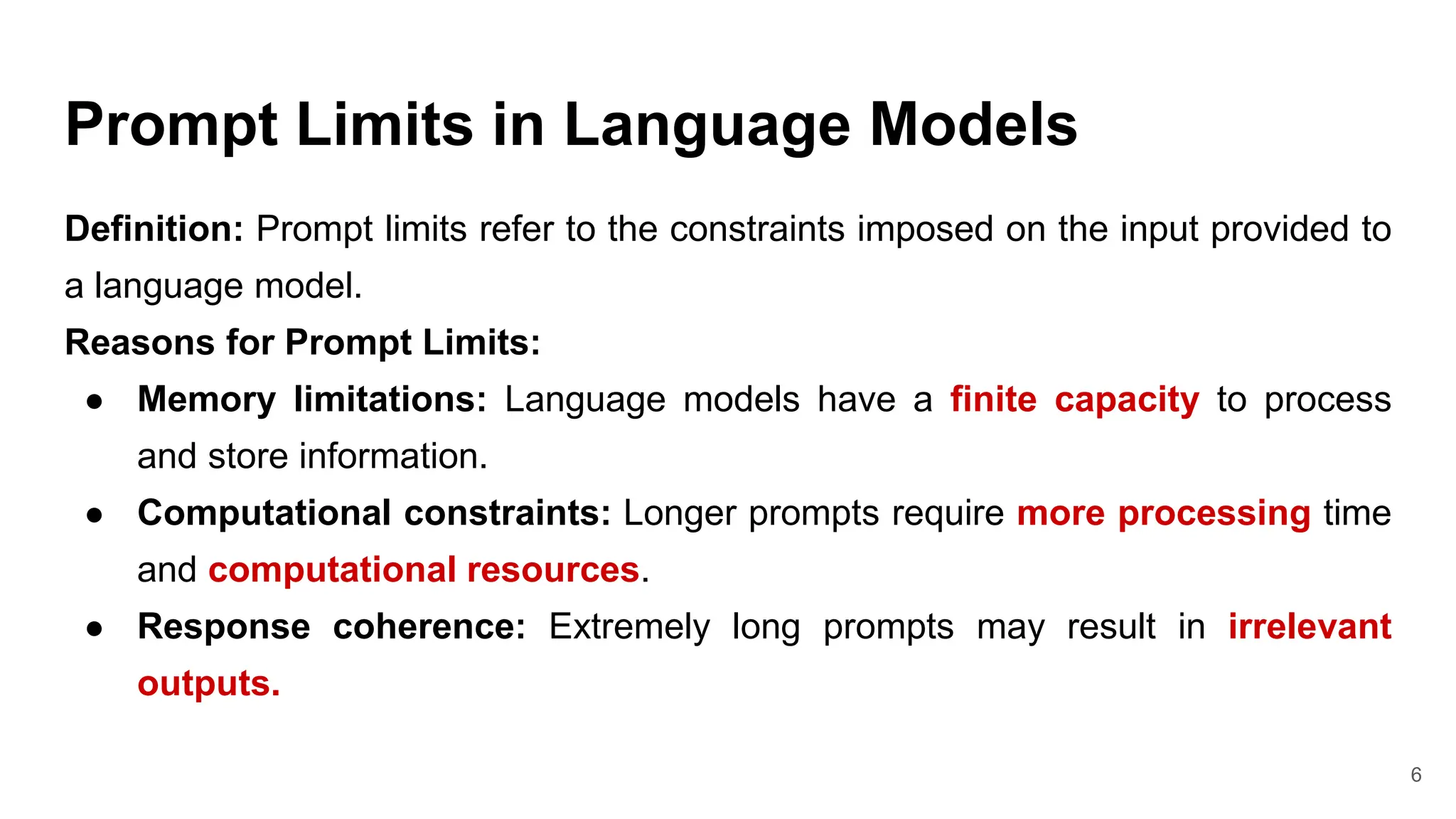
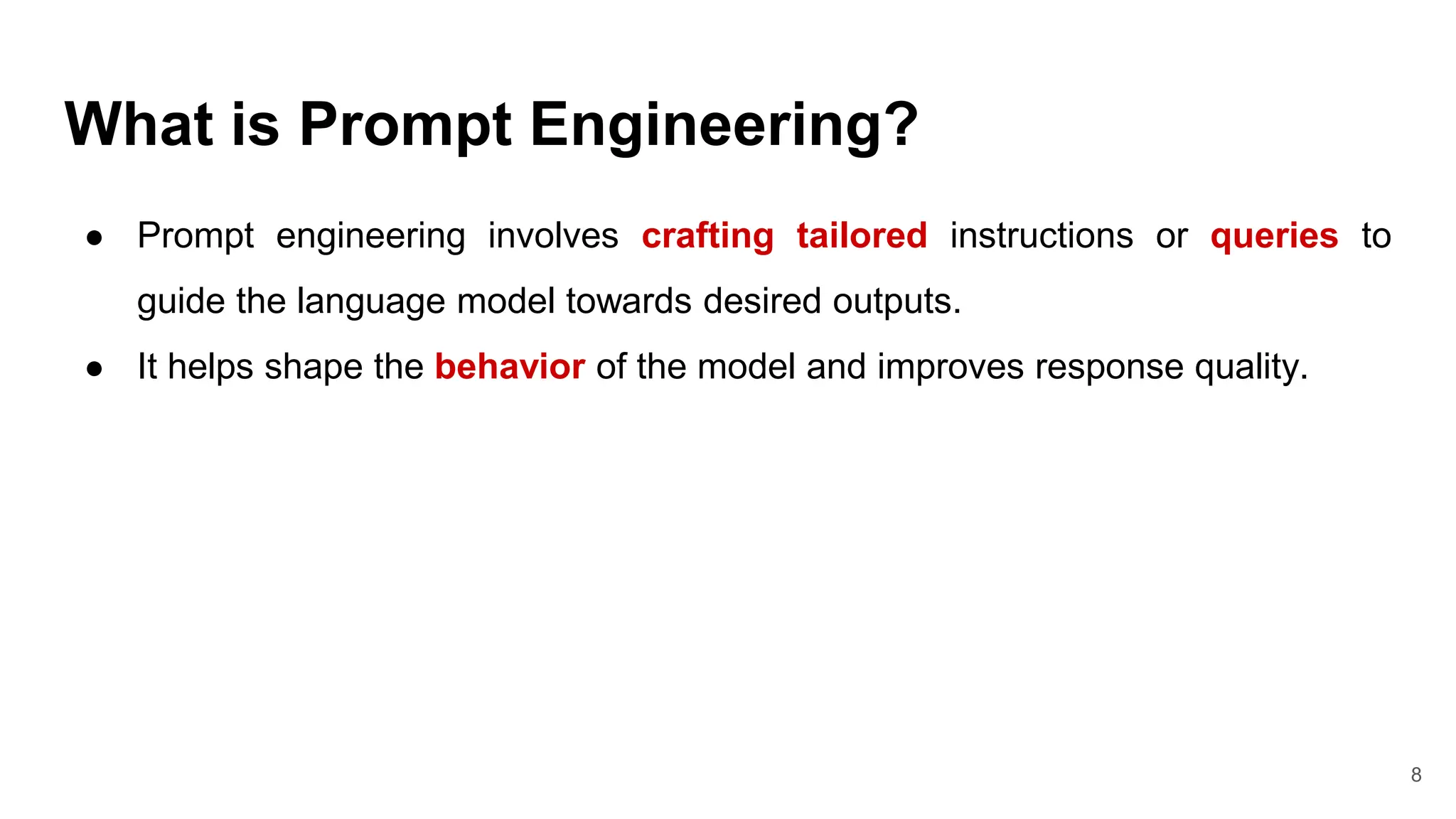
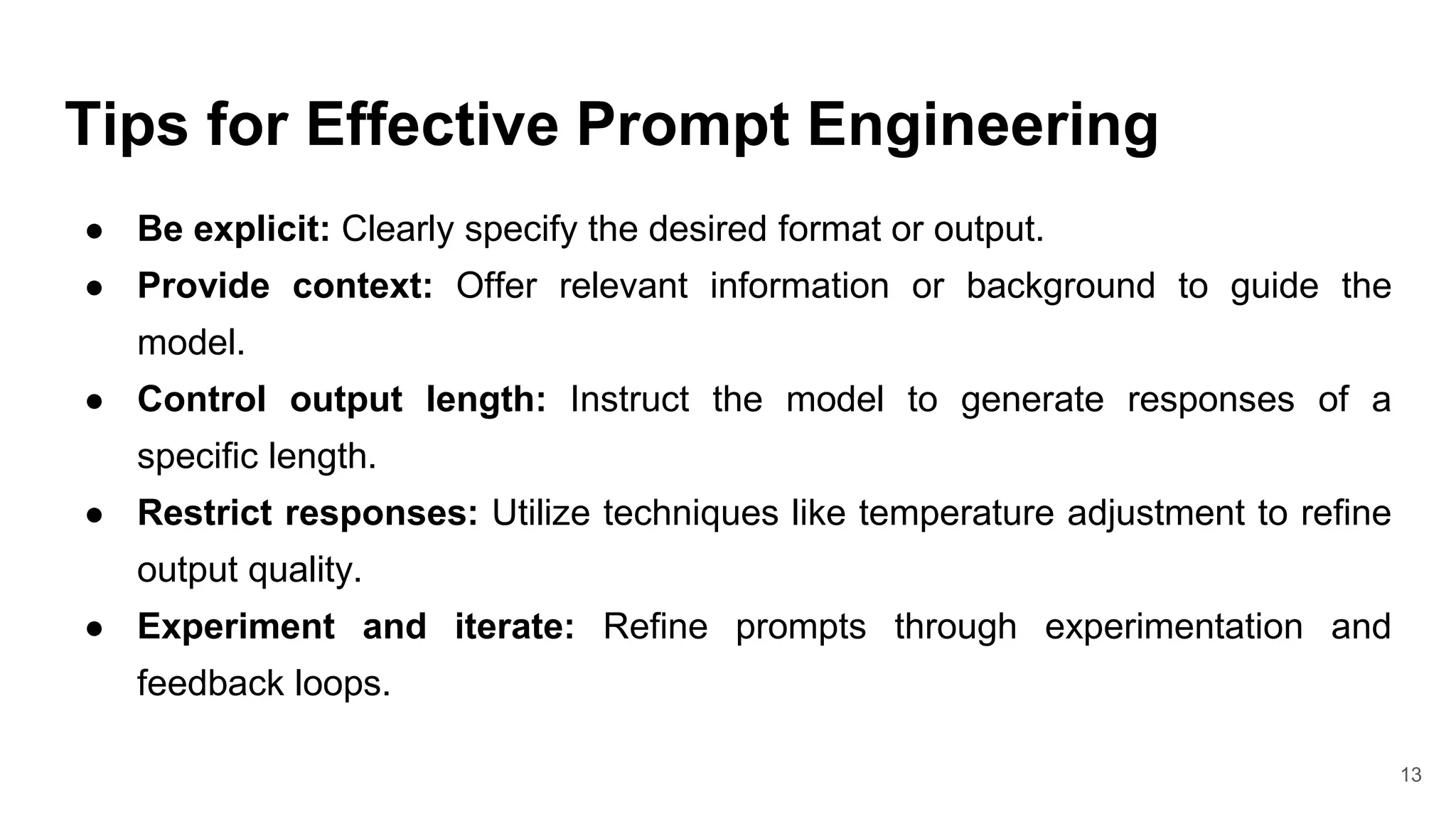
This document discusses prompt engineering for generative AI models. It defines key concepts like tokenization, prompt limits, and the anatomy of a prompt. Effective prompt engineering involves crafting instructions to guide models towards specific, high-quality outputs. Sample prompts are provided for tasks like customer service and mentorship. Tips for prompt engineering include being explicit, providing context, and experimenting through iteration. The document concludes by introducing ChatGPT Playground for practicing prompt design.