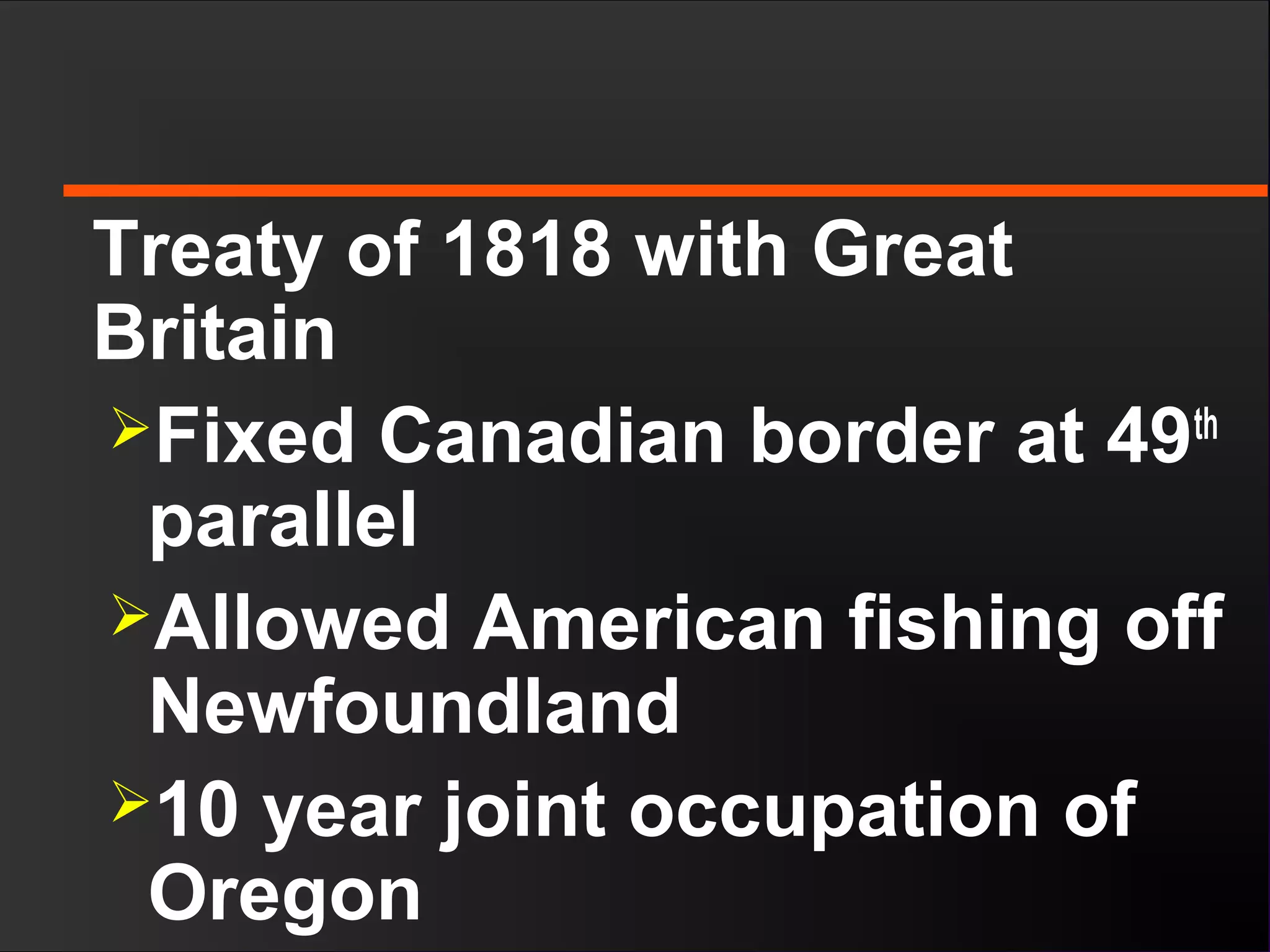
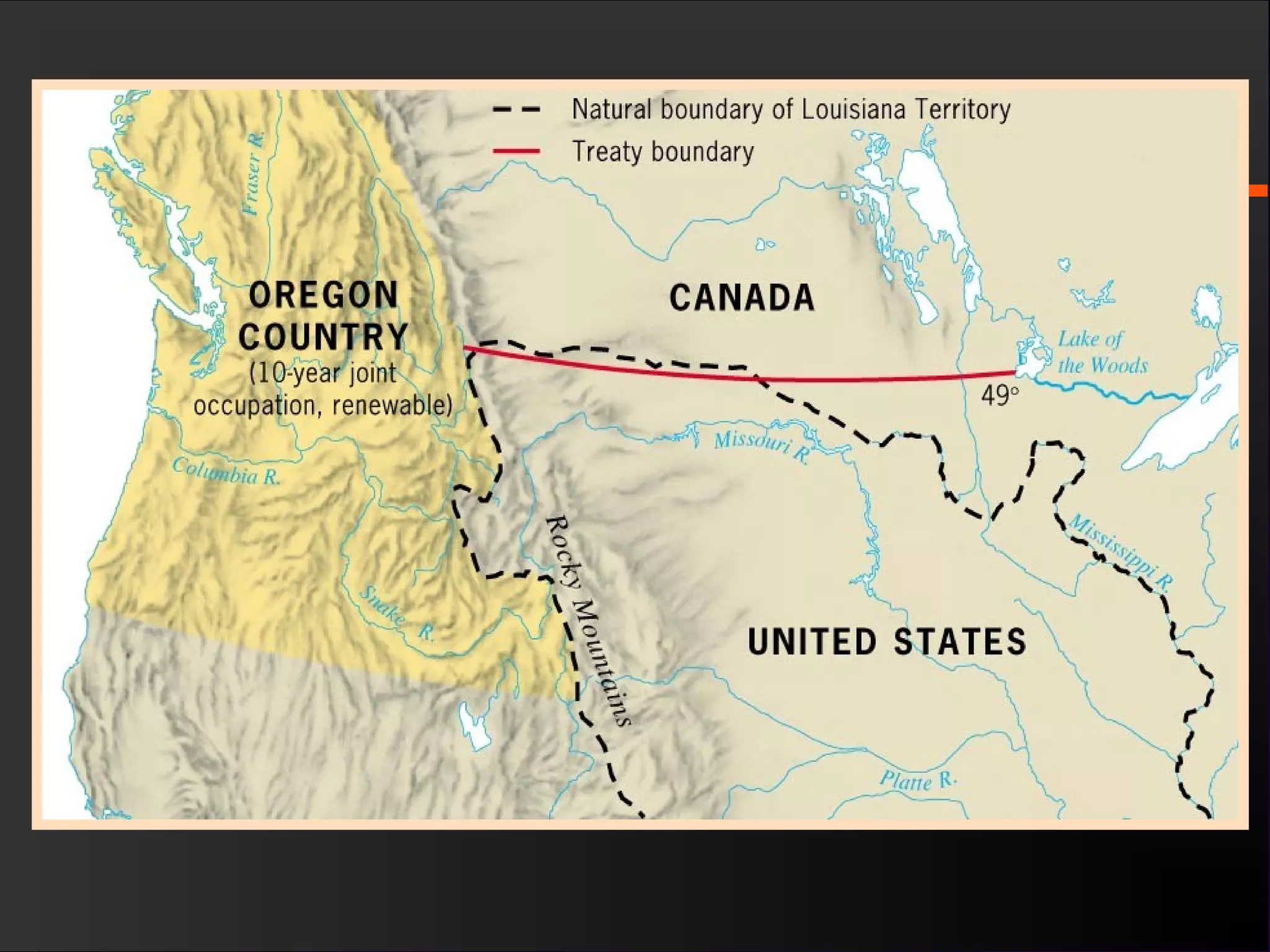
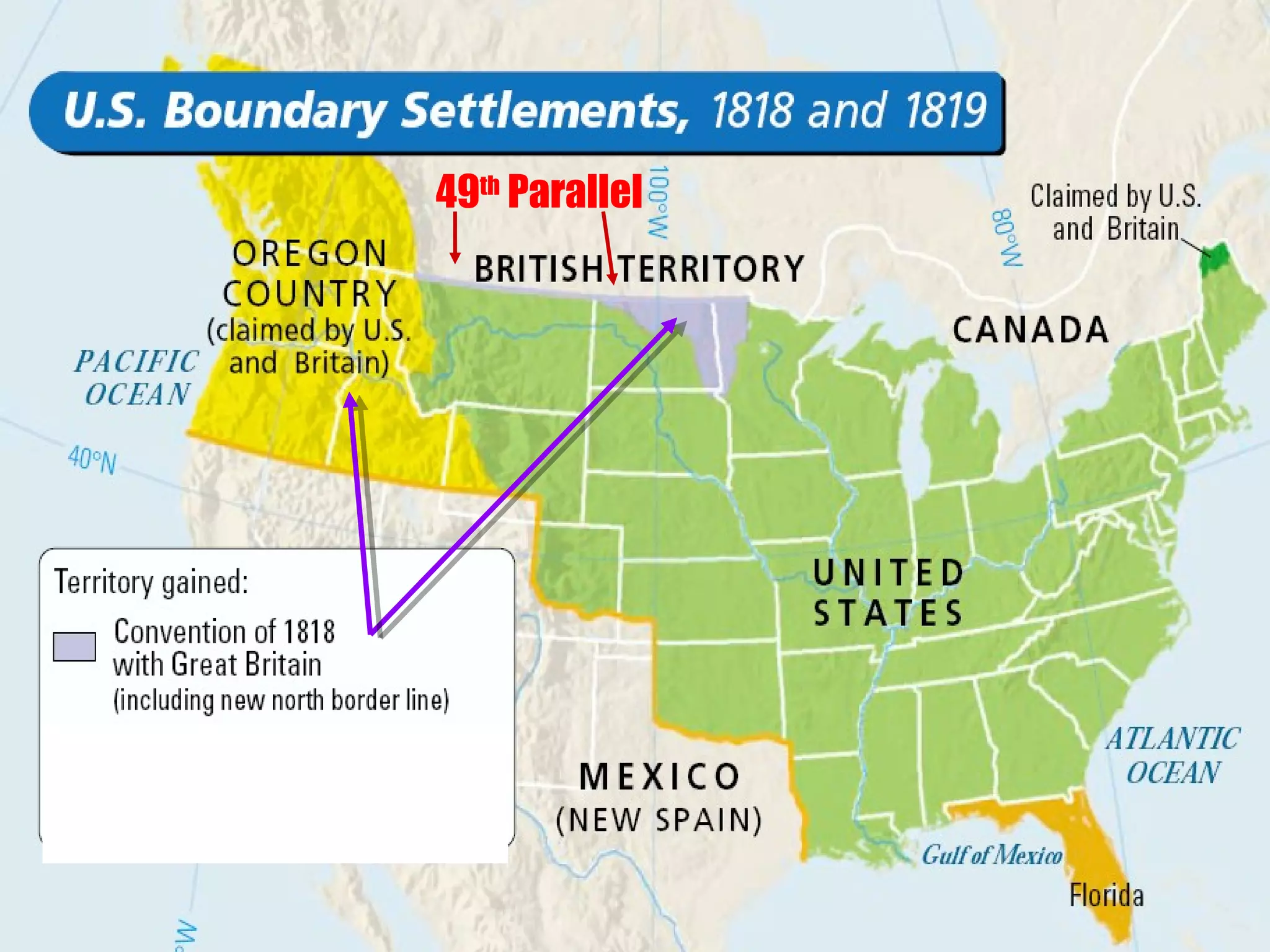
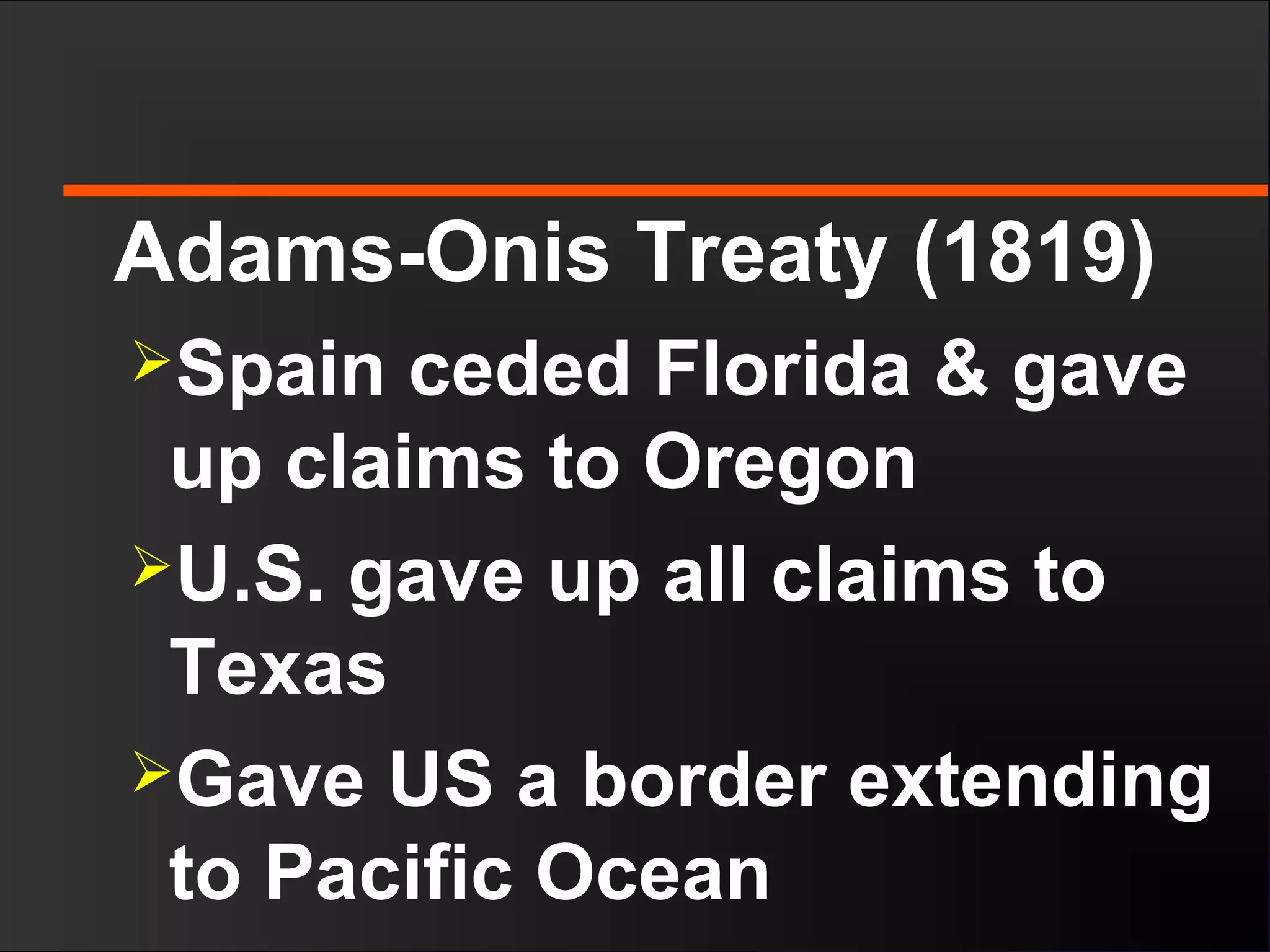
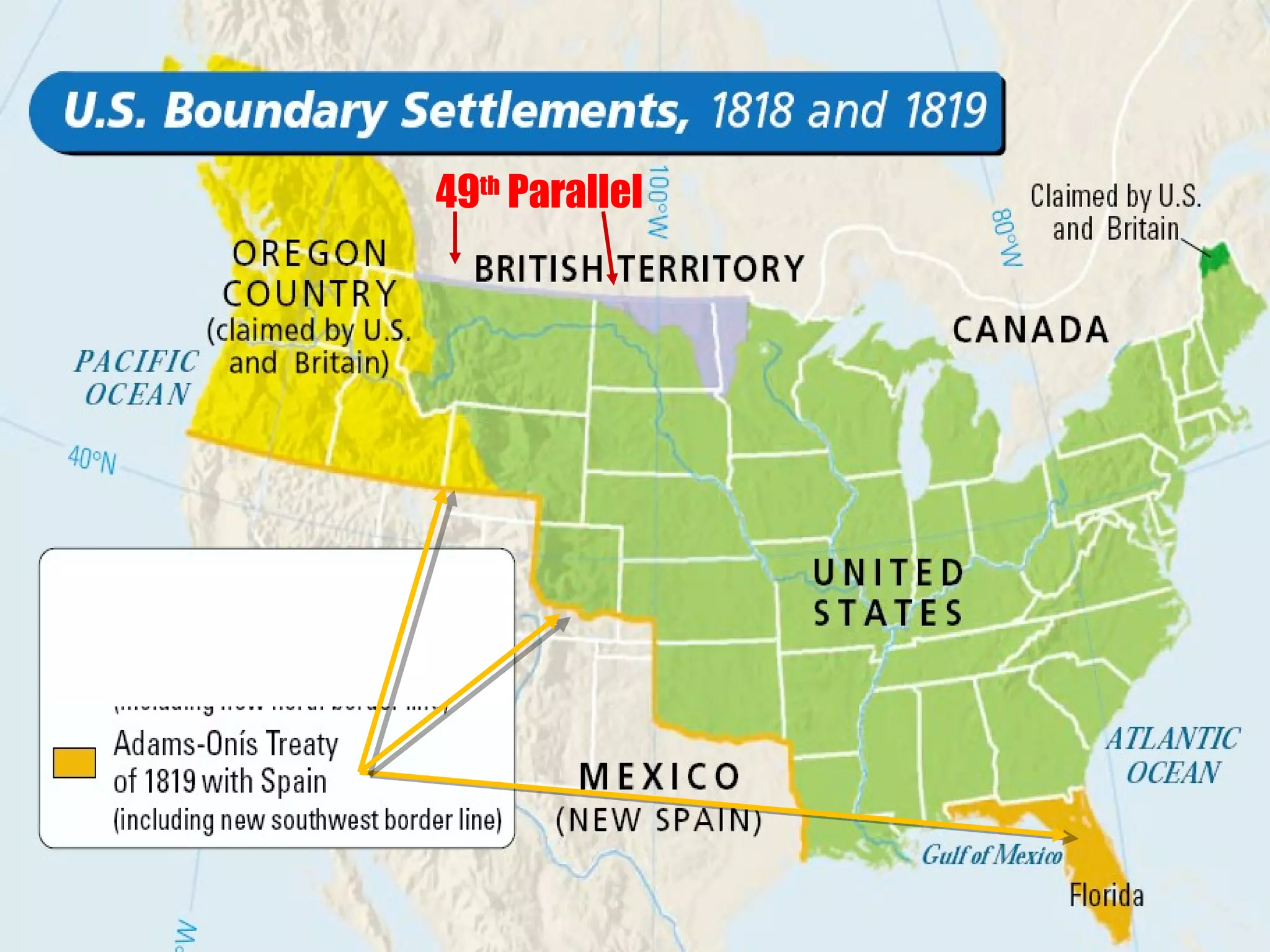
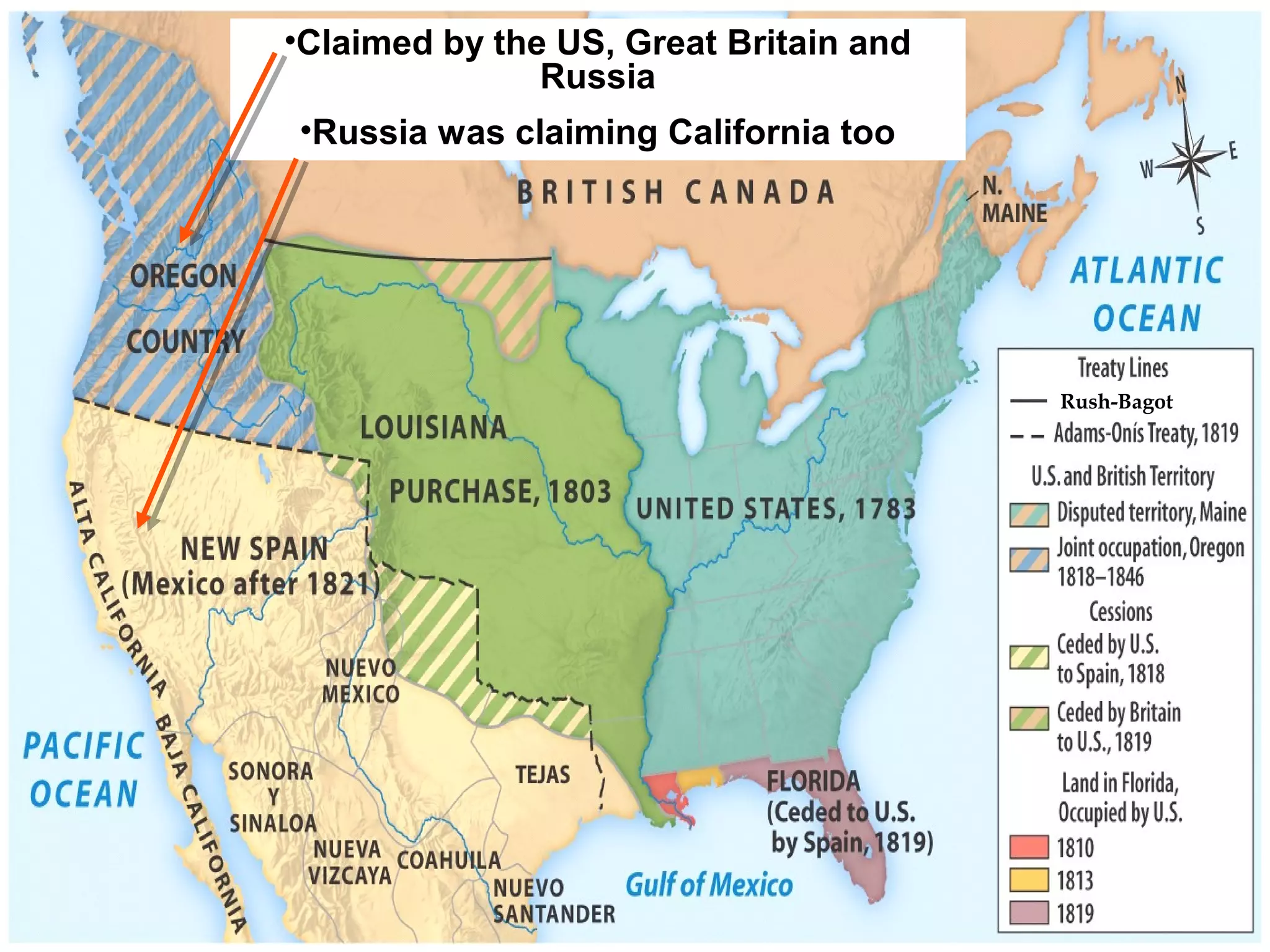
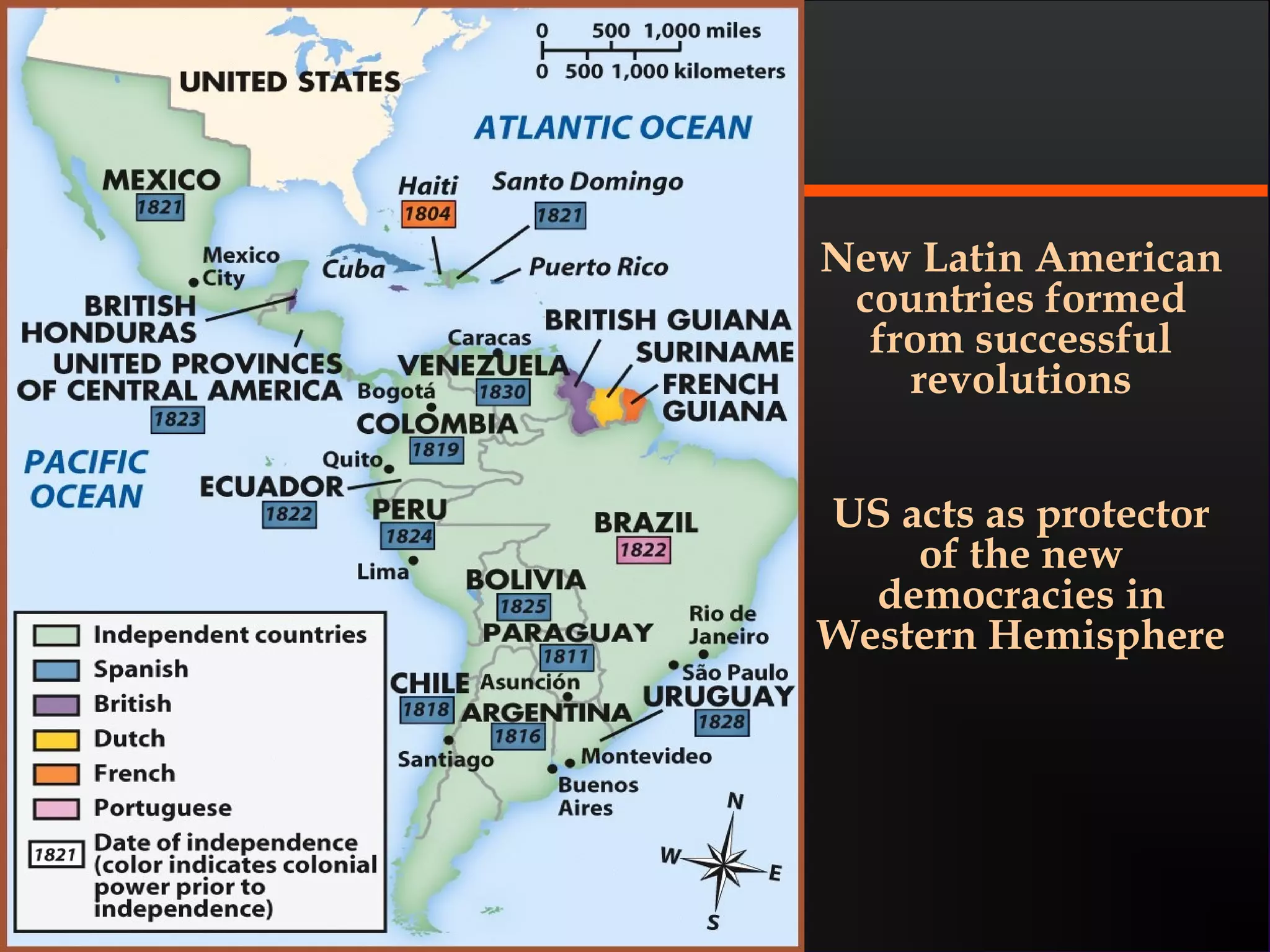
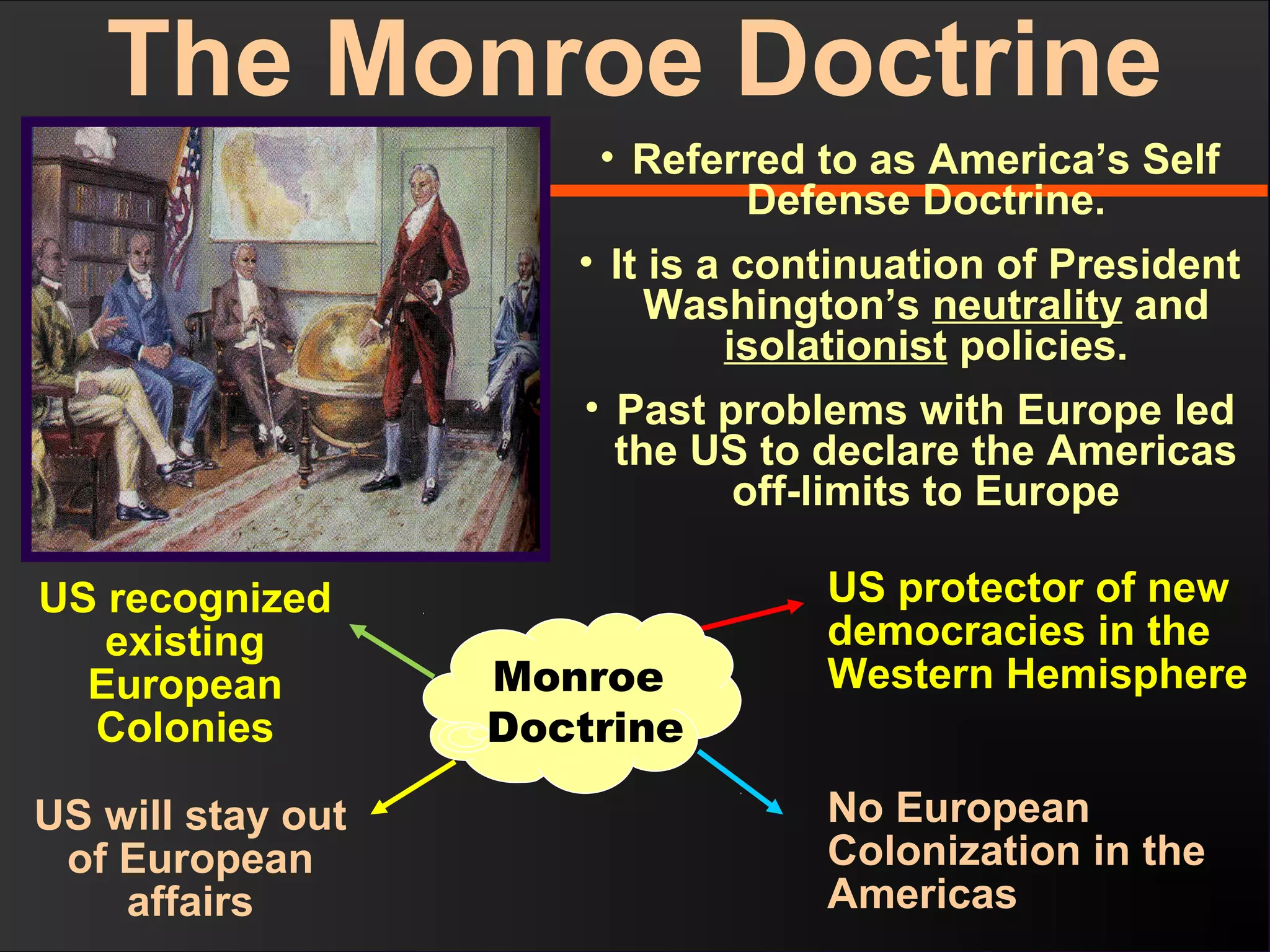
The document discusses the political divisions that emerged in the U.S. during the presidency of James Monroe, known as the Era of Good Feelings. Sectional differences arose over issues like tariffs and the role of the federal government. The nation was dividing into three sections - the Northeast, South, and West - each promoting their own economic self-interest. The Missouri Compromise of 1820 maintained the balance of power between slave and free states as the nation expanded.