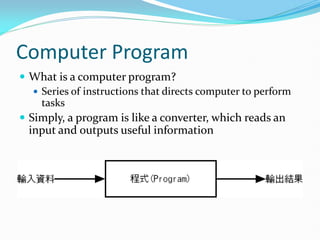
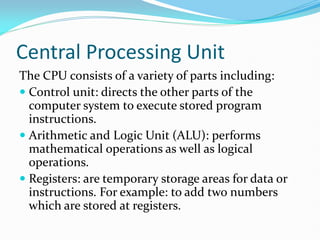
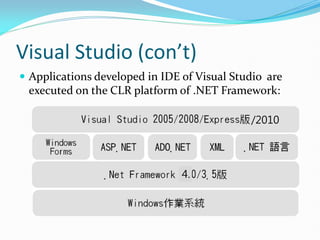
This document provides an introduction to programming concepts including computer programs, programming languages, execution of programs, and central processing units. It then discusses specific topics like .NET Framework, C#, and the Visual Studio integrated development environment. The key points are that computer programs are sets of instructions that direct computers, programming languages can be high-level or low-level, and Visual Studio is an IDE for developing applications using languages like C# within the .NET Framework.