This presentation provides a comprehensive guide to modern prompt engineering. Learn how to effectively communicate with AI models like ChatGPT to generate optimal outputs. Covers essential techniques including Zero-Shot, Few-Shot, Chain-of-Thought, and ReAct prompting, complete with practical examples. Also delves into critical risks and misuses such as prompt injection, poisoning, and data exposure, with guidance on how to prevent them. Perfect for developers, content creators, and anyone looking to leverage AI tools more effectively.

![STUDIO SHODWE Contact
About Us
Service
Home
03
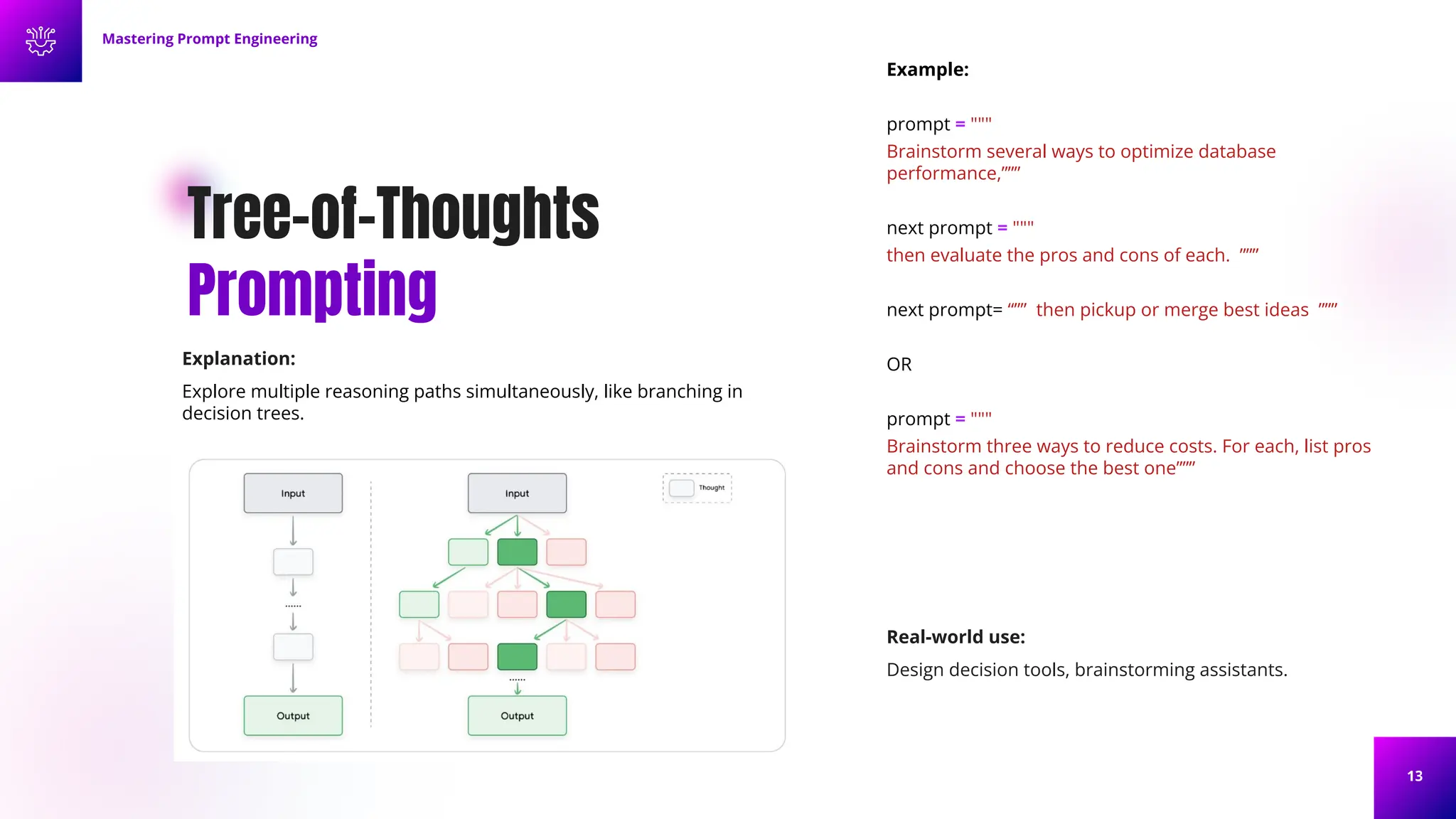
Elements of a Prompt
• Instruction (“Translate to French”),
• Context (“You are a translator”),
• Input Data (“Hello!”),
• Output Format (“Respond only with translation”)
+ Tone (Professional, casual, instructional, etc.)
+ Length (How detailed the response should be)
Prompt = [Instruction] + [Context] + [Input] + [Output constraints]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prompt-engineering-presentation-final-v2-250914183025-777997b5/75/Mastering-Prompt-Engineering-Techniques-3-2048.jpg)



![08
Contextual
Prompting
Explanation:
Feed relevant background information along with the prompt.
Importance: More context = better answers.
Types of Context: User history, previous conversation, external data.
Example:
prompt = """
Given the following error log from our Java application,
suggest possible fixes: [insert error log here].""“
OR
prompt =“””Given the following customer complaint and
their purchase history, draft a response…”””
Mastering Prompt Engineering
Real-world use:
Debugging assistants, code review tools.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prompt-engineering-presentation-final-v2-250914183025-777997b5/75/Mastering-Prompt-Engineering-Techniques-8-2048.jpg)


![11
Chain of Thought (CoT) using few-shot
Prompting
Mastering Prompt Engineering
prompt = """ Question: If there are 2 bags with 3 oranges each, how
many oranges are there in total?
Answer: 2 bags, 3 oranges each. 2 * 3 = 6 oranges.
Question: If there are 4 cars with 2 passengers each, how many
passengers are there in total?
Answer: 4 cars, 2 passengers each. 4 * 2 = 8 passengers.
Question: If there are 3 baskets, and each basket has 5 apples, how
many apples are there in total?
Answer: (Think step by step.)"""
prompt = """ Generate a comprehensive market analysis report for a
new product category in the finance industry. The target audience is
small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Use the attached
template to structure the report into categories. [attach report
template]
The following examples are market analysis reports for previously
released products.
Example 1: [insert example market analysis report]
Example 2: [insert example market analysis report]"""
02
Since LLMs predict their answer one token at a time, the best practice is to ask them to think step by step, and
then only provide the answer after they have explained their reasoning.
01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prompt-engineering-presentation-final-v2-250914183025-777997b5/75/Mastering-Prompt-Engineering-Techniques-11-2048.jpg)








![21
Automatic
Prompting
Explanation:
Letting the AI propose its own prompts or improvements to existing
prompts, then testing and refining them to optimize outcomes.
Purpose: Enhance prompt effectiveness,
Accelerate prompt development,
Reduce manual trial-and-error
Real-world Use: Chatbots, content generations and data labeling
Example:
prompt = """
I want to generate content about [topic] for [purpose].
1. Suggest 3 different prompts that would help me achieve
this goal
2. Explain why each prompt would be effective
3. Recommend which prompt would work best and why”””
Mastering Prompt Engineering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prompt-engineering-presentation-final-v2-250914183025-777997b5/75/Mastering-Prompt-Engineering-Techniques-21-2048.jpg)