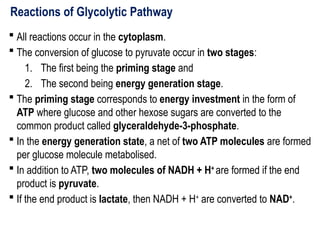
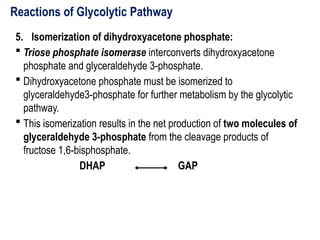
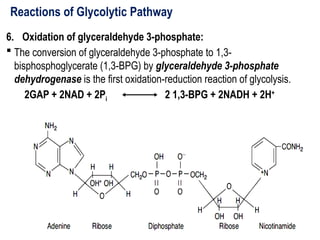
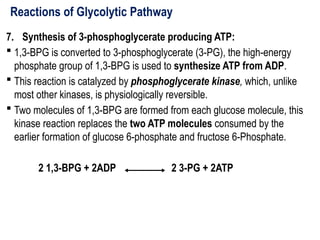
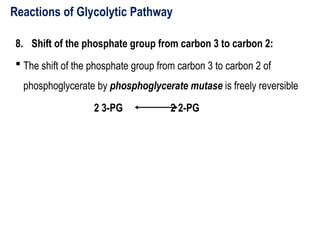
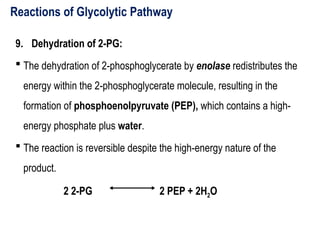
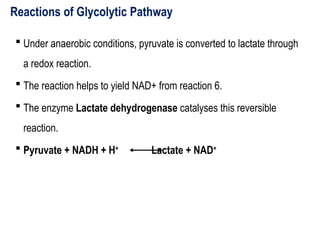
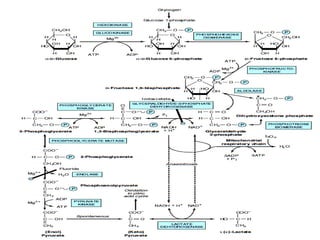
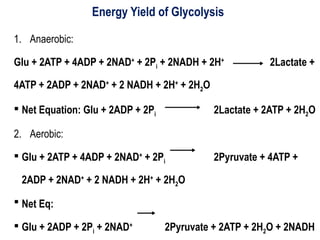
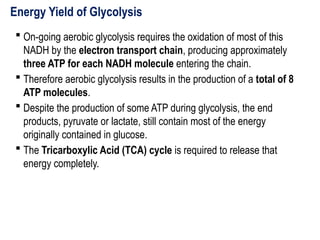
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate and occurs in two main stages: a priming stage that invests energy and an energy generation stage. Key reactions include the phosphorylation of glucose, the conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, and the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate, with the latter producing ATP. The process can occur anaerobically yielding lactate or aerobically producing pyruvate, which further enters the citric acid cycle for complete oxidation.