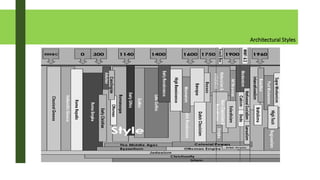
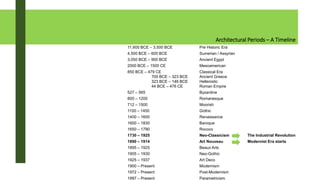
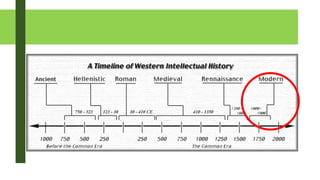
The document provides an overview of architectural theory and history from prehistoric times to modernism. It defines architectural theory as discussing and writing about architecture. It notes Vitruvius as formally starting the idea of architecture and his three principles of firmitas, utilitas, and venustatis. The document then summarizes various architectural styles and periods from prehistoric structures to modernism, highlighting examples from each era.