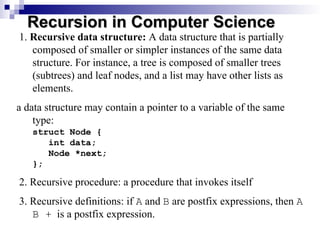
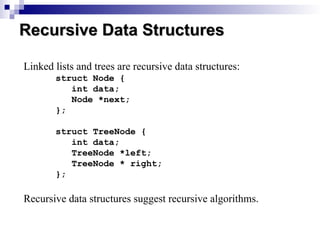
Recursion is a problem-solving technique that involves dividing a problem into smaller subproblems which can also be further divided until they can be solved directly. It is defined in terms of itself through recursive algorithms and includes concepts like recursive data structures, such as linked lists and trees, which reference themselves. The document provides examples and definitions of recursion, illustrating its application in computer science.