The document contains details about a Microprocessor & Microcontroller course syllabus including:
- The course number, name, credits, instructor details, textbooks, and reference books.
- An outline of the course topics which include introduction to microprocessors and microcontrollers, 8051 architecture, instruction set, interfacing examples, and a case study on data acquisition system design.
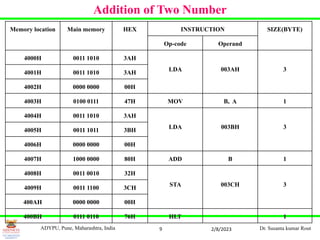
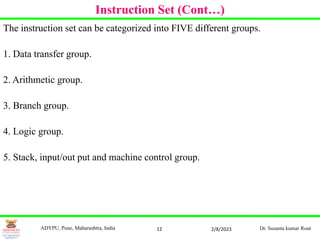
- Notes on the instruction set of 8051 and 8085 microprocessors including data transfer, arithmetic, branch, logic, and machine control instructions. Examples of instructions like MOV, MVI, ADD, and HLT are provided.









![16 2/8/2023
ADYPU, Pune, Maharashtra, India Dr. Susanta kumar Rout
5. MVI M, DATA (Move immediate data to memory)
Example:
i. LXI H, 2400H ; load H-L pair with 2400H
MVI M, 08H ; Move 08H to memory location 2400H
HLT
6. LXI RP, DATA 16 (Load register pair immediate)
(It loads immediate 16-bit data specified within the instruction into register pair or
stack pointer. The RP is 16-bit register pair such as BC, DE, HL)
[RP] = DATA 16-bit, [RH] = 8 MSBs, [RL] = 8 LSBs.
Example:
LXI H, 2023H
Data Transfer Group (Cont…)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec5mpmc-230209191933-696517e5/85/Lec_5_MPMC-pdf-16-320.jpg)

![18 2/8/2023
ADYPU, Pune, Maharashtra, India Dr. Susanta kumar Rout
9. LHLD addr (Load H-L pair direct)
L <= content of addr, H <= content of (addr+1).
Example: (2500H)= 30H, (2501H) = 60H
[L]=30H, [H]=60H
10. SHLD addr (Store H-L pair direct)
L => content of addr, H => content of (addr+1) .
Example:
i. LXI H, 1627H (It will load 16H into register H and 27H into register L)
SHLD, 2400
11. LDAX RP (It copies the contents of memory location whose address is specified
by the register pair into the accumulator. The RP is BC or DE register pair.
The register pair is used as a memory pointer.)
Example:
i. LXI B 2400H
LDAX B (This instruction will load the content of the memory location
whose address is in B-C pairs into accumulator.)
Data Transfer Group (Cont…)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec5mpmc-230209191933-696517e5/85/Lec_5_MPMC-pdf-18-320.jpg)

